Ducts design
advertisement

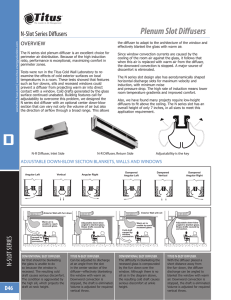
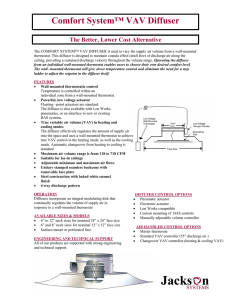
Announcement Course Exam October 11th (Tuesday) In class: 90 minutes long Examples are posted on the course website Objectives • Duct Design and Diffuser Selection • Reading assignment: thextbook Chapter 18 Duct design (part of the HVAC Design successfully integrated into BIM) Pressures • Static pressure • Velocity pressure • Total pressure – sum of the two above Relationship Between Static and Total Pressure 2 2 V1 V2 Pt Ps 2 Duct design method (defines the layout) Two design methods: - Equal friction - Static regain System Characteristic Duct Design • Static pressure drop (friction losses) in a duct is proportional to square of velocity or flow L V2 Ps f D 2 It is a function of - Dynamic pressure - Length - Pipe diameter - Friction coefficient Frictional Losses (in a staring round duct section) Ductulator Non-circular Ducts • Parallel concept to wetted perimeter Dynamic (or local) losses • Losses associated with • • • • Changes in velocity Obstructions Bends Fittings and transitions • Two methods • Equivalent length and loss coefficients Dynamics (Local) Loss Coefficients ΔPt = CoPdynamic Conversion Between Methods Leq V 2 V2 P C0 f 2 D 2 D Leq C0 f Example 18.7 • Determine total pressure drop from 0 to 4 Diffuser selection • Defines thermal comfort • Air quality Forced driven air flow Diffusers Linear diffusers Vertical Horizontal one side Grill (side wall) diffusers Diffusers types Valve diffuser swirl diffusers wall or ceiling floor ceiling diffuser Diffusers Perforated ceiling diffuser Wall diffuser unit Linear slot diffuser Jet nozzle diffuser Swirl diffuser DV diffuser Round conical ceiling diffuser Floor diffuser External louvre http://www.titus-hvac.com/techzone/ http://www.halton.com/halton/cms.nsf/www/diffusers Square conical ceiling diffuser Auditorium diffuser Smoke damper Low mixing Diffusers Displacement ventilation