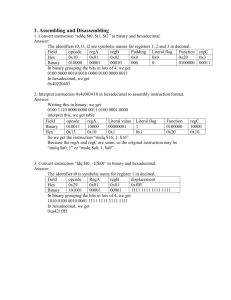
Lab 1: Introduction
advertisement

Lab 1: Introduction
1
Lab1: Introduction
• Configure ATMEL AVR Starter Kit 500 (STK500), a
prototyping/development board for Lab1. ATmega16 (4.5 -5.5 V) is
the chip used on your board. Some may have ATmega16L (low
voltage 2.7 – 5.5 V) .
– Lab1 requires
• One UART port for programming, COM1
• One UART port for communication, COM2
• Connect a 6-wire cable between Target ISP Header and 6pin ISP Header.
• Connect a 10-wire cable between Port and LEDs
• Become familiar with the C-compiler from CodeVision.
– Lab1 requires writing 3 simple C programs to activate LEDs in
different patterns.
– Lab1 requires writing 1 simple C program to talk to a terminal.
2
AVR STK 500 Components
Atmeg16
Atmeg8515
3
4
COM port connections:
COM1 for programming your code onto AVR
COM2 for communication to display your program output
COM1
To PC COM2 port
or other available
COM port
5
Connecting Switches to
PORTD
Programming
Connecting LEDs and PORTB
6
RS232 connecting to PORTD
RXD PD0
TXD PD1
7
Lab1: Introduction
• Pre-lab Assignments
– Read Chapter 1 of the textbook: Embedded C
Programming and the Atmel AVR by Barnett,
Cox, & O’Cull (BCO).
– Read STK500 user guide
– Complete the Pre-lab Questions on page 1-4.
8
Pre-Lab Questions for Lab 1
•
•
•
•
•
When setting up a timer to generate an interrupt every
half second, what value must the timer be initialized to
(if counting down)?
What is the clock frequency of the AVR mcu on the
STK500 when shipped?
On the average, how many clock cycles are required
per instruction?
Using your answers from questions 2) and 3) above,
how long does a typical instruction take to run on the
AVR mcu?
Write pseudo c-code to toggle every other light to blink
every ¼ of a second. Example: 01010101 -> 10101010
-> 01010101 ->…
9
In-Lab Tasks
•
•
•
•
Program 1 called led.c; almost a duplication of
a program in the tutorial “Getting Started with
the CodeVision AVR C Compiler.”
Program 2 called led2.c; different patterns of
LEDs
Program 3 called led3.c; different patterns of
LEDs and different delay
Program 4 called HelloWorld.c; program
COM2 to display program output on a terminal
10
CodeVision Wizard
11
CodeVision Wizard
Select the chip
on your board
Select the right
frequency
12
CodeVision Wizard
Set Port A as Output Port
Need to set Ports as input or
Output depending on your
programs
13
CodeVision Wizard
Set USART parameters
Baud rate, Data, Stop bit
Parity.
14
CodeVision Wizard
Set the timer
parameters
15
CodeVision Wizard
CodeVision Wizard
generates C code according to
specifications you selected, i.e.,
I/O Ports, Timer, UART parameters
etc.
16
CodeVision Wizard
#include <mega16.h>
// LED's are on PORTB
unsigned char ledStatus = 0xFE;
// Timer 1 overflow interrupt service routine
interrupt [TIM1_OVF] void timer1_ovf_isr(void)
{
// Reinitialize Timer 1 value
TCNT1H=0xF8;
TCNT1L=0xFB;
// Place your code here
......
......
}
17
CodeVision Wizard
// Declare your global variables here
void main(void)
{
// Declare your local variables here
// Input/Output Ports initialization
// Port A initialization
// Func0=In Func1=In Func2=In Func3=In Func4=In Func5=In Func6=In Func7=In
// State0=T State1=T State2=T State3=T State4=T State5=T State6=T State7=T
PORTA=0x00;
DDRA=0x00;
// Port B initialization
// Func0=Out Func1=Out Func2=Out Func3=Out Func4=Out Func5=Out Func6=Out
Func7=Out
// State0=1 State1=1 State2=1 State3=1 State4=1 State5=1 State6=1 State7=1
PORTB=0xFF;
DDRB=0xFF;
18
CodeVision Wizard
// Port C initialization
// Func0=In Func1=In Func2=In Func3=In Func4=In Func5=In Func6=In Func7=In
// State0=T State1=T State2=T State3=T State4=T State5=T State6=T State7=T
PORTC=0x00;
DDRC=0x00;
// Port D initialization
// Func0=In Func1=In Func2=In Func3=In Func4=In Func5=In Func6=In Func7=In
// State0=T State1=T State2=T State3=T State4=T State5=T State6=T State7=T
PORTD=0x00;
DDRD=0x00;
// Timer/Counter 0 initialization
// Clock source: System Clock
// Clock value: Timer 0 Stopped
TCCR0=0x00;
TCNT0=0x00;
19
CodeVision Wizard
// Timer/Counter 1 initialization
// Clock source: System Clock
// Clock value: 3.594 kHz
// Mode: Normal top=FFFFh
// OC1A output: Discon.
// OC1B output: Discon.
// Noise Canceler: Off
// Input Capture on Falling Edge
TCCR1A=0x00;
TCCR1B=0x05;
TCNT1H=0xF8;
TCNT1L=0xFB;
OCR1AH=0x00;
OCR1AL=0x00;
OCR1BH=0x00;
OCR1BL=0x00;
20
CodeVision Wizard
// Timer/Counter 2 initialization
// Clock source: System Clock
// Clock value: Timer 2 Stopped
// Mode: Normal top=FFh
// OC2 output: Disconnected
TCCR2=0x00;
ASSR=0x00;
TCNT2=0x00;
OCR2=0x00;
// External Interrupt(s) initialization
// INT0: Off
// INT1: Off
GIMSK=0x00;
MCUCR=0x00;
21
CodeVision Wizard
// Timer(s)/Counter(s) Interrupt(s) initialization
TIMSK=0x04;
// Analog Comparator initialization
// Analog Comparator: Off
// Analog Comparator Input Capture by Timer/Counter 1: Off
// Analog Comparator Output: Off
ACSR=0x80;
// Global enable interrupts
#asm("sei")
while (1)
{
// Place your code here
};
}
22
CodeVision Wizard
from a student’s Lab1 Report
Results and Discussion:
1. Following the “Getting Started” instructions as closely
as possible actually worked as advertised and resulted
in the AVR flashing the LEDs in order. I was pleased
with how straight forward the process was and
experimented some with changing the interrupt time
and the order of the flashing lights.
2. …
23
Lab 1: Introduction
• led.c; led2.c; led3.c;
– Different delays can be implemented by including
delay.h; or you can write your own subroutine.
#include <delay.h> // delay_ms(125)
• HelloWorld.c
– Needs I/O functions, the Wizard will add
#include <stdio.h> into the generated C program after
specifying UART parameters.
#include <mega16.h>
// Standard Input/Output functions
#include <stdio.h>
24
Part of HelloWorld.c
#include <mega16.h>
#include <delay.h>
// Standard Input/Output functions
#include <stdio.h>
void main(void)
{
…………………………….
// UART initialization
// Communication Parameters: 8 Data, 1 Stop, No Parity
// UART Receiver: On
// UART Transmitter: On
// UART Baud rate: 9600
UCR=0x18;
UBRR=0x17;
while (1)
{
// Place your code here
delay_ms(500); //Use delay function to generate ½ second interval.
printf(“Hello World “); //Output “Hello World”.
};
}
25
Lab Report Format
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Cover page (include date due, date turned in)
Prelab questions and answers (typed)
Summary of the lab tasks
In-lab tasks, questions and solutions including
software and hardware
Results and Discussion
Code listing for each task
All lab report should be typed and turned in a hard copy on time
26
Check Out Sheet
Box Number:
Name:
Date:
27
In-lab demo (EN 229)
Create project
Configure peripherals
Add C-code
Hook up STK500
Compile and build
Download and run
28