one word hyphen
advertisement

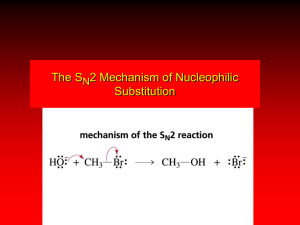
Naming Organic Molecules Naming Hydrocarbons: Hydrocarbons are molecules made from carbon and hydrogen. H H C H H H Methane H H H C C H H Ethane H H H C C C H H H H Propane H H H H H H C C C C H H H H Butane H Naming Hydrocarbons Number of Carbons Name 1 Methane 2 Ethane 3 Propane 4 Butane 5 Pentane 6 Hexane 7 Heptane 8 Octane 9 Nonane 10 Decane Naming hydrocarbons: 5 Rules 1. Identify the longest continuous carbon chain (the parent chain), which may or may not be shown in a straight line, and name the chain. H3C CH2 CH2 CH CH3 pentane CH3 CH3 CH CH2 CH3 CH2 CH2 CH3 hexane 2. Number the carbon atoms in the parent chain from the end of the nearest substituent (alkyl group). 1 2 H3C 3 CH2 5 4 4 CH2 3 5 CH CH3 2 1 CH3 CH3 3 4 CH CH2 4 2 1 3 CH2 5 CH3 6 6 5 CH2 2 CH3 1 3. If only one alkyl group is present, name and locate it (by number), and attach the number and name to that of the parent chain. H3C CH2 5 4 CH2 3 CH CH3 2 1 CH3 2-methylpentane one word CH3 2 1 3 4 CH CH2 CH2 CH3 5 CH2 6 CH3 hyphen 3-methylhexane Alkyl group naming – Change “ane” to “yl” when the substituent is an alkyl group. Number of Carbons Name Name 1 Methane Methyl 2 Ethane Ethyl 3 Propane Propyl 4 Butane Butyl 5 Pentane Pentyl 6 Hexane Hexyl 7 Heptane Heptyl 8 Octane Octyl 9 Nonane Nonyl 10 Decane Decyl 4. If two or more of the same kind of alkyl group are present in a molecule, indicate the number with a Greek numerical prefix (di, tri, tetra, penta…). In addition, a number specifying the location of each identical group must be included. These position numbers, separated by commas, precede the numerical prefix. Numbers are separated from by hyphens. 1 H3C 2 CH 3 CH2 CH3 4 5 CH CH3 2,4-dimethylpentane CH3 CH3 1 H3C 2 CH2 3 4 C 3,3-dimethylpentane CH3 5 CH2 CH3 5. When two kinds of alkyl groups are present on the same carbon chain, number each group separately, and list the names of the alkyl groups in alphabetical order. 5 H3C 4 CH2 3 CH 2 CH2 CH3 di, tri… doesn’t count for alphabetizing… CH3 3-ethyl-2-methylpentane CH3 1 H3C 3-ethyl-4,5-dipropyloctane CH 1 2 CH2 3 CH 4 CH 5 CH CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3 CH2 CH2 CH3 CH3 6 CH2 7 CH2 8 CH3 Example 1 2 H3C 3 CH 8 4 CH2 7 CH3 6 6 5 CH2 5 CH CH2 4 CH2 7-methyl M 3 8 CH 2 CH3 2-methyl CH3 2,7-dimethyl 7 4-ethyl E 4-ethyl-2,7-dimethyloctane CH3 1 Beyond Hydrocarbons: Other Functional Groups Functional Groups A. Multiple Bonds Single Bond H H H C C H Ethane H Double Bond H H C H Triple Bond H C H C C H Ethene “Ethylene” Ethyne “Acetylene” H B. Halides H H H C C H H H F H C C H H Cl Ethyl Chloride Ethyl Fluoride H H H H C C H H Ethyl Bromide Br H H H C C H H Ethyl Iodide I C. Alcohols and Ethers H H H C C H H OH H H H C C H H O Ethyl Alcohol Diethyl Ether “Ethanol” “Ether” H H C C H H H D. Aldehydes and Ketones H H O C C H Ethanal “Acetaldehyde” H H H O H C C C H Dimethyl Ketone “Acetone” H H E. Carboxylic Acids and Esters H H O C C H Ethanoic Acid “Acetic Acid” OH H H O C C O H Ethyl Acetate H H C C H H H F. Amines H H H C C H H H NH2 H H H H H C C N C C H H H H Diethyl Amine H Ethyl Amine H H C H C H H H H H H C C N C C H H H H Triethyl Amine H H G. Amides H H O C C H “Acetamide” NH2 H. Thiols and Disulfides H H H C C H H Ethanethiol SH H H H C C H H S S Diethyl disulfide H H C C H H H III. O R-Groups are “Generics” R Cl R R R C OH Halide O OH O Carboxylic Acid R' Alcohol R C R Ether O N R' R" Ester Amine R' O R C H O R C R' O Aldehyde R Ketone R C NH2 R SH S S Amide Thiol R' Disulfide