Radar Love - Industrial Energy Technology Conference
advertisement

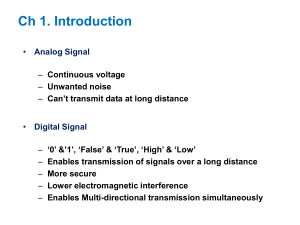
Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Authors: Ramin Taheri Seresht & Hassan Khodaei Jalalabadi Presented by: Ramin Taheri Seresht Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology The objectives of presentation: Introduce the conventional natural gas pressure reducing station. Introduce the turboexpander & its applications. Express thermodynamically difference between throttle valve and turboexpander. Select case study. Exergy analysis on the selected case study. Simulate the using of turboexpander in the selected case study. Economical analysis. Conclusion. Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Introduce the conventional natural gas pressure reducing station The different types of the conventional station: 1. City gate station (C.G.S.). 2. Town broad station (T.B.S.). 3. Combinatory station (C.G.S./T.B.S.). 4. Station for industrial consumptions. 5. Station for domestic consumptions. Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Introduce the conventional natural gas pressure reducing station Comparing the different types of conventional station on the base of pressure: Type of Station Inlet Pressure Outlet Pressure psi MPa psi MPa C.G.S. 1000 6.8 250 1.7 T.B.S. 250 1.7 60 0.4 C.G.S. / T.B.S. 1000 6.8 60 0.4 Industrial 1000 6.8 Domestic 60 0.4 60 0.4 Home Regulator 60 0.4 0.25 0.0017 Desired Pressure Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Introduce the conventional natural gas pressure reducing station The main components of a conventional station: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Ball / Globe valves. Filter. Regulator (Throttle valve). Relief valve. Safety shut off valve. Meter. Heater. Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Introduce the conventional natural gas pressure reducing station Please pay attention: All of types of gas stations just differ in size, inlet & outlet pressure, capacity and exitence of some components. But all of them reduce the gas pressure by using throttle valves (regulators). Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Introduce the conventional natural gas pressure reducing station Most important roles of the regulator in a conventional station are: 1. Reducing pressure. 2. Adjusting pressure. Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Introduce the conventional natural gas pressure reducing station How does a regulator (throttle valve) reduce the pressure? In the throttle-valve gas pressure is reduced in result of the isenthalpic expansion. In this process not only no energy is produced but also the energy of high-pressure gas is lost. Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Could the energy of high-pressure gas be recovered? Yes, of course. Why not? $ Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology How could the energy of high-pressure gas be recovered? It is so easy just by using the turboexpander. Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Introduce the turboexpander & its applications What are turboexpanders? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Turboexpanders are expansion turbines, rotating machines similar to steam turbines. Commonly, the terms “expansion turbines” and “turboexpanders” specially exclude steam turbines and combustion gas turbines. Turboexpanders can also be characterized as modern rotating devices that convert the pressure energy of a gas or vapor steam into mechanical work as the gas or vapor expands through the turbine. If chilling the gas or vapor stream is the main objective, the mechanical work so produced is often considered a byproduct. If pressure reduction is the main objective, then heat recovery from the expanded gas is considered a beneficial byproduct. In each case, the primary objective of turboexpanders is to conserve energy. Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Introduce the turboexpander & its applications The different designing types of turboexpanders: 1. Axial Type. 2. Radial Type. That the each of types has three typpes itself: Impulse. Reaction. Complex. Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Introduce the turboexpander & its applications The different power absorption methods in turboexpanders: 1. Direct-connected compressor. 2. Gear and generator. Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Introduce the turboexpander & its applications Turboexpander applications: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Recovering high pressure gas energy & power generation. Cryogenic process. Chemical & Petrochemical industries (included: FCC process and producing Nitric acid, Acetic acid, PTA & Terephtalic acid.). Oil & gas industries (included: LPG & LNG processes.). Separating air components. Liquefaction gases (like Helium). Separating condensable components of natural gas. Power generation from geothermal energy. Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Express thermodynamically difference between throttle valve & turboexpander As thermodynamically point of view: In the throttle-valve gas pressure is reduced in result of the isenthalpic expansion. In the throttle valve not only no energy is produced but also the energy of high-pressure gas is lost. In the turboexpander the gas pressure is reduced in the isentropic expansion. But in the turboexpander the energy of high-pressure gas is recoverd. Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Express thermodynamically difference between throttle valve & turboexpander On the other hand: Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Select case study The C.G.S. No. 2 of Tehran was selected as case study for following reasons: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Existing enough space for turboexpander installation. Existing three heaters that they could be heated the entering gas to turboexpander if it was needed. In this station, the changes of inlet pressure gas is less than the other stations in the country. In this station, the changes of passed flow rate gas is less than the other stations in the country. In this station, just for a few days in the year the passed flow of gas is cut off when the annual maintenance operations are done. This station is next to some residential areas and a few industrial manufacture so that, it might be used of power generation directly if it was needed. Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Select case study The chemical compounds of gas that is passed through the C.G.S. No. 2 of Tehran are as table: Chemical Compounds No. Name Chemical Formula Mole Percent 1 Nitrogen N2 3.70 2 Methane CH4 89.80 3 Dioxide Carbon CO2 1.10 4 Ethane C2H6 3.70 5 Propane C3H8 0.98 6 Iso Butane C4H10 0.22 7 Normal Butane C4H10 0.29 8 Iso Pentane C5H12 0.10 9 Normal Pentane C5H12 0.07 10 Hexane C6H14 0.04 Tatol 100.00 Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Select case study The physical properties of gas that is passed through the C.G.S. No. 2 of Tehran are as following table: No. Physical Property 1 Calculated Average Molecular Weight 2 Calculated Gas Specific Gravity, Air = 1.000 (MW of Air = 28.964 gr/mol) 3 Calculated Gas Density (P = 1013.25 mbar , T = 15 °C) 4 5 Unit Quantity gr/mol 17.93 --- 0.619 Kg/m3 0.758 MJ/m3 34.4 Btu/ft3 920.4 MJ/m3 38.2 Btu/ft3 1020.1 Calculated Net Calorific Value (P = 1013.25 mbar , T = 15 °C) Calculated Gross Calorific Value (P = 1013.25 mbar , T = 15 °C) Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Select case study The monthly average quantities of inlet pressure, outlet pressure, outlet temperature & flow rate of gas that is passed through the C.G.S. No. 2 of Tehran (in 1385) are as table: Monthly Average Quantities Months in 1385 Inlet Pressure Outlet Pressure Outlet Temperature Flow Rate MPa psi MPa psi °C °F Nm3/hr Kg/sec Farvardin 4.4 644 1.7 250 7.7 45.9 176,880 37.24 Ordibehesht 4.6 670 1.7 250 10.7 51.3 104,105 28.31 Khordad 4.9 726 1.7 250 8.0 46.4 170,514 35.90 Tir 5.3 775 1.7 250 8.7 47.7 154,239 32.48 Mordad 5.3 775 1.7 250 8.8 47.9 132,929 27.99 Shahrivar 4.9 726 1.7 250 10.2 50.4 184,663 38.88 Mehr 4.2 619 1.7 250 10.4 50.6 178,689 37.62 Aban 3.9 566 1.8 259 10.4 50.6 262,381 55.25 Azar 2.4 350 1.8 270 10.8 51.4 346,470 72.95 Day 2.3 337 1.7 257 10.9 51.7 427,071 89.92 Bahman 3.2 470 1.8 271 10.3 50.5 398,845 83.98 Esfand 3.0 445 1.8 267 10.4 50.8 355,395 74.83 Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Select case study The curves of monthly average inlet & outlet pressure profiles in 1385 for C.G.S No. 2 of Tehran are as follow: 1000 900 800 4 700 Pressure (psi) 5 3 6 2 1 7 600 8 500 11 12 400 300 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 7 9 10 9 10 11 12 200 100 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Months of Year Outlet Pressure Inlet Pressure 9 10 11 12 6.8 6.4 6.0 5.6 5.2 4.8 4.4 4.0 3.6 3.2 2.8 2.4 2.0 1.6 1.2 0.8 0.4 0.0 Pressure (MPa) The Curves of Average Inlet & Outlet Pressure Profiles in the Year of 1385 Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Select case study The curves of monthly average outlet temperature profiles in 1385 for C.G.S No. 2 of Tehran are as follow: The Curves of Average Outlet Temperature Profiles in the Year of 1385 20 68.0 Temperature (C) 56.0 12 2 8 7 6 10 11 12 50.0 5 4 3 1 9 8 44.0 4 38.0 0 32.0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Months of Year Outlet Temperature 9 10 11 12 Temperature (F) 62.0 16 Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Select case study The curves of monthly average flow rate profiles in 1385 for C.G.S No. 2 of Tehran are as follow: 570000 532000 494000 456000 418000 380000 342000 304000 266000 228000 190000 152000 114000 76000 38000 0 120.00 108.00 96.00 10 84.00 11 12 9 72.00 60.00 8 48.00 1 6 3 4 2 2 7 36.00 5 24.00 12.00 0.00 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Months of Year Flow Rate 8 9 10 11 12 Flow Rate (Kg/sec) Flow Rate (Nm3/hr) The Curve of Average Flow Rate Profiles in the Year of 1385 Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Exergy analysis on the selected case study At definition: Exergy is maximum work (shaft work) can be obtained from a specified quantity of energy. And exergy is equal to summation of all its components: ex exK exP exPh exDi exCh Where: exK = kinetic exergy. exP = potential exergy. exPh = physical (termomechanical) exergy. exDi = diffusion exergy. exCh = chemical exergy. Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Exergy analysis on the selected case study In the selected case stydy: exK = exP = exDi = exCh = 0. And: exPh T C P T T0 T0 ln T0 P RT0 ln P0 CP a bT cT dT 2 For calculating CP: CPmix xi CP i 3 Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Exergy analysis on the selected case study With substituting the monthly average quantities in the recent relations is obtained: Months in 1385 Calculated Monthly Average Exergy KJ/Kgmole KW KWhr Farvardin 2,158.452 4,483.031 3,335,375 Ordibehesht 2,277.888 3,596.599 1,812,686 Khordad 2,406.358 4,818.085 3,584,655 Tir 2,591.160 4,693.858 3,492,230 Mordad 2,591.866 4,046.087 3,010,288 Shahrivar 2,420.588 5,248.882 3,905,168 Mehr 2,066.357 4,335.548 3,121,594 Aban 1,768.406 5,449.216 3,923,436 Azar 660.584 2,687.652 1,935,110 Day 691.912 3,469.981 2,498,386 Bahman 1,314.629 6,157.422 4,433,344 Esfand 1,167.514 4,872.566 3,391,306 Annual Summation 38,443,578 Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Exergy analysis on the selected case study The curves of monthly average exergy profiles in 1385 for C.G.S No. 2 of Tehran are as follow: The Curves of Average Exergy Profiles in the Year of 1385 3000 6500 11 2500 5700 6 3 2 8 6 1 7 2000 3 12 4900 4 8 1 7 1500 4100 5 11 2 12 10 1000 3300 9 9 10 500 2500 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Months of Year Exergy (KJ/Kgmole) Exergy (KW) 10 11 12 Exergy (KW) Exergy (KJ/Kgmole) 5 4 Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Simmulate the using of turboexpander in the selected case study Simulation has been done by using the Thermoflow software at two following states: 1. 2. One turboexpander is installed so as parallel with the station. Three turboexpanders are installed so as parallel with each unit of the station. So that each of these states has two other states: 1. 2. Without gas preheating. With gas preheating. Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Simmulate the using of turboexpander in the selected case study The state of one turboexpander and without gas preheating: 3 10 2 1 68.0 25.0 126 68.0 25.0 42.0 13 15 17 16 68.0 68.0 25.0 25.0 42.0 42.0 10 68.0 25.0 0 11 12 68.0 25.0 0 12 14 68.0 25.0 0 9 68.0 25.0 42.0 21 2 17.0 -60.8 126 68.0 25.0 126 9 11 68.0 25.0 42.0 20 4 14 18 8 68.0 25.0 126 Q+ 19 68.0 25.0 0.013 68.0 25.0 0 15 20 13 68.0 25.0 42.0 19 22 21 68.0 68.0 25.0 25.0 0 0 16 3 68.0 25.0 0 5 Q+ 17 4 68.0 25.0 0 6 Q+ 24 17.0 25.0 0 18 5 68.0 25.0 0 THERMOFLEX Version 13.0 Ramin Taheri Home 1130 File = H:\Final Project\Work\Modified Typed Files\Simulation Files by Thermoflow\Case 7-1-1-1.tfx 01-12-2009 15:55:03 8 23 17.0 25.0 0 25 17.0 25.0 0 7 17.0 -60.8 126 7 6 17.0 25.0 0.013 1 Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Simmulate the using of turboexpander in the selected case study The state of one turboexpander and with gas preheating: 4 10 2 1 68.0 25.0 126 68.0 25.0 42.0 13 15 17 16 68.0 68.0 25.0 25.0 42.0 42.0 10 68.0 25.0 0 9 68.0 25.0 42.0 19 Q+ 3 2 17.0 -44.1 126 3 68.0 45.0 42.0 68.0 45.0 126 5 11 12 68.0 25.0 0 11 68.0 25.0 42.0 20 Q+ 4 68.0 45.0 42.0 14 68.0 25.0 0 13 68.0 25.0 42.0 21 Q+ 8 68.0 45.0 126 15 20 5 68.0 45.0 42.0 8 7 17.0 -44.0 126 23 17.0 45.0 0 19 68.0 45.0 0.013 68.0 45.0 0 6 12 16 14 18 9 22 21 68.0 68.0 45.0 45.0 0 0 17 24 17.0 45.0 0 18 25 17.0 45.0 0 THERMOFLEX Version 13.0 Ramin Taheri Home 1130 File = H:\Final Project\Work\Modified Typed Files\Simulation Files by Thermoflow\Case 7-1-1-2.tfx 01-12-2009 00:53:44 7 6 17.0 45.0 0.013 1 Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Simmulate the using of turboexpander in the selected case study The state of three turboexpanders and without gas preheating: 3 13 13 68.0 25.0 0 2 1 68.0 25.0 126 68.0 25.0 42.0 16 18 20 68.0 25.0 42.0 19 68.0 25.0 42.0 14 15 68.0 25.0 0 15 17 68.0 25.0 0 2 17.0 -60.8 42.0 68.0 25.0 42.0 17 21 12 68.0 25.0 42.0 23 22 68.0 25.0 0 6 Q+ 20 5 68.0 25.0 0 24 68.0 25.0 0 3 17.0 -60.8 42.0 7 Q+ 26 68.0 25.0 0 8 Q+ 10 17.0 -60.8 42.0 28 17.0 25.0 0 5 4 17.0 -60.8 42.0 68.0 25.0 42.0 19 25 16 68.0 25.0 42.0 25 11 21 6 68.0 25.0 0 9 17.0 -60.8 42.0 27 17.0 25.0 0 4 68.0 25.0 42.0 18 23 14 68.0 25.0 42.0 24 10 12 22 7 68.0 25.0 0 THERMOFLEX Version 13.0 Ramin Taheri Home 1130 File = H:\Final Project\Work\Modified Typed Files\Simulation Files by Thermoflow\Case 7-1-2-1.tfx 01-12-2009 01:25:57 29 17.0 25.0 0 11 17.0 -60.8 42.0 9 8 17.0 -60.8 126 1 Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Simmulate the using of turboexpander in the selected case study The state of three turboexpanders and with gas preheating: 3 13 13 68.0 25.0 0 12 68.0 25.0 42.0 23 Q+ 2 17.0 -44.1 42.0 68.0 45.0 42.0 16 18 6 19 68.0 45.0 0 5 68.0 45.0 42.0 9 8 17.0 -44.0 42.0 20 27 17.0 4 45.0 0 2 1 68.0 25.0 126 19 68.0 25.0 42.0 24 26 68.0 25.0 42.0 7 25 68.0 25.0 42.0 14 15 68.0 25.0 0 14 68.0 25.0 42.0 24 Q+ 17 6 68.0 45.0 42.0 3 17.0 -44.1 42.0 68.0 45.0 42.0 20 21 68.0 45.0 0 10 9 17.0 -44.0 42.0 21 28 17.0 5 45.0 0 8 15 17 68.0 25.0 0 16 68.0 25.0 42.0 25 Q+ 4 17.0 -44.1 42.0 68.0 45.0 42.0 18 22 7 68.0 45.0 42.0 23 68.0 45.0 0 22 THERMOFLEX Version 13.0 Ramin Taheri Home 1130 File = H:\Final Project\Work\Modified Typed Files\Simulation Files by Thermoflow\Case 7-1-2-2.tfx 01-12-2009 01:58:37 29 17.0 45.0 0 11 10 17.0 -44.0 42.0 12 11 17.0 -44.0 126 1 Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Simmulate the using of turboexpander in the selected case study The results of simulation has been summarized as following: The States of Simullation Produced Power (KW) Produced Annual Energy (KWhr) One Turboexpander without Gas Preheating 19,347.6 164,841,552 One Turboexpander with Gas Preheating 20,728.1 176,603,412 Three Turboexpanders without Gas Preheating 19,347.6 164,841,552 Three Turboexpanders with Gas Preheating 20,728.5 176,606,820 Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Economical analysis Tuboexpander price is obtainable by using following relation or figure: Price (million$) 0.005312 Output (kW) 0.7294 Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Economical analysis The local price of electrical energy is as the following table: Local Price of Electrical Energy (KWhr / Rls.) Year Domestic General 1383 104.20 151.41 1387 773.00 1123.22 Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Economical analysis The global price of electrical energy is obtained by the following curve: Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Economical analysis The results of economical calculations is summarized into the tables: Table Legend: A = The Installation & Commissioning Cost (mil. Rls.). B = The Maintenance Cost (mil. Rls.). C = The Investment Cost (mil. Rls.). D = The Annual Income of Produuced Electrical Energy with Considering Local Price (mil. Rls.). E = The Annual Income of Produuced Electrical Energy with Considering Global Price (mil. Rls.). F = The Time of Investment Payback with Considering Local Price (Years.). G = The Time of Investment Payback with Considering Global Price (Years). Turbine Numbers The Price of One Turbine (mil. Rls.) The Price of Total Procurement (mil. Rls.) A B C D E F G 1 75,000 75,000 1,500 750 76,500 43,181 46,132 1.8 1.7 3 34,000 102,000 2,040 1,020 104,040 43,181 46,132 2.5 2.3 Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Conclusion According to that was mentioned, using turboexpanders at natural gas pressure reducing stations not only is economical but also its produced electrical energy in compare of other sources has following advantages: 1. For producing that doesn’t need to very high investment like power plants & water dams systems. 2. For producing that doesn’t need to consumption of fossil fuel. 3. Producing that doesn’t emit any pollutant in environment. 4. Maintenance cost of its facilities is so less than a power plant or a water dam. 5. For producing that doesn’t need to a lot personnel. 6. For producing that doesn’t need to occupy a lot space. Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Last Word Using the turboexpanders at the natural gas pressure reducing stations could be a historical opportunity. And if we don’t apply them now, perhaps tomorrow would be too late. Retrofit of Tehran City Gate Station C.G.S. No.2 by Using Turboexpander Yasun Farayand Company & K.N. Toosi University of Technology Any Question? Thanks for your attention.
![Amir Shams [ card ] 02](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005340099_1-e713f7ae67edd60d4c53ae5bb9448166-300x300.png)