Chi_-_Ploidy_level_e.. - breedingtropicalacacias.com
advertisement

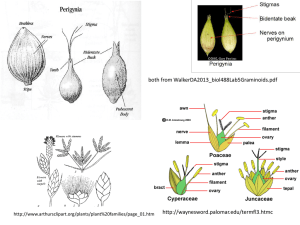
Ploidy level effects on floral morphology of Acacia mangium and its comparison to A. auriculiformis Nghiem Quynh Chi Supervisors: Rod Griffin Chris Harwood Anthony Koutoulis Jane Harbard Species to be studied 1. Acacia mangium Willd (A.m) 2. Acacia auriculiformis A.Cunn ex Benth (A.a) - adaptable to a wide range of site conditions - produce pulp logs and small sawlogs in period of 7 to 10 years Together with Eucalyptus and Acacia hybrid, they are the main species for short -rotation tree plantations in Vietnam Plantation Area (ha) A.a: 92,000 A.m: 154,000 A.m x A.a hybrid: 232,000 (Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Dev. 2009) Acacia plantation in Vietnam Background ACIAR project FST/2003/002 - collaboration between Australia, South Africa, and Vietnam Prof. Rod Griffin – Australian Project Leader Objective: Develop polyploid breeding methods for Acacia species - Hybrids (2X or 3X) Provide genetically improved material (hybrid vigour in growth and timber quality, occurs in natural Acacia hybrids) - Triploids Increase woody biomass (triploid hybrids of white Poplars was used in China to obtain heterosis in growth and resistance (Li S et al. 2004; Kang X et al. 2000)) Reduce invasive weeds in exotic environments (sterility) … Continued … Ha Tay prov., the North 32 polyploid A. mangium clones came from cochicines induction on seeds (from Shell Company) Quang Tri prov., the Central Propagation Binh Duong prov., the South Somatic chromosome number of A.m & A.a: 2X = 2n = 26 (Shukor et al., 1992) 3 field trials were established in 2003 with the same design Trial Design - rows of a mix of polyploid clones interplanted with rows of a mix of A.m clones and a mix of A.a clones - single trees plots/ 4 replicates A.a 2X A.m 4X A.m 2X A.m 4X 4m 2.5m 20 trees per row Polyploid A.m: Diploid A.m: Diploid A.a: 30 clones 10 clones 10 clones Breeding system 1.2 Study with microsatellite markers showed that tetraploid A. mangium at Bau Bang had much higher selfing rates than diploid (Tran Duc Vuong, 2009) Outcrossing rates 1 0.8 Diploid 0.6 Tetraploid 0.4 0.2 0 2006 2007 Combined -0.2 Polyploidy in angiosperms is frequently associated with increased selfcompatibility. Chromosome doubling often produces new allelic interactions in pollen that lead to a breakdown of self-incompatibility (de Nettancourt, 2000). Barrier to pollination between diploids and tetraploids Insect behaviours Pollination 2x A.a 2x A.m 4x A.m Bau Bang trial Is there a strong barrier for crossing of 2X and 4X trees within species? 3X hybrid (A.a x A.m) seedling Reproductive barriers to interploid crosses 1. Pre-mating (e.g. flowering time, pollinator behaviour) 2. Post-mating a. Pre-zygotic barriers (e.g. flower structure or preventing pollen tube penetration in stigma or style) b. Post-zygotic barriers (e.g. embryo abortion) My research question The feasibility of producing Acacia triploids and hybrids via sexual reproduction Different species Different ploidy levels (A.m x A.a and A.a x A.m) (4X x 2X and 2X x 4X) Spike & Flower - Length of spike - Total number of flowers per spike - The ratio of male to hermaphrodite flowers - Length of flower Style & Stigma Floral Morphology and Seed number (compare 4X & 2X) - Length of style - Stigma diameter Polyad - Polyad diameter - Polyad germination Ovary & Ovule - Number of ovules per ovary Seed - Number of seeds & full seeds/pod Materials and Methods Flowers and pollen were sampled in Vietnam Spikes 10 clones x 1 ramet x 3 spikes = 30 spikes/species Flowers 10 clones x 1 ramet x 1 spike x 30 flowers = 300 flowers/species Polyad diameter and no. of ovules/ovary 10 clones x 1 ramet x 30 polyads & ovaries = 300 polyads & ovaries/species Seed number 10 clones x 1 ramet x 30 pods = 300 pods/species Flowers fixed in 3:1 methanol:acetic acid solution and preserved in 70% alcohol Observation using light microscope, fluorescence microscope with UV light, and scanning electron microscope (SEM) Spike parameters Species Ploidy level Length of Spike (mm) A. mangium 2X 99.6 Total no. of flowers/ spike a (±12.7) 4X 86.6 2X 57.6 (±10.3) A. mangium 2X a (±41.9) b (±12.0) A. auriculiformis 205.0 Percentage of male flowers/ spike 194.5 90.4 (±17.7) A. mangium 4X b (±23.4) a (±35.7) c 11.2 20.3 a (±16.8) b 22.5 a (±26.0) A. auriculiformis 2X Length of flower and style Species Ploidy level Length of flower (mm) A. mangium 2X 5.1 (±0.3) a 4.2 (±0.3) a 4X 4.8 (±0.3) b 3.8 (±0.3) b 2X 4.3 (±0.5) c 3.4 (±0.5) c A. auriculiformis A. mangium 2X A. mangium 4X Length of style (mm) A. auriculiformis 2X Polyad and stigma diameter and number of ovules Polyad diameter (µm) Stigma diameter (µm) Number of ovule Species Ploidy level A. mangium 2X 33.2 48.2 14.0 c (±1.6) 4X 42.2 (±2.6) a (±2.3) A. auriculiformis 2X 37.1 (±1.9) A. mangium 2X c 59.7 (±1.5) a (±3.9) b 49.9 (±1.8) A. mangium 4X b 12.9 a (±1.4) b 15.2 b (±1.5) A. auriculiformis 2X Pollen viability in vitro No. of germinated polyads 12.0 10.0 8.0 6.0 4.0 2.0 0.0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 > 12 No. of pollen tubes per polyad A. mangium 4X A. mangium 4X A. mangium 2X A. auriculiformis 2X A. mangium 2X A. auriculiformis 2X Number of seeds and full seeds Number of seeds/pod Number of full seeds/pod Species Ploidy level A. mangium 2X 9.7 8.7 a (±1.1) 4X 4.3 (±1.3) c 2.8 (±1.3) A. auriculiformis 2X 7.9 2 3 c (±1.0) b 5.3 (±1.8) 1 a b (±1.7) 4 Seed score: - Small and empty seed: Big and empty seed: Small and full seed: Big and full seed: 1 2 3 4 Conclusion There are significant differences in floral morphology between 4X & 2X A. mangium and 2X A. auriculiformis spike length total number of flowers/spike, the ratio of male to hermaphrodite flower/spike flower and style length polyad and stigma diameter number of ovules/ovary number of seeds & full seeds/pod However, the size of the stigma cup is always greater than that of polyad regardless of whether they are diploids or tetraploids This allows at least one polyad to be accommodated on the stigma for pollination Style Stigma Polyad Controlled pollination has been carried out 1. Thinning and emasculation 3. Applying pollen 2. Put sugar solution on stigma 4. Bagging To answer the question “Whether we can produce triploids of A.m and acacia hybrid (A.m x A.a) by sexual reproduction ” We need to compare the penetration of pollen tubes in different crosses of two species (A.m & A.a) 2X x 2X (controlled pollination) 2X x 4X 4X x 2X 4X x 4X Pollen tube penetration (fluorescence microscopy) ♀Am58 (4X) x ♂ Am68 (2X) 2 hours 24 hours Stained with aniline blue, viewed under UV light 72 hours Enters in ovule Acknowledgement 1. Funding support - ACIAR ( Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research) Collaborative research projects John Allwright Fellowships - FSIV (Forest Science Institute of Vietnam) Field trials and personnel assistance 2. Assistance Prof. Rod Griffin Dr. Chris Harwood Ass. Prof. Anthony Koutoulis Ass. Prof. Rene Vaillancourt Ms. Jane Harbard Dr. Ha Huy Thinh Thanks for your attention