Empirical Formula
advertisement

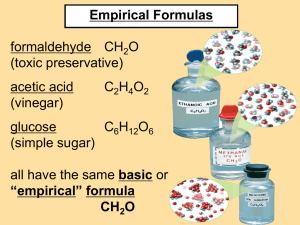
Empirical Formula Empirical: based on observation and experiment Empirical Formula • The lowest, whole number ratio of the atoms in a compound • The empirical formula of a compound does not always equal the molecular formula – Example: Hydrogen Peroxide » Molecular Formula = H2O2 » Empirical Formula = HO Ionic Formula • Ionic formula always equals empirical formula • Ionic compounds are always simple, whole-number ratios of elements • Examples: – FeS – Ammonium Phosphate – CaCO3 Determining Empirical Formula • Example: A compound has a percent composition of 27.29% carbon and 72.71% oxygen. What is the compound’s empirical formula? STEP ONE: Assume sample size is 100g STEP TWO: Determine how many grams of each element are present using percent composition » 27.29g C » 72.71g O STEP THREE: Determine the number of moles of each element in the sample Moles carbon = 27.29 g x 1 mol C = 2.27 moles C 1 12.0 g Moles oxygen = 72.71 g x 1 mol O = 4.54 moles O 1 16.0 g STEP FOUR: Convert the ratio of moles to the lowest whole number ratio by dividing each number by the lowest number of moles present C = 2.27 mol = 1 2.27 mol O= 4.54 mol = 2 2.27 mol Therefore, the empirical formula of this compound = CO2 Example #2 If 2.5 g of Al is heated with 5.28g of F, what is the EF of the resulting compound? 2Al + 3F2 2AlF3 Empirical Formula 2Al + 3F2 2.50g 2AlF3 5.28g Law of Conservation of Mass = Total mass of the compound = 7.78g Al = 2.50g/7.78g x 100% = 32.1% F = 5.28g/7.78g x 100% = 67.9% Change into grams 2.50g Al and 5.28g F Al 32.1% F 67.9% 32.1g 67.9g Determine how many moles of each you have Al F Molecular Formula • Either the same as empirical formula or a simple, whole number multiple of its empirical formula • Example: Benzene » Empirical = CH » Molecular = C6H6 • Example: Methanol » Empirical = CH4O » Molecular = CH4O Determining Molecular Formula • From empirical formula, empirical formula mass (efm) can be determined • Example: HO = 17.0 g/mol • Molar mass is determined experimentally • Example: 34.0 g/mol • Number of empirical formula units can be determined by these two values Molar Mass = Empirical Formula Multiplier efm • Example: HO 34.0 g/mol = 2 17.0 g/mol Therefore, the empirical formula of HO needs to be multiplied by two in order to find the molecular formula: (HO)x2= H2O2