Lab 6: Genetic Drift and Effective population size
advertisement

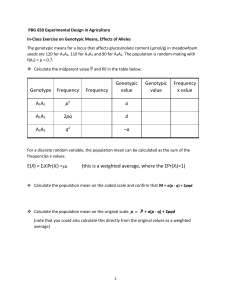
Lab 6: Genetic Drift and Effective population size Goals 1. To calculate the probability of fixation or loss of an allele. 2. To estimate mean time until fixation of an allele. 3. To estimate effective population size affected by past cataclysms. 4. To learn how genetic drift and selection interact in populations of various Ne. Probability of fixation or loss 1. Genetic drift results from chance changes in allele frequencies that result from sampling of gametes from generation to generation in a finite population. 2. Exact probability of fixation of an allele is equal to the initial frequency of that allele in absence of selection. u( p) p0 3. Probability of fixation of an allele can be calculated empirically by using Monte Carlo simulations as implemented in Populus. Problem 1. The frequencies of alleles A1 and A2 are p = 0.7 and q = 0.3, respectively. Use Populus to empirically estimate the probabilities of fixation and loss for each of these alleles. What do you think are the exact probabilities of fixation and loss for each allele? Do these probabilities depend on the population size?(15 minutes) Sr.# 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 # of run I II III IV V VI VII VIII IX X # of A1 loci lost 3 1 1 2 2 3 4 3 6 1 26 # of A1 loci fixed 7 9 9 8 8 7 6 7 4 9 74 Problem 2. Consider a population with the following genotype counts ( 15 minutes). Case 1 2 Genotype counts A1A1 A1A2 18 4 0 7 A2A2 3 21 a.) Use Populus to empirically estimate the mean time (in number of generations) until fixation for allele A1 b.) Show the mean time until fixation of A1 calculated using the diffusion approximation c.) Discuss the reasons for the differences (if any) between the two types of estimates. What are some of the assumptions underlying each method? Mean time until fixation of an allele depends on population size and initial frequency of that allele. Kimura and Ohta (1971) diffusion T ( p) approximat 4 N (1 p ) ln( 1 p ) ion : . p A1A1 A1A2 A2A2 (N11) (N12) (N22) N p q T(p) in terms T(p) of N 16 2 2 20 0.85 0.15 26.78 1.34N 0 2 18 20 0.05 0.95 77.96 3.90N Case - ? Population for allele A1 # generation when locus fixed 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 3 8 4 13 15 44 56 57 68 89 357 357/10= 35.7 Problem 3. The census populations size of an isolated population of finches on the Galapagos islands is as follows. What is the effective population size in 2010? Year 1930 1950 1970 1990 2010 Females Males 120 250 15 290 250 350 1500 2500 3500 5000 Ne t it i 1 Ne 1 Ni 4N f Nm N f Nm When time is discontinuous, a transition matrix can be used to determine the probability of fixation in the next generation. x ij P (Y t 1 i | Y t j ) ( 2 N )! ( 2 N i )! i! p (1 s ) pq (1 hs ) 2 p' p ' q ' 1 2 pqhs p s 2 i 2 N i Fitness Fitness in terms of s and h (adaptive Darwinian selection) Fitness in terms of s and h (purifying selection) A1A1 ω11 Genotype A1A2 ω12 A2A2 ω22 1+s 1 + hs 1 1 1 − hs 1−s • Using traditional setup for adaptive Darwinian (positive) selection • These can be easily converted to terms for purifying selection Let s D selection coefficien t under Darwinian Let s P selection coefficien t under purifying Let h D heterozygo us effect under Darwinian Let h P heterozygo us effect under purifying sP sD 1 sD h p 1 hD selection selection selection selection Problem 4. If adaptive Darwinian selection (characterized by h = 0.5 and s = 0.25) is operating on a locus and the frequency of allele A1 at that locus is p = 0.1, predict whether A1 is more likely to get lost or to become fixed: sD sP h p 1 hD i.) In a population with N = 10. e ii.) In a population with Ne = 100. 1 sD a.) For each of the cases, calculate the probability of A1 fixation empirically b.) If Ne affects the probabilities of fixation and loss of A1, explain why. If not, explain why not. Fitness Fitness in terms of s and h (adaptive Darwinian selection) Fitness in terms of s and h (purifying selection) A1A1 ω11 Genotype A1A2 ω12 A2A2 ω22 1+s 1 + hs 1 1 1 − hs 1−s Fitness Fitness under adaptive Darwinian selection Fitness under purifying selection Genotype A1A1 A1A2 ω11 ω12 A2A2 ω22 1.25 1.125 1 1 0.9 0.8 Problem 5. GRADUATE STUDENTS ONLY: Starting with the conditions in Problem 4-a), calculate the probability that: a.) The frequency of A1 becomes 0.1 in the next generation. b.) A1 becomes fixed in the next generation. c.) If the two transition probabilities differ dramatically, explain why. If not, explain why not.