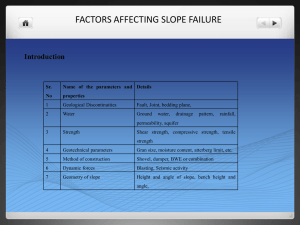
Classification systems in slope stability analysis
advertisement

Classification systems in slope stability analysis
• Slope Mass Rating (SMR)
• Chinese Slope Mass Rating System (CSMR)
• Rock slope rating (RSR)
• Slope stability rating (SSR) classification system
• Dump mass rating
Slope Mass Rating (SMR)
SMR = RMR + (F1 .F2 . F3) + F4
The RMR is computed according to Bieniawski’s 1979 proposal,
adding rating values for five parameters:
•
•
•
•
•
Strength of intact rock;
RQD (measured or estimated);
Spacing of discontinuities;
Condition of discontinuities; and
Water inflow through discontinuities
Where ‘A ‘denotes the angle between the strikes of slope face and joint.
(B)
where B denotes joint dip angle. For toppling mode of failure, F2 remains 1.
F3 reflects the relationship between the slope face and the joint dip.
F4 is a factor for the method of excavation. The adjustment factor for the method of excavation
has been fixed empirically as follows:
Adjustment ratings for method of excavation (after Romana, 1995)
Method
Natural
Presplitting
slope
F4
+15
+10
Smooth
Blasting
or Deficient
blasting
mechanical
Blasting
+8
0
-8
Rock slope rating (RSR)
P{f}
Slope Mass Quality
<20%
Highly stable
20%-40%
Stable
40%-60%
Fair
60%-80%
Unstable
80%-100%
Highly Unstable
Slope stability rating (SSR) classification system
Parameters
1
2
3
4
UCS (In Mpa)
0-10
10-25
25-50
50-100
100-150
0
7
18
28
37
Group1
Group 2
Group 3
Group 4
Group 5
Group6
0
4
9
17
20
25
Slope excavation
Waste
Poor
Normal
Smooth
presplitting
Natural
method
damp
blasting
blasting
blasting
-11
-4
0
6
10
24
Dry
0-20%
20-40%
40-60%
60-80%
80-100%
0
-1
-3
-6
-14
-18
0
0.15g
0.20g
0.25g
0.30g
0.35g
0
-11
-15
-19
-22
-26
Rock type
Ground
water
slope
rating
5
Earthquake force
rating