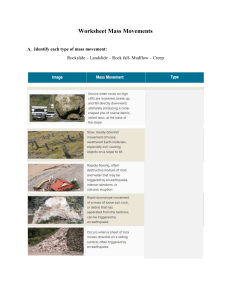
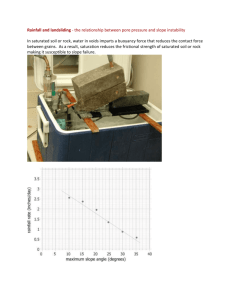
Mass Movements - Cal State LA
advertisement

Mass Movements Introduction • Explain why slopes fail under force of gravity • Explain factors influencing slope failure • Describe types of mass movements and why they usually occur • Discuss importance of mass movement processes in shaping landscapes and associated hazards Introduction • Rock, soils, and other materials move downhill – Sometimes rapidly, sometimes slowly – Pose threats to people – Modify the landscape Slope Stability and Mass Movement • Gravity is main force driving materials downslope • Slopes have threshold of steepness – Angle of repose is steepest angle at which a given material will remain stable – `sand 33-35 degrees, boulders as steep as 45 • Frictional strength of material resist movement – Rough surfaces greater frictional strength – Increased weight of material increases resistance Force of Gravity • Two components – Shear stress –pushes block parallel to slope – Other component pushes block into slope • Stress is perpendicular to slope surface • The greater the weight of block the more resistance to movement Cohesion • Besides shear stress, cohesion also resists motion • Is tendency of materials to stick together to resist movement • Cements and roots can increase cohesion Water Pressure • Increases chance of failure • Pressure of pores filled with water reduces frictional resistance Forms of Mass Movement • Mass movement – movement of earth materials by gravity – Mass wasting is term also used Creep and Solifuction • Slow almost imperceptible mass movement – Revealed by tilted trees, fence posts – Soil particles rise with freeze or wetting, settle lower on slope when warmed or dry – Flow of soil occurring mostly cold high latitudes Slides • Blocks of rocks moving on distinct plane – Landslide is general term – Slump is movement on a curved plane – Rockslides – large blocks break loose, move rapidly downslope • Important factors in slides – Groundwater pressure – Oversteepening slopes Flows • Fluid movement of loose earth materials – Earth flows are slow moving flows of mostly fine grained or clay-rich soil/sediment – Debris flows – fast-moving mixture of sediment and water • Mudflows are debris flows of mostly muddy sediment • Debris flows involve water Flows Rockslides • Mass of bedrock moving rapidly downslope • One of most dangerous mass movement types Fall • Rocks break off and fall to base of slope/cliff – Talus accumulates at base U.S. Map of Landslide Risk