Sec. IV.11 pH & pOH - Ooops!
advertisement
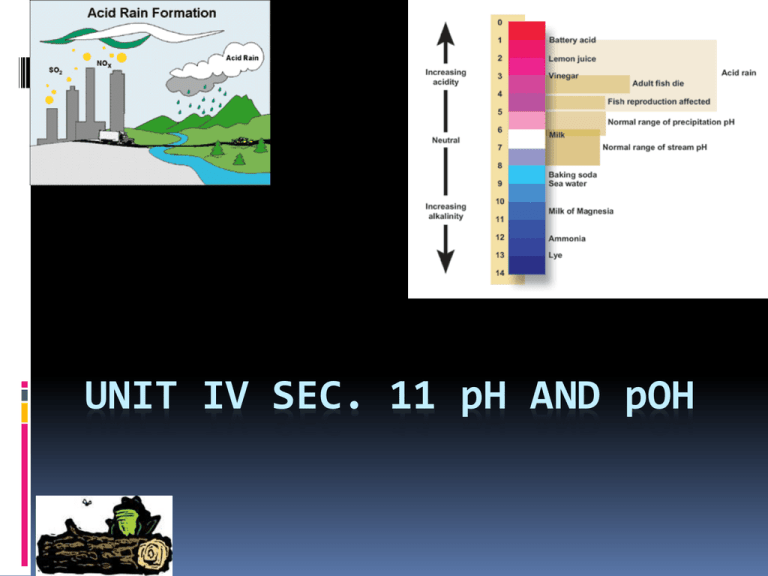
UNIT IV SEC. 11 pH AND pOH
You may have already noticed that [H+] are often very small
numbers.
For example the concentration of H+ ions in water is:
[H+] = 1.00 x 10-7 M
To deal with these very small number chemists devised a scale to
avoid using exponential numbers.
This is called the pH scale.
But what does pH represent? What is pOH? How is it related to
acid/base concentration?
This is what this section is all about.
pH stands for the negative log of the hydrogen ion
concentration.
pH = - log [H+]
pOH stands for the negative log of the hyrdroxide
ion concentration.
pOH = - log [OH-]
Remember your math:
a log is simply the exponent part of a number.
ie.
1000 = 103
log (103) = 3
ie.
0.00001 = 10-5
log (10-5) = -5
What about other numbers? (Use your calculator: log ).
1)
2.31
log (2.31) =
0.363
2)
207.4
log (207.4) =
2.317
3)
1.63 x 10-4
log (1.63 x 10-4) = -3.79
4) [H+] = 1.00 x 10-7 log (1.00 x 10-7) = -7
Calculating anti-log (real number) of a log number:
Log (x) anti-log of x 1ox
Log
Real number
(anti-log)
1)
1.35
22.4
2)
6.71
5.13 x 106
3)
-2.14
0.00724
4)
-8.94
1.14 x 10-9
Do Ex. #47 & 48 p. 134 - 135
One more math idea about logs:
Log (10x x 10y) =
log 10x + log 10y
If A = 10x and B = 10y
Then:
Log (A x B) =
log (A) + log (B)
When multiplying 2 numbers just add the logs
of those two numbers.
Back to pH and pOH:
Remember that in pure water Kw = 1.00 10-14
Kw = [H+][OH-] = 1.00 10-14
And therefore:
[H+] = 1.00 x 10-7 M
[OH-] = 1.00 x 10-7 M
In Pure
Water
Remember definition of pH and pOH
pH = - log [H+]
pH = - log [1.00 10-7 M ] = 7
pOH = - log [OH-]
pOH = - log [1.00 10-7 M ] = 7
Pure water is neutral because:
[H+] = 1.00 10-7 M = [OH-] = 1.00 10-7 M
And the pH and pOH of pure water = 7
There is a direct relationship between pH and
pOH in water:
pH + pOH = 14
If the [H+] is increased then the [OH-] must decrease
and visa versa.
ie. If pH = 1.3 then pOH = 12.7
If pOH = 10.4 then pH = 3.6
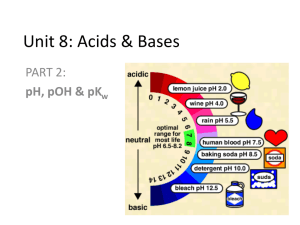
pH scale:
1.0
acidic
+
[H ]
basic
7.0
[OH-]
n
e
u
t
r
a
l
[H+]
[OH ]
14.0
Conversions: [H+] to pH and [OH-] to pOH
1) If [H+] = [H3O+] = 2.61 x 10-5 M, what is the pH?
pH = - log [H+]
pH = - log [2.61 x 10-5 ]
pH = 4.583
2) If [OH-] = 1.72 x 10-4 M, what is the pOH?
pOH = - log [OH-]
pOH = - log [1.72 x 10-4 M]
pOH = 3.764
And if either the pH or pOH is known, the other can be
determined:
If pH = 4.585 then {pOH = 14 – 4.585} = 9.415
If pOH = 3.764 then {pH = 14 – 3.764} = 10.236
3) If pH = 4.52 what is the [H+]?
Real number (Anti-log) = 1o-pH = 10-4.52
Therefore: [H+] = [H3O+] = 10-4.52 = 3.02 x 10-5 M
{Use 10x button on calculator}
4) If pOH = 1.69 what is the [OH-]?
Real number (Anti-log) = 1o-x = 10-1.69
Therefore: [OH-] = 10-1.69 = 2.04 x 10-2 M
{Use 10x button on calculator}
Now try these:
1) If pOH = 8.90 what is the [OH-], pH and [H3O+]?
(Answer: [OH-] = 1.26 x 10-9 M, pH = 5.1, [H3O+] = 7.94 x 10-6 M)
2) If pH = 3.20 what is the [H3O+], pOH and [OH-]?
(Answer: [H3O+] = 6.31 x 10-4 M, pOH = 10.80, [OH-] = 1.58x 10-11 M)
The pH Log Square:
pH = -log[H3O+]
[H3O+]
pH
[H3O+] = 10-pH
pH = 14 - pOH
pOH = 14 - pH
[OH-] =
pOH = -log[OH-]
pOH
[OH-] = 10-pOH
Kw
[H3O+]
[H3O+] =
[OH-]
Kw
[OH-]
Do Exercises # 49 – 53 on p.139
Do Exercises # 55 – 57 on p. 141