Document
advertisement
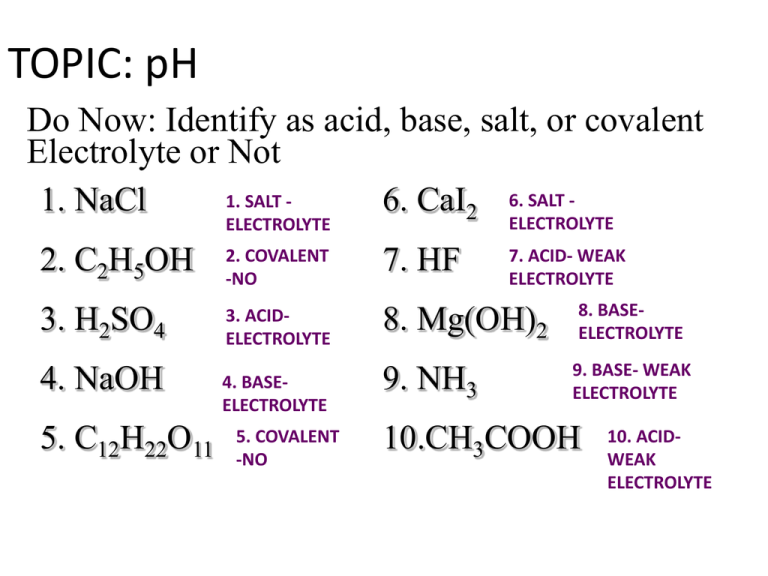
TOPIC: pH Do Now: Identify as acid, base, salt, or covalent Electrolyte or Not 1. SALT 1. NaCl 6. CaI2 6. SALT ELECTROLYTE ELECTROLYTE 2. C2H5OH 2. COVALENT -NO 7. HF 3. H2SO4 3. ACIDELECTROLYTE 8. Mg(OH)2 4. NaOH 4. BASEELECTROLYTE 9. NH3 5. C12H22O11 5. COVALENT -NO 7. ACID- WEAK ELECTROLYTE 8. BASEELECTROLYTE 9. BASE- WEAK ELECTROLYTE 10.CH3COOH 10. ACIDWEAK ELECTROLYTE Acid, Base, or Neutral • Neutral solution: [H+1] = [OH-1] • Acidic solution: H+1 > OH-1 • Basic solution: OH-1 > H+1 pH= LESS THEN 7 pH= GREATER THEN 7 pH scale measure how acidic/basic a substance is. Ranges from 0-14 0 more acidic more basic 14 more alkaline (another word for basic) Logarithmic scale (based on powers of 10) each decrease of one unit of pH represents a 10x increase in H+ concentration E: pH 4 is ten times more acidic then pH 5 Ex: pH 10 is ten times more basic then pH 9 Calculating pH • pH=-log [H+] – [H+] = concentration – Ex. 0.01M HCl has a pH of? • pH = -log(0.01) • pH=2 Concentration from pH • Which is more concentrated a HCl solution with a pH or 2 or 3? – pH 2 is 10 times more concentrated (remember changes by 10) – Try it • Antilog (2nd log) 2 = 0.01M • Antilog 3 = 0.001M Try to remember: The lower the pH – the high the concentration of H+ ions So how do you find pH of a base? • All you have are OH- ions – ONLY CAN CALC pOH • pOH=-log [OH-] – [OH-] = concentration – pH + pOH = 14 – So 14 – pOH = pH – Ex. 0.01M NaOH has a pH of? • pOH = -log(0.01) • pOH=2 • pH = 14-2 = 12 pH range • 0 to 14 –with 7 being neutral • pH = 0, strongly acidic • pH = 14, strongly basic Because it’s based on powers of 10 there is a trick • If molarity of acid is .001M =10-3 pH = 3 • If molarity of acid is .00001M = 10-5 pH = 5 • If molarity of base is .001M = 10-3 pOH = 3 pH 14-3 = 11 • If molarity of base is .00001M = 10-5 pOH = 5 pH 14-5 = 9 •If pH = 4 • +1 [H ] =? • pOH = ? • -1 [OH ] =? Antilog(-pH) = [H+1] Antilog(-4) = 1 x 10-4 M pH + pOH = 14 4 + X = 14 X =10 Antilog(-10) = [OH-1] 1x10-10 M = [OH-1] • If the -1 [OH ] • pOH = ? • pH = ? • [H+1] =? =1X -3 10 M pOH = -log[OH-1] = -log(10-3) = 3 pH + pOH = 14 X + 3 = 14 X = 11 Antilog(-11) = 1x10-11 M • If the [H+1] = 1 x 10-5 M • The pH = ? pH=-Log (10-5) =5 • The pOH = ? pH + pOH =14 5+x =14 X=9 • The [OH-] = ? Antilog(-9) = 1x10-9M How to safely test pH • Instruments – use a pH meter • Indicators – use a series of indicators • See if the substance reacts with a metal other than Cu, Ag, or Au • NEVER “taste” Indicator • substance that changes color over narrow pH range • Use several indicators to narrow down pH range of substance Practice using table M 1. What indicator is yellow with a pH 9.8 2. Which indictor is blue with a pH of 5.6 0-3.0Orange3.1.-4.4 Green Pink Purple 0-3.7 3.8-5.4 Green Green 4.5-14 7.7-14 8.4-14 5.5-14 9.7-14









![[H + ] [OH ] - CCBC Faculty Web](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005793401_1-b043355121eb738cc68e8c8b1b02be73-300x300.png)
