Wave Equations Pptx
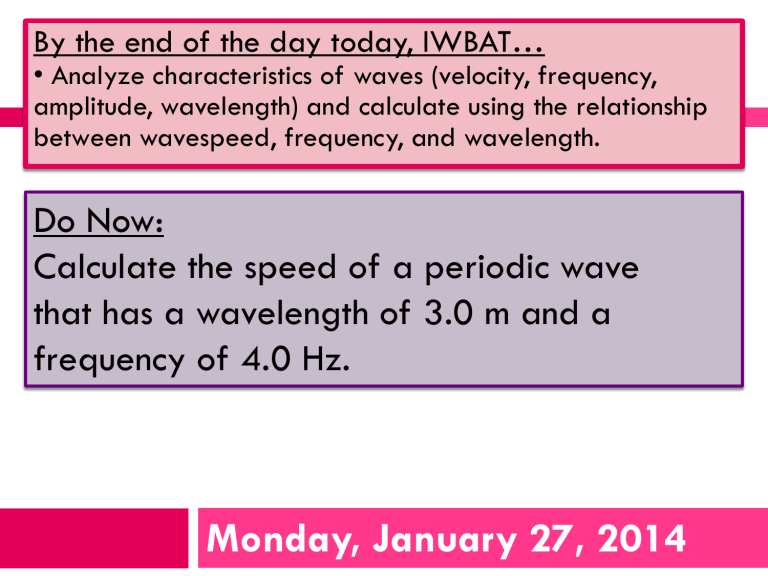
By the end of the day today, IWBAT…
• Analyze characteristics of waves (velocity, frequency, amplitude, wavelength) and calculate using the relationship between wavespeed, frequency, and wavelength.
Do Now:
Calculate the speed of a periodic wave that has a wavelength of 3.0 m and a frequency of 4.0 Hz.
Monday, January 27, 2014
Do Now:
Calculate the speed of a periodic wave that has a wavelength of 3.0 m and a frequency of 4.0 Hz.
Calculate the speed of a periodic wave
λ = 2.0 m and f = 3.0 Hz.
λ x f = 3.0 m x 4.0 Hz = 12.0 m/s
Monday, January 27, 2014
By the end of the day today,
IWBAT…
• Analyze characteristics of waves
(velocity, frequency, amplitude, wavelength) and calculate using the relationship between wavespeed, frequency, and wavelength.
Another Magic Triangle…
Do Now #2:
Calculate the wavelength of a water wave with a speed of 3.0 m/s and frequency of
4.0 Hz. (Answer in meters to the hundredths.)
Calculate the wavelength
λ x f = v → v
÷ f = λ
Monday, January 27, 2014
Do Now #2:
Calculate the wavelength of a water wave with a speed of 3.0 m/s and frequency of
4.0 Hz. (Answer in meters to the hundredths.)
Calculate the wavelength
λ x f = v → v
÷ f = λ
3.0 m/s
÷
4.0 Hz = λ = 0.75 m
Monday, January 27, 2014
Unit 9: Mechanical Waves
•
The Unit 9 Cover Sheet goes into your journals to keep track of your completed daily work prior to the exam. Record all assignments and keep it together.
Monday, 01/27/14
TEKS:
P.7B Investigate and analyze characteristics of waves, including velocity, frequency, amplitude, and wavelength…
Essential Question:
How do we calculate wavespeed, frequency and wavelength?
By the end of today,
IWBAT… calculate using the relationship between wavespeed, frequency, and wavelength.
Topic:
Mechanical Wave
Equations
Mechanical Waves Equations
Use your Mini-Books for reference
Create a sample wave on your C-Notes and label all components.
Identify each component of the waveform
Solve the sample questions using wave equations.
Y-axis = displacement, the distance of a particle from its equilibrium position
X-axis can represent either time or distance from a specified point within the medium. A displacementtime graph shows the displacement of one particle of the medium as time goes by. A displacement-distance graph shows the displacement of all particles of the medium at one instant in time.
A = amplitude, the maximum displacement from equilibrium of any particle
Crest and trough are the points of maximum displacement from equilibrium above and below equilibrium position respectively.
λ = wavelength, the distance between two consecutive identical points on the wave eg between two crests or two troughs.
Frequency = equals the number of waves that passes a given point per second.
v = velocity, the speed with which the energy is being transferred in the direction of motion.
T.Q.
What is the amplitude of the pendulum swing based on the graph?
At what time will the pendulum be at a crest?
T.Q.
A
What is the amplitude of the pendulum swing based on the graph? 2.5 m
At what time will the pendulum be at a crest?
0.5 s
T.Q.
What is the wavelength of the wave?
If the spring oscillates at a rate fo 4 times per second, what is the velocity of the wave?
T.Q.
λ
What is the wavelength of the wave? 1.0 m
If the spring oscillates at a rate of 4 times per second, what is the velocity of the wave?
λ
x f = (1.0m) x (4/1) = 4.0 m/s