Brainstem
advertisement
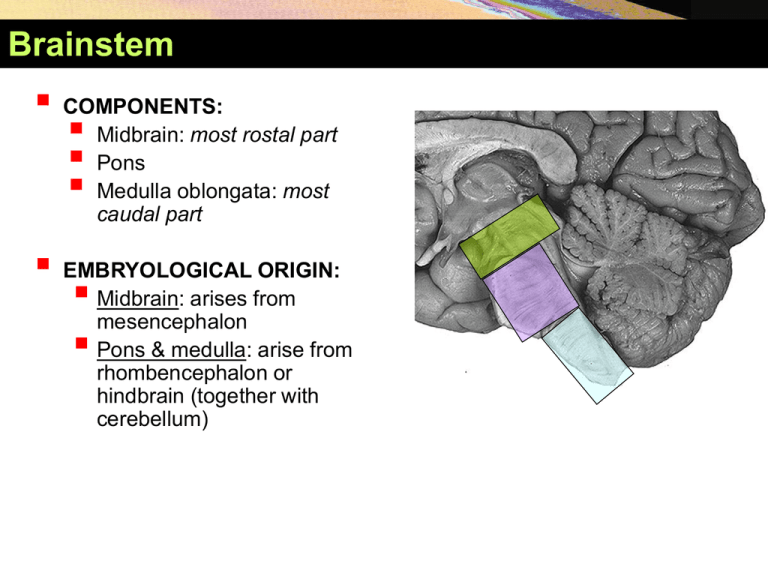
Brainstem COMPONENTS: Midbrain: most rostal part Pons Medulla oblongata: most caudal part EMBRYOLOGICAL ORIGIN: Midbrain: arises from mesencephalon Pons & medulla: arise from rhombencephalon or hindbrain (together with cerebellum) Brainstem COMPONENTS: Midbrain: most rostal part Pons Medulla oblongata: most caudal part EMBRYOLOGICAL ORIGIN: Midbrain: arises from mesencephalon Pons & medulla: arise from rhombencephalon or hindbrain (together with cerebellum) Brainstem COMPONENTS: Midbrain: most rostal part Pons Medulla oblongata: most caudal part EMBRYOLOGICAL ORIGIN: Midbrain: arises from mesencephalon Pons & medulla: arise from rhombencephalon or hindbrain (together with cerebellum) Anterior view Brainstem COMPONENTS: Midbrain: most rostal part Pons Medulla oblongata: most caudal part EMBRYOLOGICAL ORIGIN: Midbrain: arises from mesencephalon Pons & medulla: arise from rhombencephalon or hindbrain (together with cerebellum) Posterior view Brainstem Brainstem SITE: • It lies on the basilar part of occipital bone (clivus). • The midbrain is continuous rostrally with diencephalon of forebrain. • The pons is continous rostrally with midbrain & caudally with medulla. • The medulla is continuous caudally with spinal cord at the margin of foramen magnum. Brainstem CONNECTION TO CEREBELLUM: Midbrain: by superior cerebellar peduncle Pons: by middle cerebellar peduncle Medulla oblongata: by inferior cerebellar peduncle Brainstem IMPORTANCE: Pathway of tracts between cerebral cortex & spinal cord Site of origin of nuclei of cranial nerves (from 3rd to 12th) Site of emergence of cranial nerves (from 3rd to 12th) Contains groups of nuclei & related fibers known as reticular formation responsible for: control of level of consciousness, perception of pain, regulation of cardiovascular & respiratory systems Brainstem Ventral surface • MEDULLA: Ventral median fissure: • • It divides the medulla into 2 halves. • Its lower part is masked by decussation of pyramidal (corticospinal) fibers. • Pyramid: • It lies on either side of ventral median fissure. • It is an elevation produced by corticospinal tract. Anterior view Brainstem- Ventral Surface of Medulla • MEDULLA: • Olive: • It lies lateral to the pyramid & separated from it by the ventrolateral sulcus. • It is an elevation produced by inferior olivary nucleus. • Nerves emerging from Medulla (4 nerves): • Hypoglossal (12 ): between th pyramid & olive • Glossopharyngeal (9 th), vagus (10th) & cranial part of accessory (11th): dorsolateral to olive (from above downwards) Brainstem - Ventral Surface of Pons PONS: • • Basilar sulcus It divides the pons into 2 halves. • • It is occupied by basilar artery. Transverse pontine (pontocerebellar) fibers: Originate from pontine nuclei. • • Cross midline & pass through contralateral middle cerebellar peduncle to enter the opposite cerebellar hemisphere. Brainstem - Ventral Surface of Pons PONS: • Nerves emerging from Pons (4 nerves): Trigeminal (5th): from the middle of ventrolateral aspect of pons, as 2 roots: a small medial motor root & a large lateral sensory root • • Abducent (6 th): at junction between pons & pyramid • Facial (7 th) & vestibulocochlear (8th): at cerebellopontine angle (junction between medulla, pons & cerebellum). Both nerves emerge as 2 roots: from medial to lateral: motor root of 7th , sensory root of 7th , vestibular part of 8th & cochlear part of 8th Brainstem - Ventral Surface of Midbrain • MIDBRAIN: • It is formed of a large column of descending fibers (crus cerebri or basis pedunculi), on either side • The 2 crura cerebri are separated by a depression (interpeduncular fossa) • Nerve emerging from midbrain (one): • Occulomotor (3 rd): From medial aspect of crus cerebri Brainstem - Dorsal Surface of Medulla • Divided into 2 parts: • Caudal 2/3: Closed medulla • Rostral 1/3: Open medulla Brainstem - Dorsal Surface of Medulla • • • CLOSED MEDULLA Contains the rostral continuation of central canal. Composed of: • • • • • Dorsal median sulcus: divides the closed medulla into 2 halves. Fasciculus gracilis: on either side of dorsal median sulcus. Gracile tubercle: an elevation produced at the upper part of fasciculus gracilis, marks the site of gracile nucleus. Fasciculus cuneatus: on either side of fasciculus gracilis. Cuneate tubercle: an elevation produced at the upper part of fasciculus cuneatus, marks the site of cuneate nucleus. Brainstem - Dorsal Surface of Medulla • OPEN MEDULLA • Forms the lower part of floor of 4 th ventricle. • On either side, an inverted V-shaped sulcus divides the area into 3 parts (from medial to lateral): • Hypoglossal triangle: overlies hypoglossal nucleus • Vagal triangle: overlies dorsal vagal nucleus • Vestibular area: overlies vestibular nuclei Brainstem - Dorsal Surface of Medulla • PONS • Forms the upper part of floor of 4 th ventricle. • Separated from the medulla by an imaginary line passing between the caudal margins of middle cerebellar peduncle. • On either side, a sulcus divides the area into 2 parts (from medial to lateral): Medial eminence: overlies abducent nucleus. • • Vestibular area: overlies vestibular nuclei. Brainstem - Dorsal Surface of Medulla • MIDBRAIN: • Marked by 4 elevations: • Two superior colliculi: concerned with visual reflexes. • Two inferior colliculi: forms part of auditory pathway. • Nerve emerging from midbrain (one): • Trochlear (4 ): just caudal to inferior colliculus (the only th cranial nerve emerging from dorsal surface of brain stem) Fourth Ventricle Fourth Ventricle • • • • • Cavity of hindbrain Diamond (rhomboid) in shape Triangular in cross section Communications: Rostrally: with cerebral acqueduct (cavity of midbrain) Caudally with central canal (cavity of spinal cord) • • Lateral walls (boundaries): superior & inferior cerebellar peduncles Fourth Ventricle • Roof: Upper part: superior cerebellar peduncle & superior medullary velum (a layer of pia & ependyma bridging the space between the 2 peduncles) • • Middle part: cerebellum • Lower part: inferior medullary velum (a layer of pia & ependyma), has a central defect that forms the median aperture of 4th ventricle Fourth Ventricle • Floor (rhomboid fossa): formed of: • • • Whole dorsal surface of pons Open medulla (dorsal surface of rostral 1/3 medulla) Apertures: provide communication between 4th ventricle & subarachnoid space for circulation of CSF • One median aperture (Foramen of Magendi): in the roof of 4th ventricle • Two lateral apertures (Foramena of Luschka): at cerebellopontine angle Fourth Ventricle Brainstem - Ventral Surface Brainstem - Ventral Surface Brainstem - Medulla Cross-section through the medulla at the level of the sensory decussation. Brainstem - Medulla Cross-section through the medulla at the level of the caudal part of the 4th ventricle. Brainstem - Pons The pons: level of the right VI nerve nucleus and the intrapontine course of the facial nerve and, on the left, of the nuclei of V. Brainstem - Midbrain The midbrain: level of the inferior colliculus and decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncle. Brainstem - Midbrain The midbrain: level of the superior colliculus and the red nucleus. Lamina tecti (quadrigemina) Brainstem - Dorsal Surface of Medulla