Parasitology
Classification:
Parasitology
Protozology
Helminthology
Entomology
Continue
Helminthology
Platyhelminthes
(Flat worms)
Trematoda
(Flukes)
Ceastoda
(Tape worms)
Nematohelminthes
(Round worms)
Nematoda
Trematodes of medical importance in
our course
Heterophyes heterophyes
Fasciola hepatica & Fasciola gigantica
Schistosoma haematobium & Schistosoma mansoni
Schistosoma haematobium
&
Schistosoma mansoni
Name:
Definition:Distribution:
Schistosoma
haematobium
Schistosoma mansoni
Blood Flukes (Bilharzia)
Egypt, Africa &
middle east
Africa, Latin
America &
portirico.
Disease:
Urinary
Schistosomiasis
Intestinal
Schistosomiasis
Unlike trematodes
• Schistosoma has only one intermediate host.
• No reservoir.
• Schistosoma eggs not operculated.
• Forked tail cercaria.
• Cylindrical worm.
• It is the only trematode in which sex is
separated
while
hermaphrodite.
other
trematodes
are
Continue
Habitat:
Definitive host:
Intermediate host:
Reservoir:
Continue
Diagnostic
Stage:
Infective Stage:
Mode of
infection:
Treatment:
Prevention:
Schistosomiasis
Most cases are a symptomatic.
Symptoms:• Urinary Schistosomiasis
haematouria (blood in urine).
• Intestinal Schistosomiasis
gastrointestinal bleeding.
General
complications
of
chronic
Schistosomiasis are due to the presence of
Schistosoma eggs in tissues of spleen, gut
wall or urinary bladder walls.
Continue
Egg
inflammation
granuloma
fibrosis, hepatomegaly & portal
hypertension
No damage in hepatocytes
Portal hypertension
speelnomegaly
ascitis & oesophageal varicose.
S. haematobium eggs in bladder walls
fibrosis, increase
bacterial infections
or sterility.
the frequency of
bladder carcinoma
Continue
S. mansoni eggs in bladder walls
proteolytic enzymes
secrete
damage to the
distal colon.
Mortality due to Schistosomiasis occur due
to bleeding from ruptured oesophageal
varicose which treated by injection of
Sodium Valporate.
Adult worm
Continue
Continue
Schistosoma Couple
Continue
Continue
Diagnostic Stage
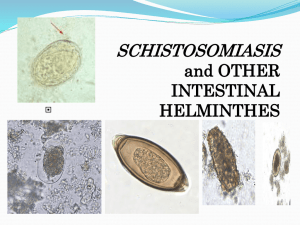
* Schistosoma haematobium :- Eggs found in urine of urinary Schistosomiasis
patients.
- Oval egg with terminal spine.
Diagnostic Stage
* Schistosoma mansoni:- Eggs found in stool of intestinal Schistosomiasis
patients.
- Oval egg with lateral spine.
Infective Stage
* Schistosoma cercaria (forked tail).
* Found in fresh water.
* Penetrate the skin of human upon contact with
water containing it.
Intermediate host
Schistosoma haematobium
Schistosoma mansoni
Bulinus truncatus
Biomphlaria alexandria
Drugs used in elimination of worms
(Praziquantel)
It
is drug of choice for all Trematodes & Cestodes
except Fasciola species & hydated sand.
The
nervous system of Trematodes and Cestodes
is not completely studied. However Praziquantel
was found to increase the calcium ion influx
inside the worm muscle causing prolonged
spasms for the worm; leading to spastic paralysis
& death of the worm.
This
action not observed on Nematodes, insects
or mammalians.
Continue
Praziquantel is very safe, taken as a single
or divided dose according to the worm
type.
Dose is calculated according to the
patient weight.
Praziquantel is swallowed, not chewed; as
it is very bitter in taste.
publichealth3rd@yahoo.com
Continue
Praziquantel
is very safe, taken as a single or
divided dose according to the worm type.
Dose
is calculated according to the patient weight.
Praziquantel
is swallowed, not chewed; as it is very
bitter in taste.