Role of surgery in treatment of
fecal incontinence disorders
Rasoul Azizi M.D
Colo-Rectal Surgeon
Associate Professor of surgery
School of Medical Sciences, Tehran University
Rasoul Akram Medical Complex
Tehran- Iran
E- mail: razizimd@hotmail.com
Factors contribute to the ability
to control feces
The consistency of the feces is important •
The peristalsis in rectosigmoid has a role in keeping the rectum •
empty.
The rectal capacity is important to store feces for some time.•
The pelvic floor muscles are of help to form a barrier when they are •
contracted.
The internal anal sphincter is contracted and gives watertight closure •
of the anal canal with the help of hemorrhoidal tissue.
Contraction of the external sphincter as additional help to internal •
sphincter.
The central nervous system has to govern the sensoric input and the •
motoric output.
All these factors form a delicate
system to keep the human continent.
When something goes wrong in one
these factors, it is depending on the
quality of the other factors whether
this lead to incontinence.
Symptoms
Fecal incontinence is a frequent problem but very much •
underreported because of embarrassment.
It is devastating disorder, which affect 2.2% community-dwelling •
adults and 45% of nursing home residents.
Fecal incontinence forms the most important reason to place •
patients in a nursing home.
In FI the compliant is often not directly voiced.•
The psychologic impact is devastating.
They often conceal their problems by complaining of chronic •
diarrhea, defecation problems or rectal urgency.
A thorough history is therefore essential in assessing patients with •
FI
Causes of Incontinence
1-Congenital
2- Pelvic floor Denervation
3- Obstetric
4- Iatrogenic
5- Traumatic
6- Radiation
Treatment
Conservative treatment
Biofeedback
Balloon Training
Electrostimulation
Sphincteroplasty
Obstetrical trauma
Fistulotomy
Sphincterotomy
Hemorrhoidectomy
Localized external trauma
Operative Treatment
Postanal Pelvic Floor Repair
Indications
Post anal repair is currently performed on patients
with idiopathic fecal incontinence with no evidence
of sphincter defect.
The patients expected to benefit most from post
anal repair are women with a history of multiple
vaginal deliveries.
Dynamic Graciloplasty
Indications
Restoration of the sphincters after
rupture due to obstetric causes.
Impalement trauma of the perineum.
Complications of perineal operations
Results
Several series have been published that indicate
success rates from 45% to 80%
However, and many complications have been
reported.
Infection – Constipation- Insufficient contraction of
gracilis.
The Artificial Bowel Sphincter
The ABS functions semi automatically
Defecation is initiated by the patient
Anal closure occurs again automatically in 5-8 min
by passive fluid transfer and a progressive return to
baseline pressure in the cuff.
Recently published Results with
ABS
The overall incidence of permanent explanation of
the ABS in the published series varied between
17% and 31% with follow up periods of between
10 and 58 months.
Revision surgery with replacement of part of or
the entire device occurred in between 7% and 25%
of patients.
Complication
Perioperative infections
Failure of wound healing
Erosion of part of the device through the skin or
the anal canal.
Late infection.
Mechanical malfunction of the device due to cuff
or balloon rupture.
Gluteoplasty
surgical approach and operative technique
Preoperative evaluation includes assessment
by multidisplinary team that comprises
members from general or colo-rectal surgery,
plastic surgery, urogynecology and
gastroentrology.
Workup involves: sigmoidoscopy, endorectal
ultrasound, rectal manometry, and pudental
nerve studies
Sacral Nerve Stimulation
Temporary, percutaniously placed, test
stimulation lead.
Permanent system consisting of an
electrode, connecting cable and pulse
generator.
Injectable Bulking Agents
In, 1938 obstetric registrar used paraurethral
injection of sodium morrhaute to stimulate the
formation of fibrous tissue.
Since, 1964, urologists have also used injectable
bulking agents to close down the bladder neck
In, 1993, Polytetrafluoroethylene(Tetron or
Polytef) injected to anal submucosa for FI
The Injectable Bulking Agents
In broad terms, an agents should be:
Biocompatible
Nonmigratory
Non allergic
Nonimmunogenic
Non-carcinogenic
Easy to inject
Able to produce durable results
Radiofrequency
Secca procedure
This procedure is not an option for
obvious sphincter defects but can be
used with a weak or thinned anal
sphincter complex. Patients with
history of IBD, extensive perianal
disease, or chronic diarrhea should
not be offered this treatment.
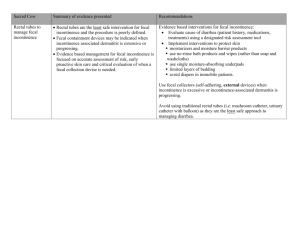
FI in elderly and •
Institutionalized Patients
Prevalence:
•Age more than 65 years
•Hospitalized patients
• Nursing home
• Hospitalization with dementia
3.7-27%
10-25%
> 50%
> 80%
Double Incontinence
A significant association between urinary
and anal incontinence was found in
patients with pelvic floor disorders
This association was found in women
with concomitant UI and pelvic organ
prolapse who have higher incidence of
anal incontinence