Hemostasis Disorders - Akademik Ciamik 2010
advertisement

1
Laboratory Approach to Patient
with Hemostasis (Bleeding)
Disorders
Dr.Nadjwa ZD, SpPK-K
16 April 2012
Hemostasis
Is the complex process by which
the body spontaneously stop
bleeding and maintains blood in
the fluid state within the vascular
compartment.
Normal hemostasis: rapid &
localized.
The major role of the
hemostasis system is to
maintain a complete balance
of the body’s tendency
toward clotting and
bleeding.
: Hemostasis can be divided into 2 stages
Primary
Hemostasis
• Platelet adhesion to exposed
collagen within the endothelium
of the vessel wall.
Secondary
Hemostasis
• Enzymatic activation of the
coagulation proteins to produce
fibrin from fibrinogen
stabilizing fragile clot formed
during primary hemostasis.
5
Primary Hemostasis
(platelet plug)
Secondary Hemostasis
(Hemostatic Plug)
Highly
integrated &
regulated
Blood Vessel
Natural
Anticoagulant
Platelets
Hemostasis
Fibrinolysis
Coagulation
Proteins
7
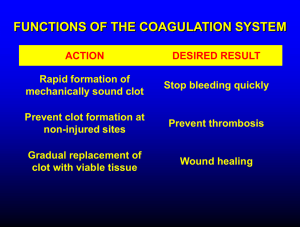
Hemostasis Disorders
Bleeding
Thrombosis
Both
• Vascular
• Platelet (ITP)
• Coagulation disorders (Hemophilia, vWD)
• Fibrinolysis
• Natural anticoagulant
• DIC
8
Approach to Hemostasis Disorders
• Clinical
History Taking Physical Examination -
• Laboratory
9
Family
History
Symptom
s
History
Taking
Drugs
Used
Previous
Disease
10
Physical Examination
•
•
•
•
•
Petechaie
Ecchimosis
Hematom
Epistaxis
Gingival bleeding
11
15
17
Any
Questions
???
Hemostasis Test
Screening
Confirmatory
20
Hemostasis Tests
Screening assays in hemostasis:
1. Patients without any signs/symptoms
preoperative
2. Monitoring of anticoagulant therapy
3. Disseminated Intravascular
Coagulation
4. Thrombophilia
5. Inhibitor (Lupus Anticoagulant, Anti
Phospholipid Antibody)
Hemostasis Screening Test
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
Tourniquet Test
Bleeding Time
Clotting Time
Clot Retraction
Platelet Count*
PT*
APTT*
TT*
Fibrinogen*
Euglobulin Clot Lysis
Test
11. D-Dimer
Thrombelastography
22
Vessels
• Tourniquette test,
Bleeding Time
Platelet
• Count, Bleeding Time,
Clot Retraction
Coagulation
Proteins
Fibrinolytic
system
• CT, PT, aPTT, TT,
Fibrinogen level
• D-Dimer, Euglobulin
Clot Lysis Time
• ATIII, Protein C/S
Natural
Anticoagulant
23
Single,
comprehensive
hemostasis
screening test
Thrombelastography
24
Tourniquete Test
= Capillary Resistance Test.
= Rumpel Leede Test
= Hess’s Test
Principle :
This test measures the ability of the capillaries to resist
pressure.
In healthy individu, the capillaries in the arm will resist a
pressure of 100 mmHg. If the capillaries can not resist,
they will break or rupture, tiny spot will then appear.
These spots are hemorrhages or petechiae.
TOURNIQUET TEST
SYSTOLIC
DIASTOLIC
5 cm
5 cm
100 mmHg
5 min
Leave for 5 min
• Normal : < 10 petechiae
• > 10 petechiae abnormal, due to:
– Increased capillary resistance
– Decreased platelet number
petechiae
BLEEDING TIME
(Duke’s Method & Ivy’s Method)
• Principle :
The skin is incised, blood
flowing out is aspirated
with a filter paper, and
then the time until
hemostasis is measured.
• Purpose :
To evaluate platelet and
vascular ability in
performing platelet plug.
Interpretation
• Time in minutes equals number of blots divided
by 2
• When the blood spot becomes 1 mm or smaller, stop the
stop watch.
• If the bleeding doesn’t stop in 10 min., discontinue
testing. Indicate the result as 10 min or longer.
• Cover the wound with a sterile gauze for a while,
hemostasis should be confirmed, after which the patient
may leave.
• The size of the blood spot about 1 cm in diameter is
desirable, but becomes larger in some cases. However
bleeding usually stops for several minutes regardless of
the size.
• Don’t wipe off the blood. Gently touch. Note so as not to
touch the wound.
CLOT RETRACTION
Principle
• When whole blood is allowed to clot
spontaneously, the initial coagulum is composed
of all elements of the blood.
• With time the coagulum reduces in mass, and
fluid serum is expressed from the clot, and its
volume stated in %.
• This is due to an action of platelets on the fibrin
network.
Clotting Time
Bedside Clotting Time
Clotting Time Lee & White
Method
BEDSIDE CLOTTING TIME
Principle :
• Record the time interval from the blood
contact with glass surface, until fibrin
network is performed at the room
temperature.
Sample :
• Capillary blood
Clotting Time : Lee & White
blood 3 ml
1 cc
37oC
N : 5 – 11 min
1 cc
1cc
Coagulation Tests
Prothrombin
Time (PT):
Extrinsic and
common
pathway
Activated
Thrombin Time
Partial
Thromboplastin
(TT):
Time (APTT):
conversion of
Intrinsic and
Fibrinogen to
Fibrin
common
pathway
34
Coagulation
Screening
Tests:
Related
to the
Coagulation
Cascade
35
Coagulometer
Prothrombin Time (PT)
• Screening test for the extrinsic and common
pathways of coagulation (factors II, VII, V, X).
• Limited sensitivity to fibrinogen.
• Normal range : 11-13 sec
INR
(International Normalized Ratio)
To overcome some of the difficulties with the
variability of thromboplastin normalizing
the responses of thromboplastin reagents
against an international standard.
• INR =
{
PTpat
----------PTn
ISI
}
ISI
(International Sensitivity Index)
• Needs to be developed for each
thromboplastin reagent and instrument
combination used in performing PT and
calculation of INR.
• Ideal reagent ISI < 1.7
Activated Partial Thromboplastin
Time (aPTT)
• Screening test for the intrinsic and common
pathways of coagulation (factors XII, XI, IX, VIII,
X, V and II).
• Limited sensitivity to fibrinogen.
• Maybe normal in some cases of vWD
• Normal range : < 35 sec
Thrombin Time (TT)
• Identified stage 3 defects in the
coagulation mechanism
• Clinical significant Prolonged TT :
– Decreased fibrinogen concentration
– Presence of dysfunctional fibrinogen
– Presence of heparin
– Presence of FDP
Prothrombin Time
Principle of the test :
Time required for the formation of a
fibrin clot when plasma is added to a
thromboplastin-calcium mixture.
Measure extrinsic and common
pathway (FI,II,V,VII,X)
42
Prothrombin Time
Purpose :
1. Evaluation of coagulation disorders
2. Evaluation of liver function
3. Monitoring anticoagulan therapy
Result inform in :
• Second
• Percent
• INR (International Normalized Ratio)
PT prolonged if coagulation factors in extrinsic pathway decreased <30%
43
APTT
Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time
(APTT)
Principle of the test :
• Time required for the formation of a
fibrin clot without additional
thromboplastin.
• Measured intrinsic and common
pathway
44
D-Dimer Test
Principle :
Is the time required for the formation
of a fibrin clot if thrombin is added.
Affected by :
• Concentration and fibrinogen reaction
• Inhibitor (also FDP and heparin).
45
D-dimer
Thromboelastography
•
•
•
•
•
Screening & control therapy
Easy to perform, no reagent needed, fast
Record clot formation and converse to graph
TEG ruler
Conversion table
r
r
k
m .a
m.e
=
=
=
=
m. a
20 mm
1. TEG NORMAL PATTERN
k
reaction time (start to amplitudo 1 mm)
coagulation time (end of r to amplitudo 20 mm)
maximum amplitudo (mm)
maximum elasticity
100 x a
m . e = ------------100 - a
m. a
2. THROMBOCYTOPENIA
r
r = normal
k = normal/prolonged
m.a. = shortened
k
3. HYPERFIBRINOLYSIS
r
k
r = normal
k = normal
m.a. = previously normal,
but suddenly become shortened
m. a
4. HEMOPHILIA
r
r = prolonged
k = prolonged
m.a. = normal/shortened
k
5. HYPERCOAGULATION
r = shortened
k = shortened
m.a = prolonged
rk
TEG
pattern
Normal
Hemophilia
Thrombocytopenia
Hyperfibrinolysis
Hypercoagulation
Thank you for your attention
53