Ch10
advertisement

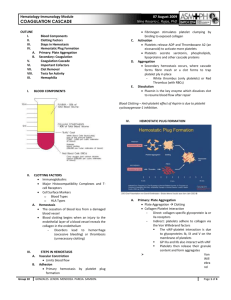
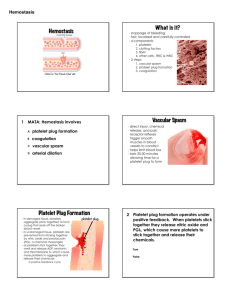
Guided Lecture Notes Chapter 10: Alterations in Hemostasis Learning Objective 1. State the five stages of hemostasis. Define hemostasis, thrombocyte, megakaryocyte, and thrombopoietin (refer to PowerPoint Slides 2–3). Identify the five stages of hemostasis, and explain the importance of each stage (refer to the Understanding Hemostasis display). Learning Objective 2. Describe the formation of the platelet plug. Define the role of the platelet plug in the process of hemostasis. Describe the importance of von Willebrand factor in the formation of the platelet plug. Identify the purpose of ADP and TXA2. Learning Objective 3. State the purpose of coagulation. Define the role of coagulation in the process of hemostasis. Describe the two coagulation pathways (refer to PowerPoint Slide 12 and Fig. 10-2). Explain the importance of factor X, prothrombin, and fibrinogen to the coagulation process (refer to Fig. 10-2). Learning Objective 4. State the function of clot retraction. Define the role of clot retraction in the process of hemostasis (refer to PowerPoint Slide 13). Describe the roles of actin and myosin in clot retraction. Learning Objective 5. Trace the process of fibrinolysis. Define the role of clot dissolution/lysis in the process of hemostasis. Explain the importance of plasmin and tissue plasminogen activator to fibrinolysis. Learning Objective 6. Compare normal and abnormal clotting. Define hypercoagulability (refer to PowerPoint Slide 15). Identify conditions associated with hypercoagulability states (refer to Chart 101). Learning Objective 7. State the causes and effects of increased platelet function. List the conditions associated with increased platelet function. Describe the result of increased platelet function. Define thrombocytosis. Explain how atherosclerosis promotes platelet adherence. Learning Objective 8. State two conditions that contribute to increased clotting activity. Identify hereditary clotting disorders. Identify acquired clotting disorders. Learning Objective 9. Describe the manifestations of thrombocytopenia. Define thrombocytopenia, and identify diagnostic platelet levels. Identify the causes of and clinical manifestations associated with thrombocytopenia. Discuss treatment for thrombocytopenia. Learning Objective 10. State the mechanisms of drug-induced thrombocytopenia and idiopathic thrombocytopenia and the differing features in terms of onset and resolution of the disorders (refer to PowerPoint Slide 19). Identify drugs that may cause thrombocytopenia, and explain how platelets are destroyed. Tell how long it takes for platelet levels to drop. Explain how drug-induced thrombocytopenia is treated. Identify possible causes of idiopathic thrombocytopenia. Discuss treatments for idiopathic thrombocytopenia. Learning Objective 11. Describe the role of vitamin K in coagulation. Explain the importance of vitamin K to the clotting process. Discuss the effects of increased and decreased levels of vitamin K. Identify sources of vitamin K. Learning Objective 12. Differentiate between the mechanisms of bleeding in hemophilia A and von Willebrand disease. Describe the types of genetic defects that lead to hemophilia A and von Willebrand disease. Identify the clotting factors that are affected in hemophilia A and von Willebrand disease. Explain where bleeding typically occurs in hemophilia A and von Willebrand disease, and discuss treatments for each disorder. Learning Objective 13. Describe the physiologic basis of acute disseminated intravascular coagulation. Describe the paradox in hemostatic sequence that results in DIC. Identify conditions that are associated with DIC (refer to Chart 10-2). Describe the pathophysiology of DIC (refer to Fig. 10-4). Discuss the treatment of DIC. Learning Objective 14. Describe the effect of vascular disorders on hemostasis. Identify the source of bleeding in vascular disorders. List several causes of vascular disorders. Describe signs and symptoms of vascular disorders.