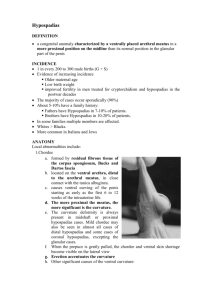
3rd Surgical Workshop Of CUGRS
(Complex Uro-Genital Reconstructive Surgery)
Surgical challenge in patients who underwent
failed hypospadias repair: is it time to change?
Salvatore Sansalone MD
Senior Lecturer in Urology
University of Tor Vergata
Rome, Italy
FAILED HYPOSPADIAS POPULATION
• Incidence
• Characteristics
UNKNOWN
European Center for Failed Hypospadias Repair
For many years, failed hypospadias repair was
considered a complex chapter in reconstructive
urethral surgery, and any book on the urethra
includes “hypospadias cripple” or re-operative
hypospadias surgery as a special topic
Stecker JF, Horton CE, Devine CJ, McCraw JB: Hypospadias cripples.
Urol Clin N Amer 1981;8:539-544.
European Center for Failed Hypospadias Repair
J Urol 2010
observational, descriptive survey
1998 – 2007
1176 failed hypospadias repair
urethral strictures & penile defects
European Center for Failed Hypospadias Repair
Age range in 1176 patients
age (years)
N. patients
1 – 16
250 (21.2%)
16 – 20
451 (38.4%)
20 – 40
358 (30.5%)
40 – 60
112 (9.5%)
> 60
5 (0.4%)
< 16 years 250 (21.3%)
> 16 years 926 (78.7%)
Center for Reconstructive Urethral Surgery
Primary site of meatus
position
n
%
glandular
193
16.4
penile
702
59.7
penoscrotal
281
23.9
European Center for Failed Hypospadias Repair
Number of operations to repair primary hypospadias
in 1176 patients
N. operations
N. patients
1
130 (11.1%)
2
347 (29.5%)
3
320 (27.2%)
4
159 (13.5%)
5
108 (9.2%)
>5
112 (9.5%)
minimum: 1 maximum: 23 mean: 3.3
Center for Reconstructive Urethral Surgery
Number of operations to repair complications following
primary hypospadias repair in 1176 patients
N. operations
N. patients
1
760 (64.6%)
2
280 (23.8%)
3
82 (6.9%)
4
31 (2.7%)
5
9 (0.8%)
>5
14 (1.2%)
minimum: 1 maximum: 8 mean: 2.3
Center for Reconstructive Urethral Surgery
Total number of operations to repair primary
hypospadias repair and complications in 1176 patients
N. operations
N. patients
2
102 (8.7%)
3
289 (24.6%)
4
369 (31.4%)
5 – 10
311 (26.4%)
11 – 20
91 (7.7%)
> 20
14 (1.2%)
minimum: 2 maximum: 23 mean: 5.8
Center for Reconstructive Urethral Surgery
In 1176 patients underwent a mean of 5.8 surgical
operations to repair primary and failed
hypospadias
No other congenital abnormality of the body requires a mean
of 5.8 surgical operations to be cured !
Center for Reconstructive Urethral Surgery
QUERIES
• proximal > distal?
• older techniques > new techniques ?
• single staged procedures ?
European Center for Failed Hypospadias Repair
• Failed hypospadias repair may consist in defects of single
compartments of the male genitalia (urethra, corpora
cavernosa, glans, penile and scrotal skin), or in a
combination of them
• It is a reasonable hypothesis that the outcome of repairing
failed hypospadias depends on the number of
compartments involved
• This widespread survey allowed to us to focus on some
concepts and concerns, developing a new view of this old
problem.
The main reason for dissatisfaction was
smaller penile size and curvature.
European Center for Failed Hypospadias Repair
THE JOURNAL OF UROLOGY Vol. 182, 1736-1743, October 2009
THE JOURNAL OF UROLOGY Vol. 180, 1080-1084, September 2008
……..we assume that satisfaction with genital self-perception by our patients will
decrease with advancing age.
European Center for Failed Hypospadias Repair
European Center for Failed Hypospadias Repair
59-year-old patient with 7 previous surgeries - one
stage repair
Artificial erection shows severe Elipsoid excision of longitudinal layer
ventral curvature
of albuginea at several points
Running suturing of
wounded surfaces
(PDS 3-0)
Complete penile
straightening
Neourethral reconstruction and “spongioplasty”
Creation of abundant dartos flap for suture line covering
Glans wings
Dartos flap
Dartos flap
Aspect at the end of
surgery
Outcome after one year
34-year-old patient with 6 previous surgeries - one stage
repair
Diverticular skin urethra
Double - “S” curvature
ventral
dorsal
Ellipsoid excision of longitudinal tunical layer and
plication at two points (arrows)
Longitudinal
tunica excision
Urethral tailoring by external plication
Reconstruction of penile skin using remaining penile skin
and scrotal flaps
Peno-pubic and peno-scrotal angles are formed by tacking
penile base skin to the albuginea (arrows)
Fixation of loose compressive dressing at the base and at
subcoronal level
European Center for Failed Hypospadias Repair
39-year-old patient with 33 previous surgeries
Two stage repair
Fixed and elevated
testicle
Extensive degloving and partial urethral augmentation with
buccal mucosa
Buccal
mucosa
inlay
Urethral
stricture
Testicular
mobilization
Penile skin reconstruction using scrotal flap
Scrotal flap
Buccal mucosa
inlay
Scrotal flap
Bilateral
orchiopexy
Second stage urethroplasty after 6 months - buccal mucosa
tubularisation, glans, penis and scrotum plasty
CRIPPLED PENIS: Severe curvature and short, strictured,
fistulous neourethra with small, deformed glans
Severe curvature and short, strictured, fistulous neourethra and
small deformed glans
I-stage: Penile lenghtening by ventral grafting
(InteXen® 3x7cm)
Graft
Meatus
III-stage: Tubularizing urethroplasty
Completely straightened and lenghtened penis
Glanular and urethral reposition; skin reconstruction
Outcome after 14 months
Before
After
Take home message
Urethral complications in patients with failed
hypospadias repair are less frequent than
complications involving the corpora cavernosa,
and the esthetic appearance of the genitalia.
To repair these defects, collaboration
between the urethral surgeon and the surgeon
who has developed vast experience in plastic and
reconstructive surgery of the male genitalia is
indeed mandatory
www.failedhypospadias.com
URETHRAL
P
E
D
I
A
T
R
I
C
MULTI
SPECIALIZED
SKILLS
ANDROLOGICAL
P
L
A
S
T
I
C