Septic Arthritis
advertisement

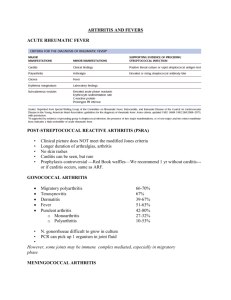
Septic Arthritis Pamela Gregory-Fernandez, PA-C SVCMC PA Education Program Definition Inflammation of a synovial membrane with purulent effusion into the joint capsule, often due to bacterial infection Synonyms Bacterial, suppurative, purulent or infectious arthritis, gonococcal or nongonococcal A Big Problem Despite advances in diagnostic studies, powerful antibiotics, and early drainage, significant joint destruction commonly occurs Why? Lack of clinical suspicion Delay in definitive diagnostic needle aspiration Failure to adequately drain the joint Frequency 2-10 cases per 100,000 in the general population 30-70 cases per 100,000 in patients with immunological disorders or deficiencies, and joint replacements Gonococcal: women 3x > men Etiology Staph aureus Streptococci In all age groups, 80% due to gram-positive aerobes, 20% due to gram-negative anaerobes Neonates and infants < 6mos S aureus and gramnegative anaerobes Incidence of H. influenzae has decreased due to the vaccine Pathophysiology Adults Knee 40-50 % Hip 20-25 % Infants and young children Hip 95 % Infection Sources Trauma: direct Hematogenous: IV drug injection Osteomyelitis adjacent to joint capsule Soft tissue infections: cellulitis, abscess, bursitis, tenosynovitis Clinical Presentation: “red, hot, painful joint” Fever Erythema Edema Heat Pain Markedly decreased passive and active ROM Age Related Presentation Young sexually active pts: + fever, tenosynovitis, migratory polyarthralgia and dermatitis ( papular rash over trunk and distal extremity extensor surfaces that may turn hemorrhagic ) = Suspect N gonorrheae IVDU = Pseudomonas Infants and young children = difficult Pediatric Presentation Fever, decreased appetite and irritability without obvious joint involvement is common Differentiation from transient synovitis important: 4 independent variables History of fever Non-weight-bearing ESR > 40mm/h WBC > 12,000/uL Diagnosis Needle aspiration, open drainage and lavage (arthroscopically or arthrotomy) Contraindications to arthrocentesis: 1. avoid aspirating from an area that has overlying soft tissue infection 2. Bleeding disorders 3. Anticoagulation therapy Lab Studies CBC with diff: leukocytosis and left shift ESR: monitor treatment CRP: monitor treatment Blood cultures: may be + in 50% S aureus Urethral, cervical , pharyngeal and rectal swabs: N gonorrheae Synovial fluid analysis: Gram stain, culture, cell count, and crystal analysis Synovial Fluid Classification (Modified from Schumacher HR. Pathologic Findings in Rheumatoid Arthritis) Quality Reference Range Noninflammatory Inflammatory Septic Volume, mL <3.5 >3.5