Arthritis and Fevers..
advertisement
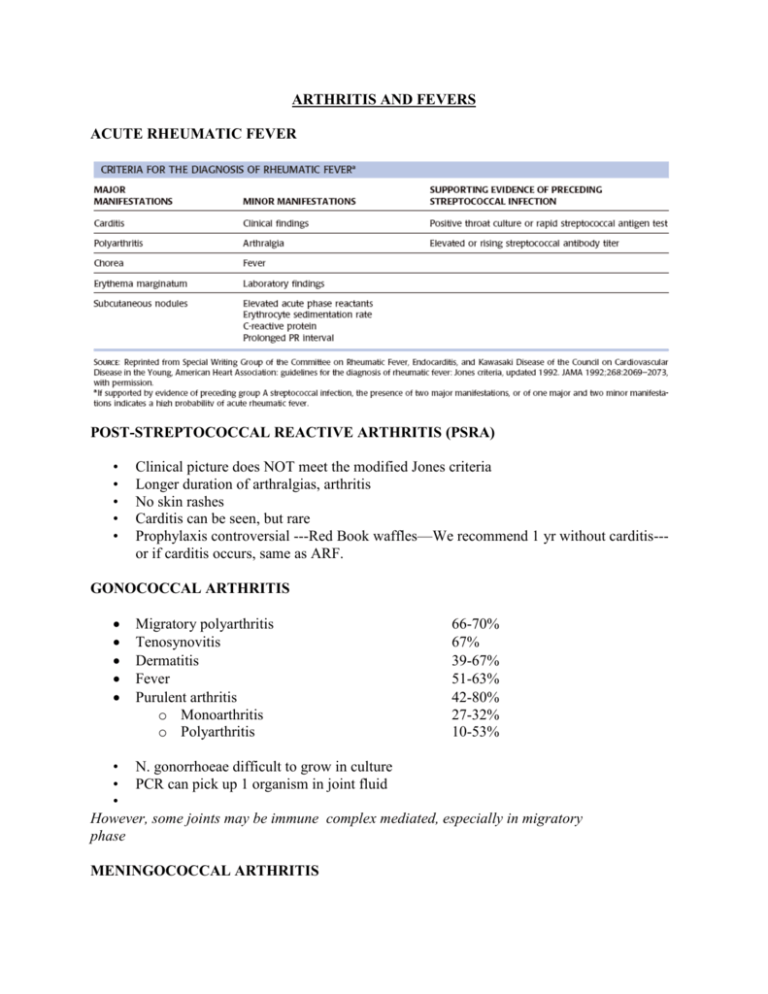
ARTHRITIS AND FEVERS ACUTE RHEUMATIC FEVER POST-STREPTOCOCCAL REACTIVE ARTHRITIS (PSRA) • • • • • Clinical picture does NOT meet the modified Jones criteria Longer duration of arthralgias, arthritis No skin rashes Carditis can be seen, but rare Prophylaxis controversial ---Red Book waffles—We recommend 1 yr without carditis--or if carditis occurs, same as ARF. GONOCOCCAL ARTHRITIS Migratory polyarthritis Tenosynovitis Dermatitis Fever Purulent arthritis o Monoarthritis o Polyarthritis 66-70% 67% 39-67% 51-63% 42-80% 27-32% 10-53% • N. gonorrhoeae difficult to grow in culture • PCR can pick up 1 organism in joint fluid • However, some joints may be immune complex mediated, especially in migratory phase MENINGOCOCCAL ARTHRITIS LYME ARTHRITIS • • • Recognized in 1975 with an unusual epidemic of JRA in Lyme, Conn. Now recognized in North America, Europe, Russia, China, Japan and ?Australia 3 endemic areas in US: Northeast, Great Lakes, Northern California, Oregon STAGE 1 EARLY LOCALIZED EARLY DISSEMINATED STAGE 2 STAGE 3 CHRONIC ARTHRITIS CHRONIC NERVOUS SYSTEM DISEASE -Erythema migrans -Secondary skin lesions -Headache -Musculoskeletal pain -Flu-like illness -Onset weeks to months -15% total cases -Cardiac (5%): Fluctuating AV block, first degree, Wenkebach, complete -Sometime carditis -Organisms can be found in tissue -Acute neurologic : Meningitis +/- encephalitis (15%) Cranial neuritis, radiculoneuritis, chorea, transverse myelitis, focal demyelinating encephalitis, polyneuropathy -Not clearly local infection -Months after onset, 60% of pts -1-2 large joints, esp. knees -Popliteal cysts -PCR often positive -Usu resolves with treatment but 10% can become chronic -Onset months to years, 5% of pts -Cognitive dysfunction -Parasthesias -Changes in EMG, NCV To diagnose it…. • Clinical syndrome and exposure • Lyme ELISA--high false positive rate (very rare false-negatives with arthritis) • Positive ELISA needs to be confirmed with Western Blot • Serology may not be positive for a few weeks after infection • PCR may be positive in joint fluid VIRAL ARTHRITIS Parvovirus B19 -Small single stranded DNA virus -Erythema infectiosum (Fifth’s Disease) -Rash fades in 10 d but may recur -7% of children have arthralgias -Arthritis occurs in up to 50% adults and 5% children -Arthritis involves multiple joints, hands, fingers, feet -No infectious virus detected but PCR + -Can see chronic disease Hepatitis B -“Serum sickness” early -Rash maculopapular or urticarial -Nonmigratory polyarthritis -Immune complex mediated -Symptoms decrease as jaundice increases -Can see arthritis following Hep B vaccination Hepatitis C -Multiple autoimmune syndromes including arthritis Rubella -33% of older patients (adolescents and older), -Onset 2-3 days following rash -Polyarthritis -Duration usually 1 week -? Chronic forms, ? Relation to JRA -Virus present in blood and synovial fluid Rubella vaccine -Occurs 10-28 d after immunization -5-11% of adult women, much lower in children Less common viruses associated with arthritis: Alpha viruses (Australia, S. Pacific, Africa, Asia) Mumps CMV EBV Varicella Enteroviruses HIV (Reiter’s Syndrome) OTHER INFECTIONS WITH ARTHRITIS Brucellosis Cat scratch fever Mycoplasma and ureaplasma -Joint involvement in 33%, sacroiliitis 47%, peripheral 38% -Monoarthritis -Associated with hypogammaglobulinemia ARTHRITIS ASSOCIATED WITH MYCOBACTERIA AND MYCOSES Coccidioidomycoses -Polyarthritis with E. nodosum -Monoarthritis of knee Blastomycosis Cryptococcosis Histoplasmosis Sporotrichosis Tuberculosis Atypical TB Candidiasis Actinomyces Leprosy -Monoarthritis of large lower extremity joints associated with skin and joint involvement, spondylitis -Monoarthritis secondary to osseous infection, spondylitis -Polyarthritis with E. nodosum -Monoarthritis of knee, wrist or hand; -polyarthritis with disseminated skin lesions -Spondylitis, monoarthritis of large weight bearing joints -Arthritis/tendonitis in hand or wrist or bone/joint/tendon involvement in AIDS -Monoarthritis of knee with serious systemic illness -Spondylitis -Polyarthritis with E. nodosum; -destruction of small bones of hands and feet; neuropathic joints PRESUMED INFECTION-RELATED SYNDROMES Toxic synovitis, Henoch-Schoenlein purpura, Kawasaki syndrome, Discitis FEVER OF UNKNOWN ORIGIN (A RHEUM PERSPECTIVE) Cryopyrinopathies Hereditary Autoinflammatory Syndoromes LessMore Severity One MUST exclude infectious/oncologic causes before considering the following: Disease Fever Characteristics Other Characteristics Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Variable See above (SLE) Systemic JIA 1-2x/d Characteristic salmon-colored rash linked to fevers; associated with Macrophage Activation Syndrome (MAS) / Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) Behcets Variable Scarring oral/genital ulcers, arthritis; rarely colitis, aneurysms Vasculitis Variable Must think of individual dz for w/u: ANCA, U/A, CXR (Wegener’s), 4 limb BP’s (Takayasu’s), etc. Familial Mediterranean Fever 12-72h Q 7-28d Most common Mendelian autoinflammatory syndrome; (FMF) response to colchicine can help w/ dx; Mediterranean heritage Familial Cold 12-24h Cold triggering Autoinflammatory Syndrome (FCAS) Muckle-Wells Syndrome 2-3d Rare cold triggering (MWS) Neonatal Onset Multisys- Continuous No cold triggering; developmental delay temic Inflammatory Disease (NOMID) / Chronic Infantile Neurologic Cutaneous and Articular Syndrome (CINCA) Tumor Necrosis Factor >1-4wks AKA Familial Hibernian Fever; migratory rash w/ underlying Receptor-Associated Periodic myalgia; conjunctivitis, periorbital edema; frequently Syndrome (TRAPS) associated w/ pleuritis Hyperimmunoglobuminemia D 3-7d Q 14-28d High IgD levels; northern European heritage; severe abd pain, with Periodic Fever Syndrome vomiting, diarrhea > constipation, rarely peritonitis; symmetric (HIDS) poly-arthritis/arthralgias Cyclic Hematopoiesis (CH) / Cyclic 3-5d Q 21-28d ANC <200 during flare and low-normal to normal in between Neutropenia cycles Periodic Fever with Aphthous Q 21-28d NSAIDs as tx; colchicine, cimetidine as prophylaxis; Stomatitis, Pharyngitis, and (cervical) glucocorticoids as abortive Adenitis (PFAPA)