Antibiotics
advertisement
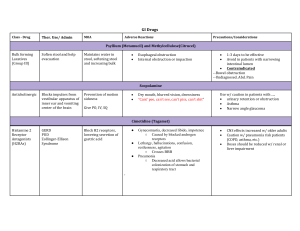
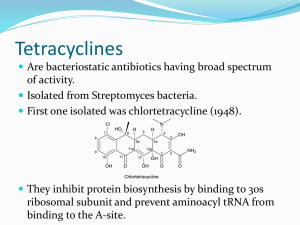
Antibiotics Ch 37 Definition Medications to treat bacterial infections Ideally, culture of suspect area should be done BEFORE starting antibiotic Classifications Sulfonamides Penicillins Cephalosporins Tetracyclines Macrolides Aminoglycosides Quinolones Uses Treatment of exisiting infection Prevention of infection Responses Therapeutic – decrease in s/s of infection Subtherapeutic – s/s of infection do not improve Superinfection Antibiotic resistance Allergic reactions Actions Bactericidal = kill bacteria Bacteriostatic – slow or interfere with growth of bacteria Sulfonamides Bacteriostatic Treat: utis Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP) URIs Otitis media Often in combinatiion Bactrim, Septra, Pediazole, Gantrisin Sulfonamide Side Effects Anemia, thrombocytopenia Photosensitivity Avoid tanning beds Avoid sunlight N-V-D uriticaria Penicillins Natural Penicilllin G Penicillin V Aminopenicillins Amoxicillin Ampicillin Penicillinase-resistant Oxacillin Nafcillin PCN Adverse Effects Allergy Rash, swelling, itching Cephalosporins Semisynthetic Related to penicillin Bactericidal 4 generations Cephalosporin Uses Surgical prophylaxis URIs Otitis media Cephalosporin Examples Ancef Kefzol Mefoxin Ceftin Rocephin – also used to tx meningitis Cephalosporin Side Effects Similar to PCN Macrolides Erythromycin Zithromax Biaxin Macrolide Uses Strep infections Mild-to-moderate URIs Lyme disease STDs Macrolide Side Effects GI N-V-D Hepatotoxicity Flatulence anorexia Tetracyclines Tetracycline Vibramycin Minocycline Bacteriostatic action Tetracycline Uses Syphilis Lyme disease Pleural & pericardial effusions Tetracyclines Effectiveness reduced by Dairy products Antacids Iron Will discolor teeth May slow fetal skeletal development Tetracycline Side Effects N-V-D Superinfection Pseudomembranous colitis Aminoglycosides Gentamicin Kanamycin Neomycin Streptomycin amikin Aminoglycosides Poor oral absorption No oral forms, only IV TOXICITY cautions Nephro oto Bactericidal action Aminoglycosides Pseudomonas E.coli Klebsiella Often used along with other antibiotics Quinolones Cipro Floxin Levaquin Tequin Quinolones Excellent oral absorption Antacids interfere with absorption bactericidal Quinolones Lower respiratory tract infections Bone & joint infections Infectious diarrhea UTIs Skin infections STDs Anthrax Quinolone Side Effects HA N-V-D Allergic reaction Others Vancomycin Tx of MRSA Must monitor blood levels Caution: oto & nephro-toxic Nursing Instruct pt to take meds for full length of time – do not stop when feeling better Assess for s/s of superinfection All oral antibiotics are better absorbed if taken with a minimum of 6 – 8 ounces of water