Inflammatory Disorders of the
Male
Penne Mott
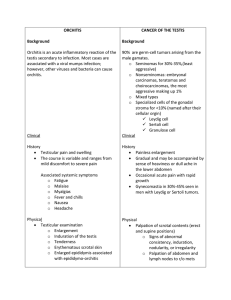
Gonococcal /Non Gonococcal
(NGU) Urethritis
• Causes
– Gonorrhea
– Chlamydia (NGU)
Gonococcal /Non Gonococcal
(NGU) Urethritis
•
•
•
•
•
Thick yellowish green purulent discharge
Appears 3 – 14 days after sexual exposure
NGU – scant to moderate amount
Pain in urethra
Redness / irritation
Gonococcal /Non Gonococcal
(NGU) Urethritis
• Treatment
–
–
–
–
Rocephin or Zithromax – Gonorrhea
Doxy or tetracycline – Chlamydia
Condom use
Treatment of sex partners
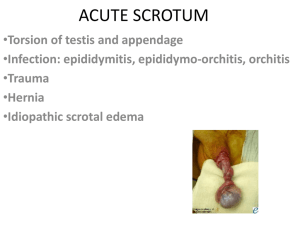
Epididymitis
• Convoluted tubules top of each testicle
• Inflammation / infection epididymis
• High incidence young males
Epididymitis - Causes
• Infection – E-coli from lower urinary tract
or prostate
• Trauma
• STD’s – Chlamydia / gonorrhea
Epididymitis - Assessment
• “Duck Waddle” walk
• Acute painful scrotal swelling (unilateral)
• Prehn’s sign – lifting the scrotum onto
symphysis relieves pain
• NV
• Fever / chills
• Dysuria, frequency, urgency
Epididymitis - Treatment
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Bedrest
Scrotal elevation
Ice
Sitz
Analgesics / antipyretics
Antibiotics
Treatment of STD
Epididymitis - Complications
• Epididymal Abscess – may extend testicles
• Chronic epididymitis
– Tx epididymectomy
• Sterility
Orchitis
• Rare, acute testicular inflammation
• Associated with mumps, pneumonia, TB,
syphilis, parasites, trauma
• Can be SE
–
–
–
–
Epididymitis
Mono
Flu
catheterization
Orchitis- Assessment
• Red, edematous extremely tender testicles
• Fever
Orchitis - Treatment
•
•
•
•
•
•
BR
Scrotal Support
Local heat
Analgesics
Antibiotics
***Preventable with immunization
Testicular Torsion
• Torsion of spermatic cord = twisting of the
testis that cuts off blood supply to testis
• Adolescent males
Testicular Torsion – S/S
•
•
•
•
•
•
Acute scrotal pain
Nausea
Vomiting
No urinary complaints
U/A – no WBC’s or bacteria
MEDICAL EMERGENCY!!!!
Testicular Torsion - Treatment
• Surgery – Surgical exploration of the
scrotum & bilateral testicular fixation
• Necrosis – orchiectomy
Hydrocele
• Collection of fluid between visceral &
parietal membranes of the tunica vaginalis
(membranes that surrounds the testis)
Hydrocele - Causes
• Trauma
• Infection (Epididymitis or orthitis)
• Cancer of testis
• Most commonly occurs
– Infants
– Males > 40
Hydrocele – S/S
• Painless swelling scrotum
• Positive transillumination
Hydrocele - Treatment
• None unless swelling large &
uncomfortable
• Fluid aspiration – may be repeated 1-3 mos
• Hydocelectomy –excision of membrane
Varicocele
• Distention of testicular veins
• Infertility
Varicocele – S/S
• Wormlike mass “Bag of Worms” above the
testis when patient stands
• Dragging sensations
• Dull aching
• Pain relieved by masturbation or sex
(relieves venous congestion)
Varicocele - Treatment
• Scrotal support
• Varicocelectomy
• Sclerosing agent injections
Priapism
• Prolonged state of erection not associated
with sexual desire
• Painful
• Rare
• Urologic emergency
Priapism - Treatment
• Ketamine HCL (Ketalar)
– Rapid acting nonbarbiturate anesthetic
– IM / IV
– SE: unpleasant psychic sx. (dreams,
hallucinations) vomiting, hypersalivation, skin
rashes
Hypospadias
• Congential malposition of the meatus on the
ventral side of the penis
• Associated with infertility
Cryptorchidism
• Failure of the testes to descend
Cryptorchidism – S/S
• No palpable testes
Cryptorchidism - Treatment
• Orchiopexy before age 2-3
• After age 3 increased risk infertility
• *Increased risk of Testicular CA
Cryptorchidism – Pre op
• Psychologic Problems RT genital surgery in
children
– Fear / punishment
– Body mutilation
– Castration
Cryptorchidism – Pre op
• The earlier a repair can be made, the more
likely the possibility that the child will
develop a normal body image
• Ideal time 6-15 months
Cryptorchidism – Post op
•
•
•
•
Care of the surgical site
Tub baths often discouraged 1st week
Catheter care
Restriction of activites –pushing, lifting,
playing with staddle toys, sandboxes, rough
activites
Testicular Exam
• Testicular cancers can occur as early as
adolescence
• Monthly
• Shower – warms the scrotum
• Use both hands to palpate scrotal contents
• Roll each testicle between thumb and 1st
three fingers
Testicular Exam
• ID structures
–
–
–
–
S –permatic cord
V –as deference
E –pididymis
T -estes
Testicular Exam
• Testis should feel round soft – hard boiled
egg without shell
• Epididymis – not as smooth
• One testicle may be larger
• Spermatic cord -firm smooth
• Check – lumps, irregularities, pain,
dragging sensations
Testicular Exam
• Consult health care provider when
abnormalities are discovered