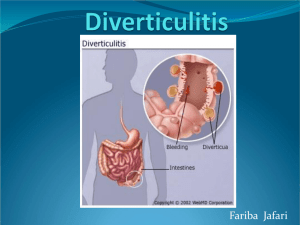
DIVERTICULAR DISEASE Overview • Acquired condition mostly in the colon • Associated with ‘western diet’ • Present in >60% of over 70s • Mostly asymptomatic but: – Change in bowel habit – Abdominal pain – Rectal bleeding Anatomy • From deverticulum – “off the main track” • Anywhere from oesophagus to colon True False Pathogenesis • Peristalsis requires smooth muscle contraction • Exaggerated or abnormal contraction causes high-pressures on walls • High pressure causes herniation Pathogenesis II • Higher pressure in smaller tube • Sigmoid colon is narrowest • Weaker where blood vessels traverse the muscle layer Risk Factors • Strong – Age > 50 years • Moderate – Low dietary fibre • Weak – “Western diet” – Obesity – NSAID use (associated with symptoms) Signs and Symptoms Diverticulosis Diverticulitis Presence of diverticula Inflammation of diverticula Usually asymptomatic Pain (commonly LLQ) Discomfort / change in bowel habit Fever Bleeding (often painless) Not associated with bleeding Bloating Tenderness + guarding Complications • Fistulae – Colovesical – Colovaginal • Abscess • Perforation – Hinchey I to IV • Strictures – Obstruction Differential Diagnosis • • • • • • • • Colorectal cancer Appendicitis IBD Pyelonephritis Ischaemic colitis Pelvic inflammatory disease Irritable bowel syndrome Pancreatitis Investigations • Bloods: – FBC: raised WCC and neutrophilia • Imaging: – Abdo XR – CT abdomen – CXR / USS if CT cannot be obtained • Interventional: – Colonoscopy / sigmoidoscopy (if suspicious Management • Asymptomatic – No treatment required • Symptomatic diverticular disease – Dietary modification and fibre supplementation – Oral co-amoxiclav (500mg oral 8-hourly for 7 days) • If evidence of infection – Bleeding: consider endoscopic haemostasis Management II • Symptomatic diverticulitis – Pain relief (WHO analgesic ladder) – Oral antibiotic therapy •Co-amoxiclav 500mg 8-hourly for 7 days OR, •Ciprofloxacin AND metronidazole for 7-10 days – Temporary low-residue diet (i.e. foods low in • Recurrent diverticulitis / fistulae – Elective colectomy Management III • Diverticular abscess (> 3cm or refractory to antibiotics): – Analgesia – Radiological drainage or surgery – IV piperacillin/tazobactam • Peritonitis: Hinchey stage Findings Management I Pericolic abscess IV antibiotics II Distant abscess IV antibiotics and drainage III Purulent peritonitis Left colectomy, laparoscopic lavage and drainage, or Hartmann’s procedure IV Faecal peritonitis Hartmann’s procedure Questions?