Prepared by:
Ancy Varghese
Staff Nurse
ICU Department
Patient Name : xyz
Age & sex
: 80yrs/female
MRN
: 196388
Admission Date : 11-2-13@1200h
Nationality
:Saudi
Diagnosis
:AF with
Poplitial Artery
embolization(embolectomy done)
∙The patient is 80yrs old female, approximately
Weight 75kg.
.on 12th February she was intubated on A/C
mode .she was under sedative & ionotropics
support.
→.BP :130/80mmhg
→.PR : 70/mt
→.RR :12
→.Temp:36.5◦C
→.SpO2 :98%
SKIN
.Fair Complexion
.Warm(but in second day lower extremities
were cold)
.No Palpable mass or lesions, with good
tigor
HEAD
.No palpable masses & lesion
.No areas of deformity
LEVEL OF CONSCIOUS & ORIENTATION
.patient was conscious & oriented on
admission . She was intubated on second
day (12/2/13 ) and then on fully sedation.
EYES
.Pupils equally round and reactive to light
EARS
.No unusual discharges noted
.Pink nasal mucosa
NOSE
.No unusual discharges
.No tenderness in sinus
MOUTH
.Pink and moist oral mucosa and free of
swelling and lesions
NECK AND THROAT
.No palpable limb nodes
.No masses and lesions seen
CHEST AND LUNGS
.Equal chest expansion
.Bilateral basal crept present
ABDOMEN
. Soft abdomen
.Bowel sounds present
GENITALS
.Minimal pubic hair
PAST MEDICAL HISTORY
No past medical history
PRESENT MEDICAL HISTORY
80yrs old female patient came in ER
with the complaint of shortening of breath
and burning micturation. Primary care given
from ER and then shifted to new ICU.Chest
x-ray done ,it shows patchy opacity was
seen in both lower areas and
cardiomegaly.Her ECG shows AF with
controlled rhythm.
The next day patient developed cold lower
extremities with absent pulses ..So urgent
vascular surgery consultation & arterial
doppler done. Bilateral poplitial artery
embolus seen in doppler. Patient was
urgent taken to the OT by vascular surgeon
and bilateral poplitial artery embolectomy
was done under L/A.Patient developed
bradycardia , hypotension, hypoxia and mild
bleeding from the wound site, patient was
resuscitated with IV fluids and ionotropic
Support and was mechanically ventilated. After
all management patient was extubated and
fully conscious and oriented. Patient shifted
to peadia ward.
MEDICATIONS
DRUG
DOSE
ROUTE
ACTION
Inj.augmentin
1.2gm
iv
Antibiotic(broad
spectrum)
Inj.nexium
40mg
iv
H2 receptor
Inj.clexane
60mg
s/c
Low molecular
heparin
Tab. Aspirin
81mg
p/o
Ant platelet
Tab .astatin
40mg
p/o
Lipid lowering
agent
TEST
PATIENT VALUE
NORMAL V ALUES
WBC
8.5
4.23-9.07
Hb
10.5
13.7-17.5
PLT
221
163-337
UREA
6.28
1.8-8.3
CREATININE
107.84
46-92
TROPONIN
0.101
0.120
CPK
37
26-308
CPKMB
7
7.0-25.0
SODIUM
138
135-150
POTTASIUM
4.4
3.5-5.0
CHLORIDE
101
98-111
Patchy opacity is seen in both lungs.
Apparent cardiomegaly
Vascular markings are normal
DOPPLER BOTH LIMBS
It reveals thrombus filling the lumen of both
lower limbs poplitial arteries with flow
obstruction distal to it.
CAROTID DOPPLER
There is normal colour filling and flow pattern.
No evidence of any stenosis or plaque seen
DOPPLER OF BOTH UPPER LIMB
Normal colour flow in the both
subclavian,axillary,brachial,radial and ulanar
arteries.
ULTRASOUND KUB
Bilateral kidneys are normal in shape
with increase cortical echogenicity with
partial loss of cortico-medullary
demarcation. Bilateral renal disease.
AFIB: very common arrhythmia and leading
cause of embolic CVA
Initial Workup: trop, ECG, TSH, Echo, CXR
Management: First must determine if stable or
unstable (medically manage or cardiovert
immediately)
For stable Afib: rate and rhythm control (equal
in efficacy).
CHARACTERISTICS
P Waves absent
Rhythm irregular
HR is above 150/mt
QRS complex is narrow
Answer
Rhythm - Regular
Rate - (68 bpm)
QRS Duration - Normal
P Wave - Visible before each QRS complex
P-R Interval - Normal –0.20sec(<5 small Squares. Anything above and this
would be 1st degree block)
Indicates that the electrical signal is generated by the sinus node and
travelling
normal fashion in the heart.
afib
Unstable
Urgent
Cardiovert
Stable
Rate or rhythm
Control
Anti arrhythmic
agent,Anticoagulate*
*
AFIB
SBP
100
to
120
SBP
90-110
DIGOXIN
Load: 0.5mg
IV6 hrs later;
0.25mg IV6 hrs
later; 0.25 mg IV
Maintenance:
0.125 mg daily
B-Blocker
Initial: Metoprolol 5mg
IV 5min x3doses
Prn: metoprolol 5mg IV
q6h
Maintenance:
Metoprolol 25 mg po
BID (max 100mg BID)
SBP >120
Ca2+ Blockers
Initial and prn:
Diltiazem 10mg
IV q6hrs
Maintenance:
Diltiazem 30mg
PO q6hs
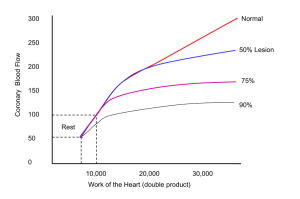
The popliteal artery, like any other peripheral
artery, can be affected by embolism.
Macroemboli have a tendency to lodge in the
popliteal artery at the bifurcation into the
tibioperoneal trunk and anterior tibial artery.
An embolus in the lower extremities most often
has a cardiac source. Other sources include
aortic aneurysms and proximal arterial plaque
or ulceration. Regardless of the source, acute
arterial embolism almost always requires
urgent treatment.
Figure 1b. Normal anatomy.
©2004 by Radiological Society of North America
ANATOMY OF ARTERY
acute bilateral ischemia of the lower extremities shows abrupt occlusion of both popliteal
arteries
©2004 by Radiological Society of North America
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Embolism in the most common cause of arterial occlusion
Emboli may consist of thrombus , athromatous debris or
tumor
Emboli most commonly originate in the heart as a result of
AF, MI or Heart failure
Arteriosclerosis may cause roughening or ulceration of
atheromatous plaque which can lead to emboli .
May also be associated with immobility , anemia and
dehydration .
Emboli lead to lodge at bifurcations & atherosclerotic
narrowing
Other cause of acute occlusion include
A . Trauma
B . Thrombus
C. venous outflow obstruction
Immobility,anemia,dehydration
heart
arteriosclerosis
Roughening or ulceration of artery
lodge in the roughened artery
arterial occlusion
AF,MI
emboli
Acute pain
Paralysis of part
Pallor & coldness
Edema
Rigidity of extremity
Pulselessness
Numbness of the part
EMBOLUS
THROMBOSIS
TRAUMA
AF
Vascular grafts
Blunt
MI
Atherosclerosis
Penetrating
Endo carditis
Thrombosis of aneurysm
latrogenic
Valvular disease
Entrapement syndrome
Aneurysm
Low flow rate
Atherosclerotic
plaque
1.MEDICAL MANAGEMENT
Thrombolytic therapy
Heparin and anticoagulants
2.SURGICAL MANAGEMENT
Embolectomy
Balloon embolectomy
Aspiration embolectomy
Surgical embolectomy
Balloon embolectomy
Typically this is done by inserting a catheter with
an inflatable balloon attached to its tip into an
artery, passing the catheter tip beyond the clot,
inflating the balloon, and removing the clot by
withdrawing the catheter. The catheter is called
Fogarty, named after its inventor
Aspiration embolectomy
Catheter embolectomy is also used for aspiration
embolectomy, where the thrombus is removed
by suction rather than pushing with a
balloon. It is a rapid and effective way of
removing thrombi in thromboembolic
occlusions of the limb arteries below the
inguinal ligament
Surgical embolectomy
Surgical embolectomy is the simple surgical removal
of a clot following incision into a vessel by open
surgery on the artery.
COMPLICATIONS
MI
TIA
Gangrene
Stroke
Septic embolism
Monitor vital signs(peripheral pulse)
Assess the wound area,if any bleeding
present or not.
Provide comfortable position
Prevent infection and potential complication
Ventilator care
30˚ head end elevation
Mouth care
Sedation score
Suction appropriately
Prevent infection
Prevent hemodynamic instability
Manage the airway
Meet the patient nutrional needs
Wean the patient appropriately
Educate the patient and family
Impaired physical mobility related to
monitoring devices , mechanical ventilation
and medication as charecrized by imposed
restrictions of movement ,decreased muscle
strength &limited range of motion.
Ineffective breathing pattern related to
decreased energy as characterized by
dyspnea.
Knowledge deficit related to health
condition, new equipment& hospitalization as
characterized by increased frequency of
Questions posed by the relatives
Risk for impaired skin integrity related to
prolonged bedrest,proloanged intubation
Risk for infection related to surgery
Pain related to surgery
NURSING DIAGNOSIS
ASSESSMENT
Subjective
data:
patient in
mechanical
ventilator
Objective
data:1.rapid
shallow
breathing
2.Nail bed
cyanosis
PLANNING
EVALUATION
NURSI
NG
DIAG
NOSIS
GOALS OR
DESIRED
OUTCOME
NURSI
NG
INTER
VENTI
ON
ACTION
OR
RATION
ALE
Ineffective
breathing
pattern
related to
decreased
energy as
characterize
d by
dyspnoea
After 12 hrs of
nursing intervention
patient will maintain
good breathing pattern
Endotrach
eal
suctioning
done every
30mts.
Patient
head is
elevated at
30⁰
Placed
patient on
ventilator
with 75% o2
To maintain
patent airway
To reduce
the breathing
difficulties
To increase
the oxygen
saturation
Breathing pattern
maintained with the help
of ventilator
ASSESSMENT
Objective
data:
General
body
weakness
present,ina
bility to
perform
motor
skills due
to
sedation,pa
ralysed for
restricted
movement
PLANNING
EVALUATION
NURSI
NG
DIAGN
OSIS
GOALS OR
DESIRED
OUTCOME
NURSI
NG
INTERV
ENTIO
N
ACTION
OR
RATIONA
LE
Impaired
physical
mobility
related to
monitoring
device
,mechanical
ventilation
&
decreased
muscle
strength
and limited
range of
motion
After 24hrs of nursing
intervention patient
will maintain good
physical activity
Position
changed
2hrly.Suppo
rt the bony
prominence
with
pillows.
Isometric
exercise
given 6th
hrly
Deep
breathing
exercise
given 2nd
hrly
To prevent
bedsore
Head end
elevated 30⁰
To avoid
aspiration
Sedation
tapered
slowly
To help for
weaning
To improve
the blood
circulation
To helps to
expand the
lungs
Goal fully met ,patient
started obeying orders of
nurse, physiotherapist for
exercise, mobilizing the
legs &hands.
Teach prevention techniques, such as daily activity,
observation for skin breakdown, prevention of injury
Teach the importance of taking prescribed
medications such as oral anticoagulants.
Teach for blood checking
regularly(PT,INR,D_DIEMER).
Teaching about the nutritional status
Maintain regular health check-up
Teach the patient to wear elastic stockings as
ordered
Teach the patient to avoid restrictive
clothing(socks,shoes)
Teach the patient never to walk barefoot
80yrs old female patient came in ER with the
complaint of shortening of breath and burning
micturation. Primary care given from ER and then
shifted to ICU.Her ECG shows AF with controlled
rhythm. The next day patient developed cold lower
extremities with absent pulses ..So urgent vascular
surgery consultation & arterial Doppler done.
Bilateral poplitial artery embolus seen in Doppler.
Patient was urgent taken to the OT by vascular
surgeon and bilateral poplitial artery embolectomy
was done . Patient was resuscitated with IV fluids
and ionotropic because of desaturation. After all
management patient was extubated and fully conscious
and oriented. Patient shifted to peadia ward.
1.What are the characteristics of AF?
2.What are the layers of artery?
3.What are the etiology of arterial embolism?
4.What are the signs & symptoms of arterial
embolism?
5.What are the types of embolectomy?
6.What is the other name of balloon catheter?
7.What is atherosclerosis?
8.What are the complications of embolectomy?
WIKIPEDIA
MEDICAL AND SURGICAL NURSING
BOOK(BRUNNER)
LUCK MAN AND SORENSEN’S MEDICAL
SURGICAL NURSING
THANK YOU