File
advertisement

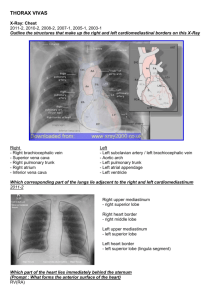
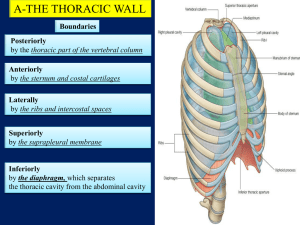
HUMAN ANATOMY Dr. Sarwar Hossain Khan THORAX • HUMAN BODY 1.Head & neck 2.Upper extremity 3.Thorax 4.Abdomen 5.Lower extremity Thorax -upper part of the trunk -supported by a skeletal framework (thoracic cage) -contains the lungs & heart Thoracic cage /skeleton of thorax -an osseo-cartilaginous, elastic & conical cavity -the upper opening /inlet is narrower than the outlet -flattened antero-posteriorly BOUNDARIES Ant.- Sternum Post.- Bodies of 12 thoracic vertebrae with their intervertebral disc Side - 12 ribs with their cartilages SHAPE – Conical Difference bet. Adult & infant thoracic cage In transverse section: Adult-kidney/oval/bean shaped( transverse diameter >ant. Post. Diameter) Infant(<2yrs)-circular In ribs placement: Adult -obliquely placed -so their movement help in respiration alternatively up & down - this present the thoracic-abdomen respiration in adult Infant – ribs are horizontally placed - respiration movement is abdominal APPLIED ANATOMY 1.Fractures of ribs are rare in child , the chest wall is highly elastic in children. 2.In adults it usually occurs at the weak point of ribs (angle of ribs) 3.The upper 2 ribs & the lower 2 ribs are rarely injured INLET OF THORAX Def.-the narrow upper end of thorax which is continous with the neck is called the inlet of thorax Shape :- reniform in shape -ant.post diameter -5cm -transverse diameter – 10cm -slopes downwards & forwards -sternal end of 1st rib lies about 3-4cm lower than the vertebrae end BOUDARIES Front –upper border of manubrium Behind- superior surface of the body of T1 Sides-1st ribs with its cartilage Partition of inlet/ Sibson’s fascia -placed bet.the neck & thorax -partly seperates them so incomplete -has two halves –rt. & Lt. -triangular in shape -apex is attached to the tip of the transverse process of C7 vertebrae -base to the inner border of 1st rib & its cartilage -it is also called Sibson’s fascia or suprapleural membrane Importance It provides rigidity to the thoracic inlet The root of the neck cannot be puffed of & down during respiration Structures passing through inlet Viscera-1.trachea 2.oesophagus 3.apices of lungs with pleura Vessels-1.brachiocephalic artery (rt.) 2.left common carotid artery 3.left subclavian artery 4.rt. & Lt. brachiocephalic veins 5.rt. & Lt. internal thoracic artery Muscles- 1.sternothyroid 2.sternohyoid Nerves-1.rt. & Lt. phrenic nerve 2.rt. & Lt. vagus nerve 3.rt. & Lt. sympathetic nerve 4.rt. & Lt. first thoracic nerve OUTLET OF THORAX Def.-the broad lower end of thorax which is continuous with the abdominal cavity is called the outlet of thorax BOUNDARIES : In front-by the xiphoid process & 710th costal cartilage forming an intrasternal angle Behind-inf.surface of body of T12 Sides-11th & 12th ribs Partition of outlet/ diaphragm -complete ( covers whole the circumference) -separates thorax from abdomen -it is musculotendinous -called the diaphragm Structures passing through the outlet Major openings in diaphragm: 1.Venacaval opening -lies opposite to disc bet. T8 & T9 vertebrae -transmits: IVC & few branch of rt. phrenic nerve 2.Oesophageal opening -lies at the level of T10 vertebrae -transmits: oesophagus,rt.& Lt. vagus nerve,Lt. gastric artery, Lt.gastric vein 3.Aortic opening -lies behind the diaphragm at the level of lower border of T12 -transmits: aorta,thoracic duct Minor openings 1.Foramen of Morgan’s/Larry’s space -sup. epigastric vein 2.Greater & lesser splenic nerve 3.Sympathetic chain 4.Subcostal nerve & vessels 5.Musculophrenic nerve WALLS OF THE THORAX Coverings(outwards to inwards): 1.Skin 2.Superficial fascia 3.Deep fascia 4.Muscles 5.Ribs & intercostal spaces 6.Endothoracic fascia 7.Parietal pleura INTERCOSTAL SPACES: -the spaces bet.the ribs -11 in no.on eachside -last 2 spaces are open in front BOUNDARIES ABOVE-sharp lower margin of upper rib & its cartilage BELOW-blunt upper margin of lower rib & its cartilage IN FRONT-lateral border of sternum BEHIND-body of corresponding thoracic vertebrae CONTENTS: 1.Muscles 2.Blood vessels 3.Nerves INTERCOSTAL MUSCLES -3 in no. -from outward to inward 1.external intercostal muscle 2.internal intercostal muscle 3.transverse thoracic 1.EXT.INTERCOSTAL MUSCLE -forms most superficial layer Extension:-extends forward from the rib tubercle behind to the costochondral junction in front then through an aponeuorosis upto the sternum ATTACHMENT Origin-lower border of upper rib Insertion-upper border of lower rib DIRECTION -fibres are directed downwards & forwards 2.INT.INTERCOSTAL MUSCLE -forms the middle layer of muscles Extension:-extends backward from the sternum in front to the post.angle of ribs behind then by an aponunosis upto the vertebrae ATTACHMENT Origin-costal groove of upper rib Insertion-upper border of lower rib DIRECTION Downwards & backwards 3.TRANSVERSUS THORACIC -forms depest layer -direction is same to int.intercostal muscle -has 3 portion: subcostalis,intercostal intimi,sternocostalis NEUROVASCULAR BUNDLE Intercostal nerves & vessels run bet.the middle & innermost layer of muscles -they are arranged in above downwards: 1.Intercostal vein(v) 2.Intercostal artery(a) 3.Intercostal nerves(n) -lies in the costal groove FUNCTION OF MUSCLES: 1.ext.intercostal muscle-help in inspiration 2.int.intercostal muscle-help in expiration 3.Prevent blowing out or sucking in of the intercostal spaces as well as the tissues with change in internal thoracic process of respiration INTERCOSTAL VESSELS ARTERIES: Each intercostal space contains – One post.intercostal artery Two ant.intercostal arteries POST.INTERCOSTAL ARTERY: -one in each spece -11 in no. on each side -1st & 2nd arteries are branches of sup.intercostal artery-subclavian artery -3rd to 11th are branches of descending thoracic aorta Ant.intercostal arteries: -2 in each space -10th & 11th spaces do not have -upper 6 spaces are branches of internal thoracic artery -lower spaces are branches of musculophrenic artery -ant.& post.intercostal arteries meet each other at costochondral juction VEINS -correspond to the arteries ANT.INTERCOSTAL VEINS: -2 in eacs space -1st -6th drain into internal thoracic vein -7th – 9th drain into musculophrenic vein POST.INTERCOSTAL VEIN: -1 in each spce -on right side drain into azygous vein -on left side drain into – 1st to 4th :lt.brachiocephalic vein 5th to 11th :hemiazygous vein : INTERCOSTAL NERVES -11 in no.on each side -each is the ant.rami of the first 11 thoracic nerves APPLIED ANATOMY INTERCOSTAL NEURAGLIA: -sharp burning pain in the area supplied by intercostal nerves e.g.rib & herpes zoster Thank you