CHOO CHOO
advertisement

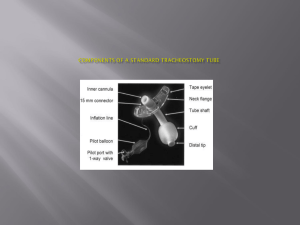
Tracheostomy By Ussana Promyothin MD. Tracheostomy • Surgical opening in the trachea for ventilation Indication • Bypass upper airway obstruction • Clearance secretion at lower respiratory • Prevent aspiration gastric content in absent of laryngeal reflex Other indication • Prolong intubation(1-3wks) children more prolong • Laryngeal injury • Fracture face neck area • • • • Also Improved oral hygiene Oral movement for communication Reduction damage larynx,nose ,mouth Contraindication • Prolong bleeding • On anti-coag, anti-pletlet medication • Elective tracheostomy • Emergency tracheostomy: should avoid, expertised surgeon,team • In children: perform only with a secured airway either from ET tube or bronchoscope in OR • Emergent tracheostomy should be avoided if possible • Risk to vascular,lung and uncontrolled airway Hyperextend the neck, 2 FB above thyroid notch ring 2,3 Skin incision,horizontal /vertical Find white line,Test tracheostomy cuff Clean trachea,aspirate air then push xylocaine Stay suture,open trachea by inverted U flap,cross,vertical (in children stay suture on both sides of incision) Standby tracheal dilator,suction, Post operation care • Irrigation with saline and suction q 15 mins • Suction not exceed 15 seconds (block airway and suck Oxygen out) • Humidification Oxygen (decrease thick mucus) • Observe bleeding and subcutaneous emphysema • Off packing 24-48hrs • Left tube in place 5-7 days • Stitch off and off stay suture 7th day • Blow Cuff when on ventilation or prevent aspiration • Not exceed 25 cm H2O • Clean inner tube • analgesic Complication Immediate • • • • Apnea :loss hypoxic drive,COPD ventilator Post obstructive pulmonary edemaPEEP Pneumothorax chest x-ray post op Injury to adjacent organ:thyroid ,vessel, esophagus,recurrent laryngeal nerve Pneumothorax Early • Bleeding HT, skin,thyroid,soft tissue • Mucus inner tube • Tracheitis humidification, minimize FiO2, Stabilize tracheostomy • Cellulitis: wound care,antibiotic • Displacement: pass E-T tube, NG tube Late Bleeding -innominate vessel:usually in 2wks,high mortality (low tracheostomy,mobilized tracheostomy tube,high pressure cuff,local infection) -granulation( stroma, tip of tube) Tracheoesophageal fistula:risk in retain NG tube Type of Tracheostomy Type/descr permanent iption ventilator Inner tube size jackson yes no yes 4-5 shiley yes yes yes 4-6-8 portex no(7-14days) yes no 7-8 blueline no(1month) yes yes 7-8 Cricothyrodotomy:maneuver to buy time Advantage • Near skin and less dissection Disadvatage • Trauma to subglottic area • Contraindication:children<12 yrs,infection at larynx,laryngeal trauma and risk transecting tumor Tracheostomy care • • • • Clean skin around stroma Change gauze Clean inner tube Aware obstruction or slip out of tube Weaning tracheostomy tube • • • • Reason for tracheostomy has resolved Stable lung status(O2<40%) Effective swallow,gag,and cough reflex Adequate nutrition, sleep, psychososial suppor • Cuff deflate trial Method • Flexible bronchoscope or IDL • Assess cord movement,granulation,stenosis area • Admit,size tube down • Plug tube day,all day night • Off tube,observe before discharge Epistaxis Abnormal bleeding per nose • • • • • • • • Cause Trauma ,nose picking ,nose blowing URI, allergic rhinitis Septum deviation Decongestant ,nasal spray Foreign body Tumor Post surgery • Hypertension, artherosclerosis • Anticoagulation drug,ASA,NSAID • Decrease plt • Liver function disease Site of bleeding MANAGEMENT • Immediate evaluation :vital sign,airway • Stop bleeding • Compress nose,cold pack Anterior epistaxis • Little’s area region • Ephridine or adrenaline pack (vasoconstrict agent) • Beware in HT • CAUTERIZATION • 30%TCA,silver nitrate, electrical cautery • Gel foam Anterior nasal packing Nasal speculum Headlight Suction Anterior nasal packing • Vasaline gauze or coated with antibiotic ointment • Apneanaso-vagal reflex bradycardia,hypotension • Remove packing 2-4 days later • Antibiotic and decongestant Posterior nasal packing Foley catheter Posterior nasal packing Anterior and posterior nasal packing • Posterior packing :oxygen face mask • Elevate head 30 degree • Antibiotic cover Staph aureus • Liquid diet • Remove packing 3-5 day later • If high fever ,hypotension, remind toxic shock syndrome • Surgery • Ligation artery • Endoscopy •Angiogram and embolization Sinusitis Anatomy and function • • • • • • • • Resonance to voice Humidify and warm air Increase the area of olfactory Absorb shock to head Keep nasal chamber moist Protect thermal to brain Contribute facial growth Lighten bone of skull Acute bacterial sinusitis • • • • • • Cause URI,AR Dental infection Obtruction ostium: structure,tumor Immotile cilia Foreign body: NG tube Symptom • • • • • • Fever Maxillofacial pain Dental pain Otalgia Posterior nasal drip Nasal congestion • • • • • • • Causative agent viral S.pneumoniae H.influenzae M.catarrhalis Other bacteria Fungus FILM SINUS Management • • • • • • • Proper antibiotic Systemic decongestant:maxiphed Beware: HT, Heart disease, urinary retention Topical decongestant: not exceed 3 days Mucolytic agent Antihistamine if suspected allergy Normal saline irrigation • • • • • • • • If failure medication Antral puncture For drainage and C/S CHRONIC BACTERIAL SINUSITIS Greater than 12 wks duration symptom Treatment: antibiotic 4-6 wks CT scan Surgery : ESS (endoscopic sinus surgery) ESS Complication sinusitis • Mucocele • Orbital complication: cellulitis abscess • Intracranial complication: meningitis brain abscess