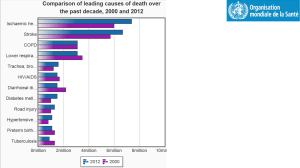
24-hour Urine
advertisement

Renal denervation in resistant hypertension, with target organ damage Darrel Francis Reader in Cardiology Imperial College, London BHS, Cambridge 2011 REACH – pilot study REnal Artery denervation in Chronic Heart failure Imperial College London 55 female Hypertension for over 20 years since the birth of her first child 15 years blood pressure >180 mm Hg tolerated well no evidence of secondary organ involvement REACH – pilot study REnal Artery denervation in Chronic Heart failure Imperial College London Extensive review tertiary (Newcastle) and at national specialist centres (Cambridge) Excluded secondary causes of hypertension Renal artery stenosis Congenital causes Malignancy Tests Normal renal function No proteinuria CT/MRI Renal vein sampling Progressive worsening of hypertension 18 months blood pressure sustained >230 mm Hg (250-270mm Hg) episodes of blood pressure exceeding 300 mmHg 6 months heart failure – moderate-severe systolic impairment Marked decrease in exercise capacity (200 yards) 3 in-patient admissions 1 ITU admission (Pulmonary oedema) pre-syncope when blood pressure <170 mmHg Pharmacological regime Primary Endpoint: 6-Month Office BP ∆ from Baseline to 6 Months (mmHg) Systolic Diastolic Diastolic Systolic • • 33/11 mmHg difference between RDN and Control (p<0.0001) 84% of RDN patients had ≥ 10 mmHg reduction in SBP 10% of RDN patients had no reduction in SBP Symplicity HTN-2 Investigators. The Lancet 2010: 376:1903-1909 7 Primary Endpoint: 6-Month Office BP ∆ from Baseline to 6 Months (mmHg) Systolic Diastolic Diastolic Systolic • • 33/11 mmHg difference between RDN and Control (p<0.0001) 84% of RDN patients had ≥ 10 mmHg reduction in SBP 10% of RDN patients had no reduction in SBP Symplicity HTN-2 Investigators. The Lancet 2010: 376:1903-1909 8 Primary Endpoint: 6-Month Office BP ∆ from Baseline to 6 Months (mmHg) Systolic Diastolic Diastolic Systolic • • 33/11 mmHg difference between RDN and Control (p<0.0001) 84% of RDN patients had ≥ 10 mmHg reduction in SBP 10% of RDN patients had no reduction in SBP Symplicity HTN-2 Investigators. The Lancet 2010: 376:1903-1909 9 Primary Endpoint: 6-Month Office BP ∆ from Baseline to 6 Months (mmHg) Systolic Diastolic Diastolic Systolic • • 33/11 mmHg difference between RDN and Control (p<0.0001) 84% of RDN patients had ≥ 10 mmHg reduction in SBP 10% of RDN patients had no reduction in SBP Symplicity HTN-2 Investigators. The Lancet 2010: 376:1903-1909 10 Primary Endpoint: 6-Month Office BP ∆ from Baseline to 6 Months (mmHg) Systolic Diastolic Diastolic Systolic • • 33/11 mmHg difference between RDN and Control (p<0.0001) 84% of RDN patients had ≥ 10 mmHg reduction in SBP 10% of RDN patients had no reduction in SBP Symplicity HTN-2 Investigators. The Lancet 2010: 376:1903-1909 11 Primary Endpoint: 6-Month Office BP ∆ from Baseline to 6 Months (mmHg) Systolic Diastolic Diastolic Systolic • • 33/11 mmHg difference between RDN and Control (p<0.0001) 84% of RDN patients had ≥ 10 mmHg reduction in SBP 10% of RDN patients had no reduction in SBP Symplicity HTN-2 Investigators. The Lancet 2010: 376:1903-1909 12 Primary Endpoint: 6-Month Office BP ∆ from Baseline to 6 Months (mmHg) Systolic Diastolic Diastolic Systolic • • 33/11 mmHg difference between RDN and Control (p<0.0001) 84% of RDN patients had ≥ 10 mmHg reduction in SBP 10% of RDN patients had no reduction in SBP Symplicity HTN-2 Investigators. The Lancet 2010: 376:1903-1909 13 Renal Denervation – practicalities of the technique Symplicity® Catheter System™ • Low profile, electrode-tipped catheter • Delivers RF energy to treatment site • Proprietary RF generator - Low power - Automated - Built-in safety control algorithms • Standard interventional technique Multiple Discrete Treatments Maximize Nerve Coverage Without Applying Circumferential Energy in a Single Segment 6-Month Histology (Porcine Model) Movat’s pentachrome stain cutting artifact Zone of energy delivery 20X magnification 100X magnification Findings: Minimal intimal thickening and minimal IEL injury overlying areas of mild full thickness medial fibrosis (yellow with green [proteoglycan deposition]), and adventitial fibrosis (yellow). No significant inflammatory cells are present suggesting that the healing process is complete. REACH Phase 1 7-patient safety study Investigator-led study Academic Health Science Centre, Cardiovascular Practice Group Aim Determine first-in-man safety of procedure in 7 patients with CHF Inpatient monitoring for 5 days afterwards Weekly and then monthly outpatient monitoring for 6 months REACH Phase 1 7-patient safety study Day Minus 1 Admission Clinical assessment QoL Bloods Electrolytes, Creatinine, NT-ProBNP Renin, aldosterone Fasting glucose, insulin 24-hour Urine Sodium output Creatinine output Chemoreflex testing Dynamic sinusoidal CO2 stimulus Rebreathing CO2 stimulus Exercise 6 minute walk test Cardiopulmonary exercise test Echocardiography Heart rate / BP variability Recumbent spontaneous Controlled breathing 24-hour ambulatory monitors BP ECG REACH Phase 1 Day 0 7-patient safety study Post-procedure Procedure Research Cath Lab Anaesthetist On standby: Interventional Radiologist Vascular surgeon Nephrologist Care plan designed with Head of Nursing Patient returns to ward Team of Specialist Research Nursing Sisters Dr Justin Davies and Dr Darrel Francis are first point of contact for ward team if any queries 5-day postprocedure stay planned, with option to extend REACH Phase 1 Day +1 Clinical assessment Bloods Electrolytes, Creatinine, NT-ProBNP Renin, aldosterone Fasting glucose, insulin 7-patient safety study 24-hour Urine Sodium output Creatinine output Metanephrines 24-hour ambulatory monitors BP ECG REACH Phase 1 Day +2 .. +4 Clinical assessment Bloods Electrolytes, Creatinine, NT-ProBNP Renin, aldosterone Fasting glucose, insulin 7-patient safety study 24-hour Urine Sodium output Creatinine output Metanephrines 24-hour ambulatory monitors BP ECG REACH Phase 1 7-patient safety study Week +1 Chemoreflex testing Dynamic sinusoidal CO2 stimulus Rebreathing CO2 stimulus Bloods Electrolytes, Creatinine, NT-ProBNP Renin, aldosterone Fasting glucose, insulin 24-hour Urine Sodium output Creatinine output Exercise 6 minute walk test Cardiopulmonary exercise test Echocardiography Heart rate / BP variability Recumbent spontaneous Controlled breathing 24-hour ambulatory monitors BP ECG REACH Phase 1 7-patient safety study Week +2 Chemoreflex testing Dynamic sinusoidal CO2 stimulus Rebreathing CO2 stimulus Bloods Electrolytes, Creatinine, NT-ProBNP Renin, aldosterone Fasting glucose, insulin 24-hour Urine Sodium output Creatinine output Exercise 6 minute walk test Cardiopulmonary exercise test Echocardiography Heart rate / BP variability Recumbent spontaneous Controlled breathing 24-hour ambulatory monitors BP ECG REACH Phase 1 7-patient safety study Month +1 Chemoreflex testing Dynamic sinusoidal CO2 stimulus Rebreathing CO2 stimulus Bloods Electrolytes, Creatinine, NT-ProBNP Renin, aldosterone Fasting glucose, insulin 24-hour Urine Sodium output Creatinine output Exercise 6 minute walk test Cardiopulmonary exercise test Echocardiography Heart rate / BP variability Recumbent spontaneous Controlled breathing 24-hour ambulatory monitors BP ECG REACH Phase 1 7-patient safety study Month +2 Chemoreflex testing Dynamic sinusoidal CO2 stimulus Rebreathing CO2 stimulus Bloods Electrolytes, Creatinine, NT-ProBNP Renin, aldosterone Fasting glucose, insulin 24-hour Urine Sodium output Creatinine output Exercise 6 minute walk test Cardiopulmonary exercise test Echocardiography Heart rate / BP variability Recumbent spontaneous Controlled breathing 24-hour ambulatory monitors BP ECG REACH Phase 1 7-patient safety study Month +3 Chemoreflex testing Dynamic sinusoidal CO2 stimulus Rebreathing CO2 stimulus Bloods Electrolytes, Creatinine, NT-ProBNP Renin, aldosterone Fasting glucose, insulin 24-hour Urine Sodium output Creatinine output Exercise 6 minute walk test Cardiopulmonary exercise test Echocardiography Heart rate / BP variability Recumbent spontaneous Controlled breathing 24-hour ambulatory monitors BP ECG REACH Phase 1 7-patient safety study Month +4 Chemoreflex testing Dynamic sinusoidal CO2 stimulus Rebreathing CO2 stimulus Bloods Electrolytes, Creatinine, NT-ProBNP Renin, aldosterone Fasting glucose, insulin 24-hour Urine Sodium output Creatinine output Exercise 6 minute walk test Cardiopulmonary exercise test Echocardiography Heart rate / BP variability Recumbent spontaneous Controlled breathing 24-hour ambulatory monitors BP ECG REACH Phase 1 7-patient safety study Month +5 Chemoreflex testing Dynamic sinusoidal CO2 stimulus Rebreathing CO2 stimulus Bloods Electrolytes, Creatinine, NT-ProBNP Renin, aldosterone Fasting glucose, insulin 24-hour Urine Sodium output Creatinine output Exercise 6 minute walk test Cardiopulmonary exercise test Echocardiography Heart rate / BP variability Recumbent spontaneous Controlled breathing 24-hour ambulatory monitors BP ECG REACH Phase 1 7-patient safety study Month +6 Chemoreflex testing Dynamic sinusoidal CO2 stimulus Rebreathing CO2 stimulus Bloods Electrolytes, Creatinine, NT-ProBNP Renin, aldosterone Fasting glucose, insulin 24-hour Urine Sodium output Creatinine output Exercise 6 minute walk test Cardiopulmonary exercise test Echocardiography Heart rate / BP variability Recumbent spontaneous Controlled breathing 24-hour ambulatory monitors BP ECG REACH – pilot patient REnal Artery denervation in Chronic Heart failure Extensive pre-procedural preparation Admission Review by clinical pharmacology team Anaesthetic review Biochemistry / Imaging performed Echo – severe LV systolic function Detailed review of notes from previous investigations REACH – pilot patient REnal Artery denervation in Chronic Heart failure Procedure Anaesthetic input to maintain SBP at 180 mmHg Uncomplicated denervation procedure Immediate after-care Immediate fall in blood pressure overnight to 150 mm Hg Medications temporary reduced, and then slowly restored to original levels REACH – pilot patient REnal Artery denervation in Chronic Heart failure Discharge Reduction in 2 of her anti-hypertensive agents Blood pressure 190-200 mmHg Felt well REACH – pilot patient REnal Artery denervation in Chronic Heart failure Follow-up (2 weeks) Large symptomatic improvement in breathlessness Blood pressure 190-200 mmHg Exercise tolerance increased from 200 m to 1 mile Medications re-introduced at full dose with the aim to slowly reduce her blood pressure REACH – pilot study REnal Artery denervation in Chronic Heart failure Follow-up (4 months) Continues to feels well Improvement in exercise capacity persists 250-280 mmHg systolic 200-205 mmHg systolic Close enough to target most of the time Close enough to target most of the time ~2 x ~2 x ~2 x REACH – pilot study REnal Artery denervation in Chronic Heart failure Follow-up (4 months) Continues to feels well Improvement in exercise capacity persists 250-280 mmHg systolic 200-205 mmHg systolic