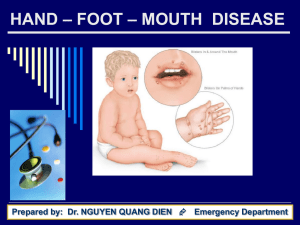
Viral Exanthems and Enanthems
advertisement

Viral Exanthems and Enanthems Amina Ahmed, MD Pediatric Infectious Disease Levine Children’s Hospital Adenovirus Epidemiology Year-round; peak in winter/spring/early summer Incubation 2-14 d respiratory disease, 3-10 enteric disease Clinical Presentation Respiratory Conjunctivitis, pharyngitis (pharyngoconjunctival fever) Exanthem- Usually mp lesions, erythematous, blanching Enteric Diarrhea Cystitis Diagnosis DFA, culture (culture more sensitive) PCR (blood, urine, secretions)- usually for immunocompromised population Treatment Enteroviruses Poliovirus 1, 2, 3 Echoviruses Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus B Enteroviruses Enteroviruses Epidemiology Peak in summer (May-October) Incubation 3-6 days Clinical Presentation Fever (“fever without a source” in infants) Respiratory- pharyngitis, URI, “summer cold,” conjunctivitis Meningitis, meningoencephalitis Diagnosis Clinical Culture, PCR (CSF typically) Treatment EV : Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease Exanthem Enanthem Vesiculopustular lesions on palms, soles Vesicular lesions in mouth Typically buccal mucosa, anterior mucosa Diagnosis Culture of oral secretions PCR EV: Herpangina Exanthem Enanthem None Vesiculopustular lesions in mouth Typically soft/hard palate Not on lips (vermilion border) Diagnosis Culture of oral secretions PCR Parvovirus B19 Erythema infectiousum, Fifth Disease Epidemiology Clinical Presentation Fever, mild URI Arthralgias/arthritis (especially young females) Aplastic anemia (hemoglobinopathies) Fetal hydrops (complication of infection during pregnancy) Exanthem Incubation 4-14 days Most contagious before onset of rash “Slapped cheek,” circumoral pallor Maculopapular, “lace-like,” reticular Diagnosis /Treatment Serology, PCR Human Herpes Virus 6 (Roseola infantum) Epidemiology Infants 6-24 months of age No seasonal pattern Incubation 9-10 days Clinical Presentation High fever for 3-4 days followed by rash Pharyngitis, occipital nodes Seizures Exanthem Discrete rose-red mp lesions on chest and trunk Spread to face and extremities Lasts hours-days Diagnosis/ Treatment Clinical Serology, PCR Morbillivirus (Measles) Epidemiology Incubation 8-12 days Highly contagious (droplets, airborne); 3-5 d before-4 d after rash Late winter, early spring Clinical Presentation Fever, cough, coryza, conjunctivitis (prodrome) Exanthem / Enanthem Starts on head, spreads cephalocaudally Coppery-red; may coalesce; desquamation Enanthem- Koplik’s spots (before exanthem) Diagnosis Serology, PCR Culture (urine) Treatment Prevention of superinfection with antibacterials Vitamin A ?Ribavirin Rubivirus (Rubella) Epidemiology Clinical Presentation Typically asymptomatic in 25-50% of cases Fever, adenopathy Congenital rubella- cataracts, bony lesions, heart defects Exanthem Incubation 14-21 days Contagious few days before to 5-7 days after onset of rash Pinkish, maculopapular Diagnosis / Treatment Culture (especially congenital rubella), serology Rubella Varicella-Zoster Virus Epidemiology Clinical presentation Incubation 10-21 days; contagious 1-2 d before rash onset Late winter, early spring Fever, URI (prodrome) Exanthem /Enanthem Lesions evolve: mp to vesicular to excoriated; pruritic Hallmark- lesions in different stages (“crops”) “Dew drop on a rose petal” Similar lesions may involve mouth Presentation altered by vaccination Reactivation: zoster (dermatomal distribution) Varicella-Zoster Virus Diagnosis Treatment VZV DFA from lesions (rapid) Tzanck not specific PCR from lesion Serology Acyclovir Immunocompromised or nonimmune neonate Encephalitis Adults, adolescents, pregnant females Prevention VZV vaccine Varicella Epstein-Barr Virus Epidemiology Clinical presentation Fever, pharyngitis (exudative), lymphadenopathy Splenomegaly Hepatitis, thrombocytopenia Exanthem Incubation 30-50 d “Kissing disease” Erythematous, mp lesions; may coalesce May follow ampicillin use Diagnosis / Treatment Clinical, serology PCR (immunocompromised host) Herpes Viruses 1 and 2 Epidemiology Incubation 2 d- 2 weeks Herpes is forever Clinical presentation Neonatal disease Skin, eye, mucous membranes Meningoencephalitis Disseminated Primary gingivostomatitis; herpes labialis Genital disease Encephalitis Herpes Viruses 1 and 2 Exanthem / Enanthem Diagnosis Vesicular lesions; coalesce with time Enanthem: friable gingiva, lesions on tongue, gingiva May be on lips, vermilion border DFA of base of lesions (rapid) Culture of secretions, vesicular fluid PCR (lesions, blood, CSF) Gold standard for meningoencephalitis Treatment Acyclovir, valacyclovir Neonates, encephalitis, immunocompromised host What’s Your Diagnosis? Lesions in mouth and crossing the vermilion border. Tongue and gingiva involved What’s Your Diagnosis? 32 year old school teacher with low grade fever, sore throat, painful swallowing Diagnostic evaluation? What’s Your Diagnosis? 2 year old with fever and refusal to eat Lesions present for 2 days What’s Your Diagnosis? 7 year old with lesions on hands; no fever Differential diagnosis? Diagnostic evaluation? What’s Your Diagnosis? 4 year old with fever for 2 weeks and rash for 1 week Differential diagnosis? What’s Your Diagnosis? What’s Your Diagnosis? 6 year old Swiss girl with fever for 7 days Mild sore throat Diagnostic evaluation? Prevention of transmission? What’s Your Diagnosis? 4 year old Swiss girl with fever, cough, and rash Diagnostic evaluation? What’s Your Diagnosis? 9 year old with headache for 1 week Diagnostic evaluation? Treatment? What’s Your Diagnosis? 15 year old with fever and sore throat Differential diagnosis? Diagnostic evaluation? Treatment? What’s Your Diagnosis? Diagnostic evaluation? Treatment?