the anatomic consequences of arthroscopic coracoplasty
advertisement

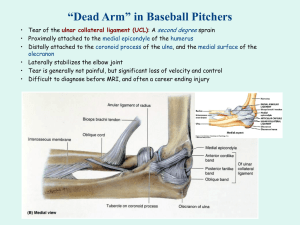
THE ANATOMIC CONSEQUENCES OF ARTHROSCOPIC CORACOPLASTY: AN ANATOMIC DISSECTION STUDY Aruna Seneviratne, MD; Ken Montgomery, MD; Babette Bevilacqua, PAC; Bashir A Zikria, MD Lenox Hill Hospital, New York, NY, USA Results: Objective: Average coracoplasty from coracoid tip: 10.3mm Figure 1 Arthroscopic coracoplasty is a surgical technique that Structure and Approximate Orientation Relative to Coracoid Tip (Normalized to a Right Shoulder) has recently been described to treat subcoracoid CCL 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 impingement. The goal of this investigation was to determine the anatomy of the soft tissue attachments onto the coracoid, and to assess how these structures may be compromised after an arthroscopic reduction of CAL the coracoid tip. structure. 7/14 tendons demonstrated perforations (Figures 2 and 3). On average, the conjoint tendon perforation Coracoid Tip PMT The coracobrachialis tendon was the most vulnerable CAL - Coraco-acromial Ligament CCL - Coraco-clavicular Ligament CJT - Conjoined Tendon MCN - Musculocutaneous Nerve PMT - Pectoralis Minor Tendon measured 4.9mm, with the largest perforation being 10mm (47.6% of the tendon width). 1/14 pectoralis minor tendons were injured. The CA and CC ligaments were not affected by coracoplasty. The musculocutaneous nerve was an average of 33 mm from tip (Figure 1). No nerve injuries were observed. Figure 3 CJT MCN Distance to Tip Methods: Figure 2 Average Width of Key Structures Anatomic dissections were performed on fourteen 25.0 cadaver shoulders to determine the soft tissue attachments onto the coracoid process (Figure 1). An within the glenohumoral joint with the shaver placed in the rotator interval, removing 10-12 mm of bone from the distal coracoid tip. Follow-up dissections were then Width (mm) arthroscopic coracoplasty was then performed from 20.0 CAL - Coraco-acromial Ligament CCL - Coracoclavicular Ligament CJT - Conjoined Tendon MCN Musculocutaneous Nerve PMT - Pectoralis Minor 15.0 10.0 5.0 Width CJT Violation (mm) performed to evaluate the consequence of the Conclusions: Arthroscopic coracoplasty is a procedure that can be safely and effectively performed through a rotator interval approach. Subperiosteal elevation of the coracobrachialis tendon occurs 0.0 coracoplasty on the soft tissues inserting on the coracoid CJT PMT CCL CAL during the procedure. Care must taken to remove only coracoid Structure bone, leaving the superficial periosteal sleeve of the coracobrachialis intact, in order to prevent complete detachment of the coracobrachialis tendon.