The regional anatomy of the upper limb
advertisement

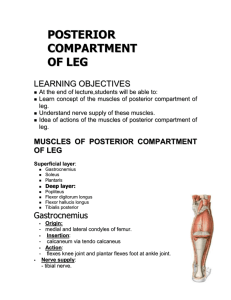
The regional anatomy of the lower limb 2. The small saphenous vein Begins the lateral side of the dorsum of the foot →runs upward posterior to the lateral malleolus → then ascends along the posterior median line of the leg, accompanying with the sural nerve → then passes between the two heads of gastrocnemius to the lower part of the popliteal fossa → finally pierces the popliteal fascia and drains into the popliteal vein. It receives a lot of the tributaries and communicates with the great saphenous vein and deep veins of the lower limb. (2) The gluteal region, the back of the thigh and the popliteal fossa 1)The subcostal nerve and the lateral cutaneous branch of iliohypogastric nerve 2)The posterior branch of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve 3)The inferior gluteal cutaneous nerve 4)The superior gluteal cutaneous nerve 5)The middle gluteal cutaneous nerve. 2) The muscles of the back of the thigh Laterally: the biceps femoris Medially: superficial semitendinosus; deep semimembranosus. posterior group of the leg Superficial--the triceps surae (gastrocnemius soleus); the plantaris. Deep--From the medial to the lateral: The flexor digitorum longus; The tibialis posterior; The flexor hallucis longus. 4. The muscles of the sole of foot ------four layers The 1st layer----From the medial to the laeral: The abductor hallucis; The flexor digitorum brevis; The abductor digiti minimi. The 2nd layer---The tendon of flexor hallucis longus; The tendon of flexor digitorum longus; The lumbricales; The quadratus plantae. The 3rd layer-----The flexor hallucis brevis; The addctor hallucis; The flexor digiti minimi brevis. The 4th layer---- The tendon of peroneus longus; The tendon of tibialis posterior; The interosseous muscles. The infrapiriform foramen lateral to medial side-----sciatic nerve; posterior femoral cutaneous n; inferior gluteal nerve; inferior gluteal artery and v; internal pudendal a and v; pudendal nerve. popliteal fossa Position: It is a diamond fossa behind the knee joint. Formation: The upper lateral boundary ----the biceps femoris; The upper medial boundary ----the semitendinosus, The semimembranosus; The lower lateral boundary the lateral head of the gastrocnemius; The lower medial boundary the medial head of the gastrocnemius. The floor--------from above downwards popliteal surface of femur; posterior wall of knee joint capsule; popliteus. The roof------- the popliteal fascia. The contents of the popliteal fossa: From the superficial to the deep layers The tibial and common peroneal nerve; The popliteal vein; The popliteal artery; The popliteal lymph nodes. (1) The tibial nerve It is a larger of the two terminal branches of the sciatic nerve. In the center of the popliteal fossa, it descends vertically from the upper angle to lower angle of the popliteal fossa, to the lower border of the popliteus drills through the tendinous arch of the soleus and enters between the superficial and deep layers of the posterior group muscles of the leg. The cutaneous branch is called the medial sural cutaneous nerve which supplies the skin of the calf and joins with the communicating branch of common peroneal nerve to form the sural nerve which supplies the lateral aspect of the ankle and foot. The muscular branches supply the muscles of the posterior group of the leg. The articular branches supply the knee joint. (2) The common peroneal nerve It is a smaller one of the two terminal branches of the sciatic nerve. It enters the popliteal fossa at the superior angle of the fossa, then follows the medial border of the biceps femoris and its tendon along superolateral boundary of the fossa. It leaves the fossa by passing superficial to the lateral head of gastrocnemius, and terminates at the lateral side of the neck of the fibula, under cover of the peroneous longus, by dividing into superficial and deep peroneal nerves. In the popliteal fossa, the common peroneal nerve gives off articular branches to the knee and proximal tibiofibular joints, also gives off the lateral sural cutaneous nerve to the skin of calf and a communicating branch which joins the sural nerve. (3) The popliteal vein It is between the popliteal artery and the tibial nerve. (4) The popliteal artery Its position is the deepest. The popliteal artery rests against the floor of the popliteal fossa and ends at the lower border of the popliteus by dividing into anterior and posterior tibial arteries. Its muscular branches supply the muscles surrounding the popliteal fossa. Its articular branches(lateral superior genicular artery, medial superior genicular artery, lateral inferior genicular artery, medial inferior genicular artery, descending genicular artery) supply the knee joint and take part in to form the arterial rete of the knee joint. (5) The popliteal lymph nodes They are placed along the sheath of popliteal vessels and 4-5 in number. They receive the lymph from the skin of the lateral side of the foot and the lateral half of the back of the leg, and the deep lymphatic vessels of the leg and foot. The efferent vessels end in the deep inguinal lymph nodes. 6. The malleolar canal Position: It is the medial side of the ankle joint. Formation: It is formed by the flexor retinaculum (which bridges across the interval between the calcaneus and the medial malleolus) together with the calcaneus. The contents of the mallelar canal: From the anterior to the posterior The tendon and tendinous sheath of the tibialis posterior; The tendon and tendinous sheath of the flexor digitorum longus; The posterior tibial artery and vein and the tibial nerve; The tendon and tendinous sheath of the flexor hallucis longus.