Back Of Leg

BACK OF LEG
Dr. Rakesh Kumar Verma
Assistant Professor
Department of Anatomy
KGMU UP Lucknow
INTRODUCTION
• Synonyms:
Flexor compartment/ region/calf compartment/Posterior
Posterior Crural
BOUNDARIES
Anterior-Posterior surface of: tibia, interosseous membrane, fibula, post. Intermuscular septum
Posterior: fascia of leg
Deep
STRUCTURE (CONTENTS)
• Skin & Superficial fascia
• Cutaneous nerves & vessels
• Lymphatics
• Fibro fatty tissue
• Deep fascia
• Muscles, nerves & vessels
CUTANEOUS NERVES
• Saphenous Nerve
• Post. division of medial cut. nerve of thigh
• Post. cut. nerve of thigh
• Sural Nerve
• Lateral cut. nerve of thigh
• Sural communicating nerve
• Medial calcaneal branches of tibial nerve
CUTANEOUS VESSELES
• Great Saphenous Vein
• Small Saphenous Vein
• Small tributeries
• Lymhatics
• Also known as fascia cruris
• Modifications:
Intermuscular septum
Flexor retinaculum
DEEP FASCIA
FLEXOR RETINACULUM
• Attachment:
Anterior-Post. Border
& tip of medial malleolus
Postero-lateralmedial tubercle of calcaneum
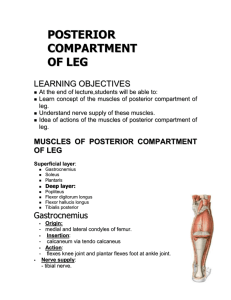
MUSCLES OF BACK OF LEG
• Gastrocnemius
• Soleus
• Plantaris
• Popliteus
• Flexor digitorum longus
• Flexor hallucis longus
• Tibialis posterior
GASTROCNEMIUS
SOLEUS & PLANTARIS
POPLITEUS
FLEXOR DIGITORUM LONGUS,
FLEXOR HALLUCIS LONGUS & TIBIALIS
POSTERIOR
S.No Muscle Origin Insertion
1.
Gastrocnemius Medial Head: Posterosuperior depression on medial condyle , popliteal surface of Femur & cpusule of knee joint
Lateral head: Lateral condyle & supracondylar line of femur, cpusule of knee joint
2.
Soleus Back of head & post.surface of fibula
Soleal line & middle 1/3 rd of medial border of tibia
Tendinous soleous arch
Middle 1/3 rd of posterior surface of calcaneum
Achilis tendocacaneus as or
3.
Plantaris Lateral supracondylar line of femur & obliqe popliteal ligament posterior surface of calcaneum medial to tendocacaneus
S.N
o
Muscle
4.
Popliteus
Origin Insertion popliteal groove
Arcuate popliteal Ligament
Lat meniscus
Above Soleal line on post surface of tibia
5.
Flexor digitorum longus
6.
Flexor hallucis longus
Upper 2/3 rd of medial part of the post. Surface of tibia below soleal line
Lower 3/4 th of post. Surface of fibula & interosseous membrane
7.
Tibialis posterior
Upper 2/3 rd of lateral part of the post. Surface of tibia below soleal line, Post. Surface of fibula & interosseous membrane
Planter surface of distal phalanx of lat.
4 toes
Planter surface of distal phalanx of great toe
Tuberosity of navicular bone & also on tarsals and 2 nd ,3 rd
& 4 th metatarsal except talus
NERVE SUPPLY & ACTIONS
• Tibial nerve for all muscle
• Plantar flexion
• Inversion
• Maintained longitudinal arch
• Unlocking of knee by popliteus
• Flexion at knee joint
20
POSTERIOR TIBIAL ARTERY
It Is Large terminal branch of popliteal artery
POSTERIOR TIBIAL ARTERY
• Branches:
Peroneal artery
Muscular
Nutrient
Cicumflex fibular
Communicating
Malleolar
Calcaneal
Terminal-medial & lateral planter artery
TIBIAL NERVE
• Large terminal branch of sciatic nerve in popliteal fossa
• Branches:
Muscular
Cutaneous
Articular
Terminal-medial & lateral planter nerve
Posterior Tibial Vein
• Formation at the level of lower border of popliteus
• By joining of venae commitantes running along Ant. & post tibial artery
• Finally drain in to popliteal vein
APPLIED ANATOMY
• Tennis leg
• Tendon of plantaris used as a graft
• Rupture of tendocalcaneus
• Ankle jerk
• Deep vein thrombosis
• Arterial insufficiency
• Varicose vein
• Tarsal tunnel syndrome
QUESTION -1
• Unlocking of knee is done by:
A) Soleus
B) Plantaris
C) Popliteus
D) Gastrocnemius
QUESTION -2
• All muscles help in plantar flexion except:
A) Tibialis Posterior
B) Gastrocnemius
C) Soleus
D) Popliteus
QUESTION -3
• Which muscle is known as peripheral heart:
A) Soleus
B) Plantaris
C) Popliteus
D) Gastrocnemius
QUESTION -4
• False statement about popliteus is:
A) Has intracapsular origin
B)Pulls the medial meniscus backwards and prevent it from being trapped at the beginning of flexion
C) Innervated by tibial nerve
D) Unlock the knee joint
QUESTION -5
• Tibialis posterior is attached on the following bone except-
A) Talus
B) Navicular
C) 2 nd metatarsal
D) 4 th metatarsal