06. Malignant neoplasm of lung

Lung cancer
Edit Csada MD
08.10.2014.
1
Epidemiology
Globocan 2012.
Lung cancer is the most frequent malignant disease
New cases:
Mortality:
1,82 million/year
1,59 million/year
(13%)
Most frequent cause of death amoung malignant diseases>colon+prostate+breast
Europe:~1000 death/day
Lung cancer fatality: breast cancer fatality:
Male/female: 2,4/1
159/1852 = 0,87
0,35
2
New diseases according to ages
Until 40 years :
40-49 years:
50-59 years:
60-69 years:
Above 70 years:
1% ↓
10% ↓
~30%
~30%
30% ↓
3
Etiologic factors
Smoking
Athmospheric pollution
Ionisation
Occupational factors asbestos, radon, etc
Other lung diseases tb, COPD, ILD
Genetic events
4
Smoking
400 chemical materials
60 carcinogens
Gas and particulate phase
Nitrosamines, aromatic amines, benzopyrene, CO, CO2, aldehids, nicotin, free radicals
Pack-year
5
Smoking and Lung Cancer
85-90% of lung cancer patients are smokers
Damages of 10-15 gens have role in the development of lung cancer
86% of smokers have damages of these gens
6
Molecular biology of lung cancer
Genetic damages
Deletion
Mutations
Amplifications
Tumor suppressor gen injury (p53, RB1)
Inhibation of proliferation
Repair mechanism
Induction of apoptosis
Protooncogen abnormalities
Autocrine growth factors membran receptors transcription factors
7
A tüdőrák molekuláris biológiája
AC SCLC SQCLC
Proliferáció/onkogen
EGFR/TK mutáció Amplifikáció(?) 30%
HER2ampl./mut.
KRAS mut.
<5%
5%
CMYC ampl.
Proliferáció/suppr.
Apoptosis
FHIT(vesztés)
20% p53 mut.
50%
Rb(vesztés, metil.) 20%
P16(vesztés, metil.) 50%(?)
80%
30% BCL2 fokozott
Kszpáz8(metil)
DAPK(vesztés) 50%
<5%
20%
20%
50%
20%
50%(?)
80%
30%
50%
LMYC
90%
90%
<10%
80%
80%
80%
Genetic defects in lung cancer
SCLC (%) NSCLC (%)
3p deletion
3p14.2
Rb
P16 (promoter metilation)
P53 (mutation)
C-Myc
Ras (H,K,N)
HER2/neu
Bcl-2 expression
Procaspase-8 decrease
Telomerase
90
80
80-90
7
80
10-40
0
?
75-90
80
100
50-80
40
15-30
16
50-60
5-10
20-30
25
25-30
?
80
9
Prevention
Primary
Smoking sessation
Secundary
Screening
X-ray
LDCT
10
Histology of lung cancer
Non small cell lung cancer
Squamous cell carcinoma (30%)
Well, or less differentiated, with or without keratinisation
Adenocancer (45%) acinar papillary bronchioloalveolar with mucus formation
Large cell carcinoma (10%↓) clear cell giant cell
11
12
Histology of lung cancer
Small cell lung cancer (15%)
Oat cell
Intermediate cell type
Combined type
Carcinoid tumor
Bronchial gland carcinomas
Adenoid cystic carcinoma
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
13
14
Hitology in Hungary
2020. 04. 12.
Korányi Bulletin 2012
15
Molecular types of adenoc.
2020. 04. 12.
2013.03.
Pathological prognostic factors
TNM
Histology
Histological differentiation
Invading vessels
Necrosis
Proliferation activity
Prognostic proteins
17
Symptoms
Cough
Dyspnoe
Haemopthysis
Weight loss
Chest pain
Hoarsness
Frequency (%)
45 - 75 %
37 - 58 %
27
–
57 %
8
–
68 %
27
–
49 %
2
–
18 %
18
Symptoms of lung cancer
Regional spread
Superior vena caval sy
Recurrent laryngeal nerve paralysis
(hoarsness)
Phrenic nerve paralysis elevated hemidiaphragm
Horner’s sy
Pancoast’s sy
Trachea obstruction
Oesophagus obstruction
Pleural effusion
Lymphatic tumor spread
19
20
Vena cava superior sy
2020. 04. 12.
Sárosi Veronika anyaga
21
Pancoast tumor
2020. 04. 12.
Pálföldi Regina anyaga
22
Ectopic parathormon productin, hypercalcaemia
Ectopic production,
ACTH
Cushing-syndrom
Osteoarthropathy, digital clubbing
Eaton Lambert syndrom
Peripherial neuropathy, subacut cerebellar degeneration
Polymyositis, dermatomyositis
Thrombophlebitis migrans, DIC
Nephrosis syndrom
Inappropriate production
(SIADH)
ADH
Squamous cell cancer
+
+
+
-
+
-
-
+
+
Adenocancer
+++
+
-
-
+
++
-
+
+
Small cell cancer
Large cell cancer
+ -
+
+
+++
+
+
+
+
+
-
+
-
+
+
+
+
-
23
Dobverő ujj, óraüveg köröm
2020. 04. 12.
Sárosi Veronika anyaga
24
Diagnostic procedures
Imaging technics
Endoscopy
Pathology
Laboratory tests (?)
25
Diagnostic procedures
Imaging technics
Chest x-rays
CT
MRI
Isotope scanning
PET/CT
Ultrasound
26
Bronchoscopy: sample taking, staging
Biopsy
Brushing
Transbronchial biopsy
Transbronchial needle aspiration
(TBNA, EBUS)
Washing
BAL
27
Other sample takings
TTB, x-ray or CT supervision
Percutan pleura biopsy
Lymphnode aspiration biopsy
Surgical biopsy
Mediastinoscopy
Parasternal mediastinotomy
(Stemmer)
VATS
Thoracotomy (10% ↓) 28
Staging 1
T1a = Tumor ≤2 cm in greatest dimension, surrounded by lung or visceral pleura, without bronchoscopic evidence of invasion more proximal than the lobar bronchus (i.e., not in the main bronchus).
T1b = Tumor >2 cm but ≤3 cm in greatest dimension
29
Staging 2
T2a = Tumor >3 cm but ≤5 cm in greatest dimension, or tumor with any of the following features: involves main bronchus, ≥2 cm distal to the carina; invades visceral pleura (PL1 or
PL2); or is associated with atelectasis or obstructive pneumonitis that extends to the hilar region but does not involve the entire lung.
T2b = Tumor >5 cm but ≤7 cm or less in greatest dimension
30
Staging 3
T3 = Tumor >7 cm or one that directly invades any of the following: parietal pleural (PL3) chest wall (including superior sulcus tumors), diaphragm, phrenic nerve, mediastinal pleura, or parietal pericardium or tumor in the main bronchus (<2 cm distal to the carina b but without involvement of the carina) or associated atelectasis or obstructive pneumonitis of the entire lung or separate tumor nodule(s) in the same lobe
31
Staging 4
T4 = Tumor of any size that invades any of the following: mediastinum, heart, great vessels, trachea, recurrent laryngeal nerve, esophagus, vertebral body, carina, or separate tumor nodule(s) in a different ipsilateral lobe.
32
Staging 5
N0 = No regional lymph node metastasis.
N1 = Metastasis in ipsilateral peribronchial and/or ipsilateral hilar lymph nodes and intrapulmonary nodes, including involvement by direct extension.
N2 = Metastasis in ipsilateral mediastinal and/or subcarinal lymph node(s).
N3 = Metastasis in contralateral mediastinal, contralateral hilar, ipsilateral or contralateral scalene, or supraclavicular lymph node(s).
33
Staging 6
M0 = No distant metastasis.
M1a = Separate tumor nodule(s) in a contralateral lobe tumor with pleural nodules or malignant pleural (or pericardial) effusion
M1b = Distant metastasis (in extrathoracic organs).
34
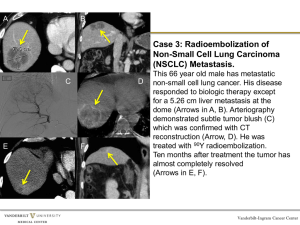
Metastases
Liver:
Bones:
CT, ultrasound, PET/CT scintigraphy, CT, PET/CT
Adrenals: CT, ultrasound, PET/CT
Brain: MRI, CT
36
Prognostic factors
Poor performance status
Karnofsky, WHO ECOG
Weight loss, more than 10%
Elevated LDH
Elevated tumormarker (CEA, NSE, SCC)
Old age
37
2
3
4
5
Performance status
Grade
0
1
ECOG
Fully active, able to carry on all pre-disease performance without restriction
Restricted in physically strenuous activity but ambulatory and able to carry out work of a light or sedentary nature, e.g., light house work, office work
Ambulatory and capable of all selfcare but unable to carry out any work activities. Up and about more than 50% of waking hours
Capable of only limited selfcare, confined to bed or chair more than 50% of waking hours
Completely disabled. Cannot carry on any selfcare. Totally confined to bed or chair
Dead
38
Performance status
Karnofsky scale Description
100 Normal; no complaints; no evidence of disease
90
80
70
60
Able to carry out normal activity; minor signs or symptoms of disease
Normal activity with effort; some signs or symptoms of disease
Cares for self; unable to carry on normal activity or do active work
Requires occasional assistance, but is able to care for most of his/her needs
50 Requires considerable assistance and frequent medical care
40
30
20
10
0
Disabled; requires special care and assistance
Severely disabled; hospitalization is indicated although death not imminent
Very sick; hospitalization necessary, active supportive treatment necessary
Moribund; fatal processes progressing rapidly
Dead
39
Therapy of lung cancer
Surgery
Radiotherapy
Radiochemotherapy
Chemotherapy
Molecular target therapy
Supportive treatment
40
Surgery
The type of surgical procedure depends on staging, the patient ’s performance status, cardiopulmonal function and comorbidities.
The aim is radical resection
Sublobar resection may have a role in very early diseases.
Thoracotomy
Video assisted thoracoscopy (VATS)
41
Surgery
Absolute contraindications:
haematogen metastases in the lungs
pleuritis carcinomatosa
III.b stage disease
multiplex distanti metastases
Relative contraindications
42
Surgery (20-25%)
NSCLC IIIA stage
Lobectomy, pulmonectomy, sleeve lobectomy, extensive resection – radical
Segmentectomy, wedge resection – mostly non radical
Early stage SCLC, as part of combined therapy
Carina resection?
Before surgery: lung function, Ecg, functional evaluation
43
Radiation therapy
NSCLC: III.A, III.B stage
SCLC: combined with chemotherapy
Inoperable patient with resecable disease
Resected N2 disease, in combined treatment
Metastasis palliation
Pancoast’s tu
Brain metastasis (stereotactic, whole brain)
PCI
Brachytherapy
Radiochemotherapy!
44
Combination of radio/chemotherapy
Sequential
ChT
RT
Concomitant
(ChT
RT
ChT)
ChT/RT
Timing
- Induction: ChT
ChT/RT
- Consolidation: ChT/RT
ChT
45
Chemotherapy
Neoadjuvant treatment
Before surgery IIIa stage
Adjuvant treatment
After surgery II-IIIa stage
First-, second-, thirdline …..
IIIb, IV stage
46
First line treatment of NSCLC
Chemotherapy
Cis-, carboplatin-gemcitabin
Cis-, carboplatin-paclitaxel
Cisplatin-docetaxel
Cisplatin-vinorelbin
Cisplatin-pemeterexed (non squamous c)
Doublet+bevacizumab(adenoc)
Adenoc.: EGFR mutácio pozitivitás
Erlotinib, gefitinib, afatinib
47
Second line treatment of NSCLC
Chemotherapy
Docetaxel monoterapy
Pemetrexed monoterapy
Adenoc.: EGFR mutation positivity/KRAS negativity
gefinitib, erlotinib
48
Maintenance treatment
Klasszikus kezelés
Elsővonalbeli kezelés
Platinaalapú kettős kombináció
(4 –6 ciklus)
Kezelési szünet
Másod- és többedvonalbeli kezelés
Diagn ózis CR/PR/SD PD PD
Új megközelítés
Bevacizumab
Pemetrexed ellotinib
Fenntartó kezelés
PDig eltelt idő megnyúlik
Diagn ózis CR/PR/SD PD PD
Surgery in SCLC
I/A-I/B: resection
Postoperative chemotherapy
Adjuvant irradiation in positive node status
Induction chemohterapy
Chemoterapy in SCLC
Absoute indication
Cisplatin/carboplatin-Vepesid
ECO (epirubicin-cyclophoscphamid-vincristin)
Topotecan (Hycamtin) (2. line)
Progression:
Within 3 months (resistant disease): new combination
Over 3 months (senzitive disease): reinduction therapy with the original drugs
Radiotherapy in SCLC
LD: radio-chemotherapy
PCI: preventíve cerebral irradiation
In LD and ED
Remission after treatment
Dose: 25-30 Gy
Possible impairment of neurocognitive functions
Molecular target therapy
EGFR tirosin kinase inhibitors
Erlotinib (Tarceva)
Gefinitib (Iressa)
afatinib
Angiogenesis inhibitors (VEGF)
Bevacizumab (Avastin)
Alk-EML4 fusion gen inhibitor
Crizotinib (Xalkori)
53
Supportive treatment
Pain control
WHO suggestion
Adverse events control
Thrombosis prophylaxis
Malignant pleural fluid treatment
Bone metastases treatment
Endobronchial palliation
Nutrition
54
WHO’s pain stairs (1986)
Strong opioid ± non opioid ± adjuvant
III.
Weak opioid ± non opioid ± adjuvant
II.
Non opioid ± adjuvant
24 h
I.
24 h 24 h
55
Supportive treatment
Pain control
Adverse events control
febrile neutopenia
Anaemia (erythropoetin)
Nausea, vomiting
Thrombosis prophylaxis
Malignant pleural fluid treatment
pleurodesis
Bone metastases treatment
bisphosphonat
Endobronchial palliation
Nutrition
56
Prognosis
I. stage: 55-80%
II. stage: 30-50%
III.a stage: 10-30%
III.b stage: 4%
IV. stage: 1%
Five year survival: 15-17%
57
58
Thank you for your attention!