the slides - ARV
advertisement

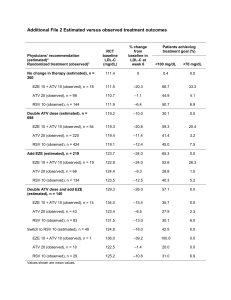
Switch to ATV/r-containing regimen - ATAZIP ATAZIP Study: Switch LPV/r to ATV/r Design Randomisation 1:1 Open-label M24 N = 121 Switch to ATV/r 300/100 mg qd 265 patients HIV+ ≥ 18 years On LPV/r + 2 NRTIs ≥ 6 months HIV RNA < 200 c/mL > 6 months* + continue NRTIs** N = 127 Continue LPV/r 400 /100 mg bid + NRTIs** * Not more than 2 previous virologic failure on PI and if genotype performed < 5 mutations ** Switch in NRTI not counted as failure Endpoints – Primary: non inferiority in the proportion of patients with treatment failure at W48 (intent-to-treat analysis), lower limit of the 95% CI for the difference = -12.5%, 80% power – Treatment failure = virologic rebound (2 consecutive HIV-1 RNA ≥ 200 c/mL), lost to follow-up, withdrawn consent, discontinuation for any reason, progression to a new CDC event or death ATAZIP Mallolas J, JAIDS 2009;51:29-36 ATAZIP Study: Switch LPV/r to ATV/r Baseline characteristics and patient disposition ATV/r N = 121 LPV/r N = 127 42 43 Female 20% 21% History of AIDS diagnosis 40% 57% Hepatitis C co-infection 36% 27% CD4 cell count at baseline < 200 /mm3 8% 10% 20% / 17% / 10% 17% / 9% / 16% Previous PI failures ≥ 1 21% 20% Previous PI mutations ≥1 ≥ 1 major 36% 14% 32% 10% 16 (13%) 18 (14%) For adverse event 6 6 For virologic failure 1 1 Median age, years NRTIs: TDF + 3TC / TDF + ddI / ZDV + 3TC Discontinuation before W48, n (%) ATAZIP Mallolas J, JAIDS 2009;51:29-36 ATAZIP Study: Switch LPV/r to ATV/r Results: W48 outcome Treatment failure % % Virologic rebound 30 30 p = 0.0018 25 Switch to ATV/r Continue on LPV/r 25 20 20 20 15 17 10 10 5 5 0 0 21/121 25/127 -2.3% (-12.0%, 8.0%) 15 p < 0.0001 7 5 6/121 Difference estimate (95% CI) 9/127 -2.1% (-8.7%, 4.2%) Time to treatment failure and time to virological failure did not differ between groups The median changes in CD4 count at 48 weeks were +27 cells/mm3 (IQR: -42 to 119) with ATV/r and +48 cells/mm3 (IQR: -5 to 112) with LPV/r (p = 0.315) ATAZIP Mallolas J, JAIDS 2009;51:29-36 ATAZIP Study: Switch LPV/r to ATV/r 3 200 p < 0.001 p < 0.001 100 p = 0.149 -100 1 0 -1 -2 -3 -200 Triglycerides Total cholesterol LDL HDL cholesterol cholesterol Switch to ATV/r 300/100 qd (N = 121) ATAZIP p = 0.185 0 -300 p = 0.043 2 TC/HDL-C ratio Median change from baseline (mg/dL) Fasting plasma lipids changes from baseline to week 48 Total cholesterol/ HDL cholesterol Continue on LPV/r 400/100 bid (N = 127) Mallolas J, JAIDS 2009;51:29-36 ATAZIP Study: Switch LPV/r to ATV/r Adverse events by W48 ATV/r, N = 121 LPV/r, N = 127 1 1 (hepatic encephalopathy) AE leading to discontinuation 5% 5% Patients with ≥ 1 Grade 3 or 4 AE 11% 16% Cardiovascular N=1 N=1 Digestive N=2 N =1 Osteomuscular N=0 N=1 Hematologic N=0 N=1 Hepatic N=1 N=1 Respiratory N=1 N=0 Transaminases N=6 N=2 Total cholesterol N=4 N=7 Triglycerides N=0 N = 13 Bilirubin > 2.5 mg/dL N = 66 (55%) N = 6 (5%) Bilirubin > 5 mg/dL N = 21 (17%) N = 2 (2%) Death Clinical Laboratory ATAZIP Mallolas J, JAIDS 2009;51:29-36 ATAZIP Study: Switch LPV/r to ATV/r Conclusions – Switching to a simplified PI-based regimen containing ATV/r provides virological suppression and treatment failure similar to those observed with continued unmodified therapy with LPV/r – Safety and tolerability profile were similar in both groups – Improved lipid parameters were observed in the ATV/r arm – High incidence of hyperbilirubinemia occurred in the ATV/r arm – Switching patients with virologic suppression on LPV/r to once-daily ATV/r can provide an effective and well-tolerated treatment option ATAZIP Mallolas J, JAIDS 2009;51:29-36



![[Share-My-Toys Membership] Marketing Plan](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005475303_1-5c5fcecf250fc9c92c1a18cc8f242409-300x300.png)





