Emerging Concepts in the
Workup of Polycythemia and
Thrombocythemia: JAK2
APMG Pathologist, MD FCAP
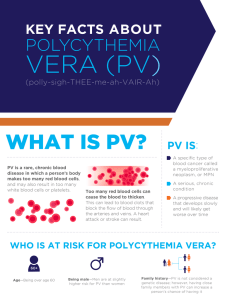
Clinical Question
• HGB over 18.5 in ♂ or 16.5 in
♀?
• Platelets over 1 million?
Are the hematologic abnormalities
reactive or the result of an
underlying neoplastic process?
JAK-STAT Pathway
• Cell signaling pathway
• Allows extracellular
chemicals to effect
nuclear DNA
expression
• Erythropoietin signals
through the JAK-STAT
pathway.
JAK2
• In Spring 2005, four separate groups independently
published discovery of a point mutation (V617F) in the
JAK2 gene of patients with the PV and ET
• Subsequent studies have identified JAK2 mutations as
key molecular events in development of the
myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs)
Incidence of JAK2 Mutation in MPNs
Polycythemia vera (PV)
99%
Essential thrombocythemia (ET)
60%
Primary myelofibrosis (PMF)
40%
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML)
<1%
JAK2: wild-type and mutant
EPO
No signal
Signal
Campbell P, N Engl J Med 2006, 355:2452-2466.
Signal
Clinical Dilemma
• HGB over 18.5 in
♂ or 15.5 in ♀?
JAK2
Testing
– JAK2 abnormal in 99% of PV
• Platelets over 1 million?
– 85% are not Essential Thrombocytosis (ET)
– JAK2 abnormal in 60% of ET
Detection of JAK2 means neoplastic process.
JAK2
Testing
Mutations
• Most common mutation is V617F
– Substitutes a phenylalanine for valine at codon 617
• Other JAK2 exon 12 mutations (not V617F)
– Found in PV that does not have V617F
– Thus nearly 100% PV have some JAK2 abnormality
• ET and CIMF can also have MPL mutations
– Found in up to 5%
– Not seen in PV
Polycythemia vera: WHO 2008
Diagnosis requires meeting both major criteria and one minor criterion OR
the first major criterion and two minor criteria.
Major criteria
1. Hemoglobin > 18.5 g/dL in men, 16.5 g/dL in women or other evidence
of increased red cell volume.*
2. Presence of JAK2V617F or other functionally similar mutation such as
JAK2 exon 12 mutation.
Minor criteria
1. Bone marrow biopsy showing hypercellularity for age with trilineage
growth (panmyelosis) with prominent erythroid, granulocytic, and
megakaryocytic proliferation.
2. Serum erythropoietin level below the reference range for normal.
3. Endogenous erythroid colony formation in vitro.
*Hemoglobin or hematocrit > 99th percentile of method-specific reference range for age, sex, and altitude of
residence; or hemo- globin > 17 g/dL in men, 15 g/dL in women if associated with a documented and
sustained increase of at least 2 g/dL from an individual’s baseline value that cannot be attributed to correction
of iron deficiency; or elevated red cell mass > 25% above mean normal predicted value.
PV Dx Algorithm
*Clinical clues for PV include splenomegaly,
thrombosis, aquagenic pruritus, and
erythromelalgia. Laboratory clues for PV
include thrombocytosis, leukocytosis, and
increased leukocyte alkaline phosphatase
score. Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) screening is to
detect the V617F mutation that occurs in
most patients with PV.
Essential Thrombocythemia:
WHO 2008
Diagnosis requires meeting all four criteria.
1.Sustained* platelet count ≥ 450 × 109/L.
2.Bone marrow biopsy specimen showing proliferation mainly of the
megakaryocytic lineage with increased numbers of enlarged, mature
megakaryocytes. No signi- ficant increase or left-shift of neutrophil
granulopoiesis or erythropoiesis.
3.Not meeting WHO criteria for polycythemia vera,† primary myelofibrosis,‡
BCR-ABL1–positive chronic myelogenous leukemia,§ or myelodysplastic
syndrome¶ or other myeloid neoplasms.
4.Demonstration of JAK2V617F or other clonal marker, or in the absence of
JAK2V617F, no evidence for reactive thrombocytosis.**
*Sustained during the workup process.
†Requires the failure of iron replacement therapy to increase hemoglobin level to the polycythemia vera range in the presence of decreased serum
ferritin. Exclusion of polycythemia vera is based on hemoglobin and hematocrit levels, and red cell mass measure- ment is not required.
‡Requires the absence of relevant reticulin fibrosis, collagen fibrosis, peripheral blood leukoerythroblastosis, or markedly hypercellular marrow
accompanied by megakaryocyte morphology that is typical for primary myelofibrosis (small to large megakaryocytes with an aberrant
nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio and hyperchromatic, bulbous, or irregularly folded nuclei and dense clustering). §Requires the absence of BCR-ABL1.
¶Requires the absence of dyserythropoiesis and dysgranulopoiesis. **Causes of reactive thrombocytosis include iron deficiency, splenectomy,
surgery, infection, inflammation, connective tissue disease, metastatic cancer, and lymphoproliferative disorders. However, the presence of a
condition associated with reactive thrombocytosis does not exclude the possibility of essential thrombocythemia if the first three criteria are met.
ET Diagnostic
Algorithm
*In addition to clinical history, laboratory tests that are helpful in distinguishing reactive
thrombocytosis from ET include serum ferritin, peripheral blood smear, and C-reactive
protein.
JAK2 Testing
• JAK2 V617F Detection
– Performed on peripheral blood or bone marrow
– Highly sensitive and specific assays
– Should be performed in CAP Accredited lab
• JAK2 Exon 12 Mutation Analaysis
– Used when suspect PV but V617F not detected
Quantification of JAK2?
diagnosis
“clinical/hematologic/
prognostic correlates”
monitoring
• Detection is sufficient.
• Quantification not
necessary
• Controversial
• Response to therapy
• Utility not well
defined clinically
Questions
• Contact pathologist with questions or to sort
out appropriate testing on a patient:
APMG Pathologist, MD FCAP
tlpath@domain.com
(888) 555-1212