Document
advertisement

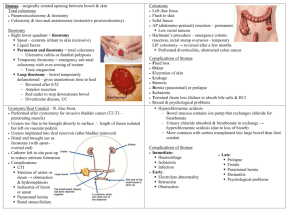
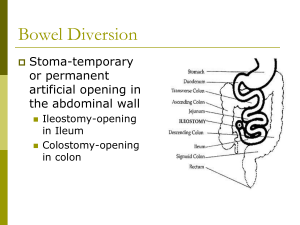
Abdominal cases for SURGICAL FINALS Dr. Anika Kaura & Dr. Upama Banerjee Approach to the surgical abdomen Surgeons want it SHORT and SIMPLE Use your normal schema for examination but be prepared to be INTERRUPTED! And to move on quickly from one aspect of examination to another Don’t bore them with all the negatives! Mention the positives and only a few RELEVANT negatives E.g. I have examined the abdominal system of this gentleman who did not complain of any pain. The most obvious finding was a well healed rooftop incision. There were no peripheral stigmata nor abdominal masses on palpation and bowel sounds were present Scars Abdo Scars Kochers Gable/Rooftop – join up R subcostal and L LANZ GRIDIRON/Mcburneys incision Loin Vascular scars Pfannenstiels STOMAS “surgically created communication between the bowel and the skin” OPTIONS : ileostomy / colostomy / ileal conduit EXAMINATION Site of the bag Contents- liquid/solid Output Bowel flush/spouted Bowel healthy? Feel for parastoma hernias Offer to digitate the stoma ALWAYS OFFET TO INSEPCT PERINEUM FOR AN ANUS!!! Beware of drain bags appearing like stoma bags Stoma complications EARLY LATE • Haemorrhage at site •Obstruction •High output •Dermatitis •Stoma ischaemia •Intussusception •Stoma retraction •Prolapse •Obstruction secondary •Parastomal hernias to adhesions •Stenosis •Fisutlae •Psychological •Failure/re-positioning STOMA summary 3 Ss and 3 Cs Site Size Skin Contents Condition- of stoma, and for which they have it Complications Important to know about stoma care and role of stoma nurses, especially psychological impact Which operation?! Cancers… Right hemi-colectomy Extended right hemi-colectomy Sigmoid-colectomy Left hemi-colectomy (rarely transverse colectomy) Which operation?! Cancers… Rectal cancers: HIGH ANTERIOR RESECTION OR LOW ABDOMINOPERINEAL RESECTION Ulcerative Colitis Pan Procto-colectomy Subtotal colectomy + rectal treatment J POUCH FORMATION (ileo-anal pouch) Perforated Diverticula Hartmans What to consider o/e SCAR RIGHT/LEFT STOMAS MUST ASK TO EXAMINE THE PERINEUM Ileostomy ANUS? ANTERIOR RESECTION NO ANUS? END ILEOSTOMY Ileostomy ANUS? ANTERIOR RESECTION HIGH RECTAL CANCER RESECTION NO ANUS? END ILEOSTOMY PANPROCTOCOLECTOMY Colostomy ANUS? HARTMANS NO ANUS? ABDOMINOPERINEAL RESECTION Colostomy ANUS? HARTMANS NO ANUS? ABDOMINOPERINEAL RESECTION PERFORATED DIVERTICULA LOW RECTAL CANCER CASE 1 Present the findings Get ready for some viva questions What do you want to know about the stoma?? Single lumen Bowel flush with the skin Solid contents Anus present No excoriations/parastomal hernia Questions Differential for midline laparotomy and left sided stoma Hartmanns- sigmoid colectomy and end colsotomy (reversible) Anterior resection with reversible end colostomy (unlikely as elective so primary anastamosis) Abdomino perineal resection- permanent end colostomy and NO anus Loop colostomy- two lumens- either to defunction distal bowel (rare) or as palliative measure for distal Ca Could always be ILEOSTOMY but just in a funny place! Hartmanns procedure EMERGENCY PROCEDURE Sigmoid colectomy with end colostomy (reversible) Usual indications: acute diverticulits especially perf! And acute obstructing sigmoid Ca Diverticulitis Outpouchings of mucosa through the bowel wall Diverticulae/diverticulosis/diverticulits Complications: diverticulitis, large PR Bleeds, perforation, abscess, fistulae, strictures leading to obstruction. Investigations: basic to complicated: bloods, AXR, colonoscopy if well NOT if risk of perf, CT in acute Diverticulitis ACUTE Mx Nil by mouth IV fluids Analgesia ABx- cef and met Most managed conservatively +/- elective sigmoid colectomy Emergency surgery for perf/not improving ---- Hartmanns --- most will not have colostomy reversed! Hernias Scar related Groin - shorts v.common Complications of hernias Groin lumps – hernias – How to dd a femoral vs inguinal – More likely be to a inguinal hernia Why? ABOVE & MEDIAL = INGUINAL BELOW & LATERAL = FEMORAL Inguinal Hernias Inguinal anatomy! Scrotal mass cannot get above it Dd in the exam by occluding the deep ring Hernias ASIS Pubic tubercle What is this called? What lies here? ASIS Pubic Symphysis What is this called? What lies here? Definitive Operative Hesselbachs triangle Lichenstein tension free mesh repair Gold standard still open Hesselbachs triangle: CASE 2 Present the findings Get ready for some viva questions What do you want to know about the fisutlae? old/ current?? Venepuncture marks Palpable thrill Audible murmur multiple.--- prev failure of fistula Thinks about complications The renal transplant patient Approach to examination LOADS of signs and clues! - Iliac fossa scar and mass – uni/bilat - Nephrectomy scars?? - Previous renal replacement Tx- old AV fistulae, HD scars in neck, PD scars abdo - Immunosuppresion SEs- cushingoid features, gum hypertrophy, BCC/SCC - Evidence of underlying renal disease- diabetic? etc PRESENTATION Example “I have just examine the abdominal system of this lady. The most obvious finding is scar in the RIF with a mass beneath consistent with a renal transplant without nephrectomy. She has an old AV fistula in the right arm and I can see well healed PD scars on the abdomen, indicating previous methods of renal replacement therapy. I notice some cushingoid features including striae and bruising on her legs. The transplant appears to still be working as the patient is euvolaemic and not uraemic; and there is no evidence of other current renal replacement therapy.” COMPLICATIONS of transplant REJECTION- hyperacute/acute/chronic IMMUNOSUPPRESION - increase opportunistic infection PCP CMV - increase risk of skin malignancies - PTLD TOXICITY OF IMMUNOSUPPRESANTS - hepato and nephrotoxic - cushings disease - ciclopsorin- gum hypertrophy COMPLICATIONS of transplant VASCULAR- thrombosis, RAS Hypertension and increased risk of CV disease URINARY- UTIs and vesicoureteric reflux Chronic graft dysfunction +/- post transplant nephrectomy Recurrence of the original disease Psychological COMPLICATIONS of haemodialysis FLUID BLANCE Hypotension vs pulmonary oedema Hypokalaemia Disequilibirum syndrome- cerebral oedema Aluminium toxicity Infection from vascular access Stenosis/thrombosis of access site Dialysis related amyloid AA Complications of av fistula Failure to mature Stenosis/thrombosis Aneurysm/pseudoaneurysm Infection Venous hypertension Steal phenomenon- distal tissue ischaemia High output CF Ishcaemic monomelic neuropathy Urology - haematauria Vascular scars Other topics to revise that we have touched on! Bowel caner: screening programme, Dukes post op histology vs staging and grading Different types of anastomsis, anastomitc leaks, complcations of a colectomy Indications for dialysis; nephrectomy CAPD and HD via tesio THE END PLEASE DO THE FEEDBACK FORMS! QUESTIONS?? ANIKA- ak8009@ic.ac.uk UPI- ub06@ic.ac.uk