San Jose State University School of Nursing Spring 2008
advertisement

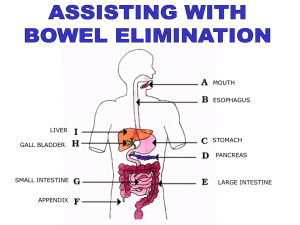
1 SAN JOSE STATE UNIVERSITY School of Nursing Nursing 155 Ostomy Care KEY Independent Learning Activities Learning Outcomes Bowel Diversions 1. List two indications for each of the following types of bowel diversions: ileostomy, loop colostomy, transverse colostomy, double-barreled colostomy, and sigmoid colostomy. 2. Differentiate among characteristics of the following types of bowel diversions: ileostomy, ascending colostomy, transverse colostomy, descending colostomy, and sigmoid colostomy. 3. Identify anatomical locations for each of the following types of bowel diversions: ileostomy, ascending colostomy, transverse colostomy, descending colostomy, and sigmoid colostomy. 4. Define loop colostomy and double-barrel colostomy. 5. List three potential complications specific to a client with a bowel diversion and nursing interventions to prevent them. 6. List two nursing diagnoses specific to a client who has had bowel diversion surgery and 3 nursing interventions for each diagnosis. 7. List four factors to include when assessing a stoma. 8. State four characteristics of an effective pouching system for an incontinent bowel diversion. 9. List four factors to consider when choosing an appropriate pouching system for an incontinent bowel diversion. 10. Describe why it is important that an ostomy appliance fit correctly. 11. Describe the difference between a 1-piece and a 2-piece pouching system. 12. Describe the purpose of colostomy irrigation. 13. Determine the types of colostomies for which irrigation is appropriate. 14. State the reason for the use of a cone appliance for colostomy irrigation, rather than a standard enema kit. 15. List at least 6 foods in each of the following categories that have potential to cause problems for the client with an ostomy: odor producing foods, gas forming foods, diarrhea causing foods, and foods that can obstruct an ileostomy. 16. Identify fluid requirements for a client with an ostomy. Urinary Diversions 17. List five indications for a urinary diversion. 18. Distinguish among characteristics of the following urinary diversions: ileal loop (conduit), cutaneous ureterostomy, nephrostomy, and continent reservoir. 19. List three potential complications of a urinary diversion and nursing interventions to prevent them. 20. List two nursing diagnoses specific to a client who has had urinary diversion surgery and 3 nursing interventions for each diagnosis. N155: Ostomy care key 2 Learning Activities Bowel Diversions 1. List 2 indications for each of the following types of bowel diversions. The same indications may be appropriate for more than one type of diversion. a. Ileostomy 1. ulcerative colitis 2. Crohn’s disease 3. familial polyposis 4. birth defect 5. trauma 6. cancer 7. diseased or injured colon b. Loop colostomy 1. usually temporary to rest the bowel after a resection for bowel obstruction, or in an emergency such as a gunshot wound, or perforated diverticulum. Usually located in the transverse colon. 2. On occasion, may be permanent. c. Transverse colostomy 1. usually temporary to rest the bowel after a resection for bowel obstruction, or in an emergency such as a gunshot wound, or perforated diverticulum. 2. On occasion, may be permanent. d. Double-barreled colostomy 1. usually temporary to rest the bowel after a resection for bowel obstruction, or in an emergency such as a gunshot wound, or perforated diverticulum. 2. On occasion, may be permanent. e. Sigmoid colostomy 1. cancer of the rectum 2. perforating diverticulum 3. trauma N155: Ostomy care key 3 2. Fill in the following table Stool Characteristics Temporary Or Permanent? Ileostomy Liquid to semi-liquid Usually permanent treatment for ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, birth defect, trauma, cancer, familial polyposis, diseased or injured colon Yes No Ascending colostomy Semiliquid Perforating diverticulitis in lower colon; trauma; inoperable tumors of colon, rectum, or pelvis; rectovaginal fistula Yes No Transverse colostomy Semiliquid to semiformed Same as for ascending; birth defect Yes Not usually Descending colostomy Formed Cancer of the rectum or rectosigmoidal area; perforating diverticulum; trauma Depends on bowel regulation Yes Sigmoid colostomy Formed Cancer of the rectum or rectosigmoidal area; perforating diverticulum; trauma Depends on bowel regulation Yes Type Of Diversion N155: Ostomy care key Requires A Pouch? Bowel Control? 4 3. Draw circles on the diagram indicating the usual locations for each of the following bowel diversions: Label each circle. Transverse colostomy Descending colostomy Ascending colostomy Ileostomy Sigmoid colostomy 4. Write a brief definition of each of the following: a. Loop colostomy A loop stoma is constructed by bringing a loop of bowel to the abdominal surface and then opening the anterior wall of the bowel. This results in one stoma with a proximal and distal opening. The loop of bowel is often held in place with a plastic rod to keep the bowel from slipping back into the abdominal cavity. c. Double-barreled colostomy When the bowel is divided, both the proximal and distal ends are brought through the abdominal wall as two separate stomas. The proximal stoma is the functioning one; the distal stoma is nonfunctioning and is referred to as a mucus fistula. 5. What are 3 potential complications specific to a client who has had a bowel diversion, and nursing interventions to prevent each complication? a. breakdown of the stoma or peristomal skin prevention: assess peristomal skin for redness, burning ,itching ,breakdown, poorly fitting pouch, leakage, lack of adequate skin care, absence of skin barrier; clean area with warm water, dry thoroughly; apply skin barrier; teach client proper kin and pouch care; plan follow up care after discharge; empty pouch when it is 1/3 to 1/2 full or inflated w/gas. b. fluid and electrolyte imbalance from fluid loss prevention: assess for signs/symptoms of dehydration; record I&O, including drainage if liquid; ensure fluid intake of at least 3000ml/day; teach client to maintain high fluid intake [unless contraindicated] and to increase fluids during hot weather; monitor serum electrolytes; teach client signs and symptoms of sodium, potassium and fluid deficit. N155: Ostomy care key 5 c. nutritional deficit prevention: assess nutritional intake; gradually introduce foods; teach client to chew food slowly and thoroughly; provide list of foods that can cause problem, e.g. obstruction; refer with dietitian 6. List 2 nursing diagnoses specific to a client who has had bowel diversion surgery and 3 nursing interventions for each diagnosis. a. risk for impaired skin integrity r/t irritation from fecal drainage, the pouch, and lack of knowledge of skin care Interventions -enterostomal therapist consult -assess stoma and peristomal skin for irritation and skin breakdown -provide appropriate skin care -apply skin barrier -teach pt proper skin care and pouch care -plan for outpatient and home care -empty pouch when it’s 1/3 full b. body image disturbance r/t presence of stoma and malodor Interventions -assess pt’s attitude -instruct pt on measures for odor control -teach pt to wear loose clothing -discuss normal emotional response to stoma -encourage family members to participate -provide pt with information about United Ostomy Association -prepare pt to do own stoma and pouch care c. altered nutrition, less than body requirements, r/t lack of knowledge of appropriate foods and decrease weight loss Interventions -assess nutritional intake -gradually introduce foods one at a time; begin w/low residue diet -teach pt to chew food slowly and thoroughly -give pt list of foods to avoid -arrange dietician consult prn N155: Ostomy care key 6 d. altered sexuality patterns r/t perceived loss of sexual appeal and possibility of accidental leaking of fecal material Interventions -assess pt’s attitude about impact of ostomy on sexual functioning -encourage discussion of meaning of sexuality to pt and significant other -discuss ways to avoid leaking pouch and ways to conceal stoma -prn, arrange visit with person of same sex and condition to discuss issues of sexuality e. risk for fluid volume deficit r/t excess fluid loss from ileostomy or diarrhea w/colostomy Interventions -assess for s/sx dehydration -record I&O, including ileostomy drainage -ensure fluid intake of at least 3000 ml/day -instruct pt to maintain high fluid intake -monitor serum electrolytes -instruct pt on signs of Na+, K+, and fluid loss 7. What are 4 factors to include when assessing the condition of a bowel diversion stoma? (Elkin, et. al. Pp 795) a. size: use a stoma measuring card to determine the correct size. b. shape: if the stoma is round, the pre-cut stoma measuring cards can be used to determine the size of the pouch opening. If the stoma is irregularly shaped, the pouch will likely need to be hand cut to match the shape of the stoma. c. color of the stoma: should be pink or bright red. Dark red, dusky blue, or black indicate problems. d. effluent: determine the amount and consistency of fecal drainage. Also assess the following: a. type: flush to the skin or protruding b. edema: the stoma will be edematous after surgery. The edema will subside and the stoma will shrink over time. c. bleeding: a small amount of bleeding is normal because the bowel is quite vascular. d. surrounding skin. 8. What are 4 characteristics of an effective pouching system for a bowel diversion? a. protects the skin b. contains fecal material N155: Ostomy care key 7 c. remains odor free d. is comfortable and inconspicuous 9. What are 4 factors to consider when choosing an appropriate pouching system for an incontinent bowel diversion? a. location of the ostomy b. type and size of the stoma c. type and amount of ostomy drainage d. size and contour of the abdomen e. condition of the skin around the stoma f. physical activities of the pt g. client’s personal preference, age, and dexterity h. cost of the equipment 10. Why is it important that an ostomy appliance fit correctly? If it’s too big for the stoma, drainage from the stoma will irritate the surrounding skin. If it’s too small, it may constrict the stoma and cause irritation of the stoma or ischemia. 11. Briefly describe how a 1-piece pouching system is different from a 2-piece pouching system. 1-piece system: the skin barrier portion is attached to the pouch. When the pouch is changed, the entire system is changed. 2-piece system: the skin barrier is separate from the pouch. The pouch can be detached from the barrier, and changed without disrupting the skin barrier. 12. What is the purpose of a colostomy irrigation? To establish a pattern of regular defecation, to treat constipation, or prepare bowel for surgery. Irrigation is used only with descending and sigmoid colostomies. 13. From the list, circle the bowel diversions that are appropriate for irrigation. Ileostomy Descending colostomy Cutaneous ureterostomy Sigmoid colostomy Ascending colostomy N155: Ostomy care key 8 14. When a colostomy is irrigated, why is a cone adapter used, rather than a standard enema kit? A standard enema kit should never be used to irrigate a colostomy. The pointed tip can potentially injure or perforate the bowel. A cone adapter is used to obtain a leak-proof fit when the enema is administered. The stoma has no sphincters, therefore the pt cannot willfully retain the fluid. The cone adapter prevents premature loss of the enema solution. 15. List at least List 6 foods in each of the following categories that have potential to cause problems for the client with an ostomy: Odor-producing foods Eggs, garlic, onions, fish, asparagus, cabbage, broccoli, alcohol Gas forming foods Beans, cabbage family, onions, beer, carbonated beverages, cheeses (strong), sprouts Diarrhea causing foods Alcohol, beer, cabbage family, spinach,, green beans, coffee, spicy foods, raw fruits Foods that can potentially obstruct an ileostomy Nuts, raisins, popcorn, seeds, raw vegetables, celery, corn 16. Identify fluid requirements for a client with an ostomy. Clients with an ostomy should take in 3000ml/day of fluid [unless contraindicated] to compensate for fluid lost via the ostomy. The client should drink more than this on hot days, or when they perspire more. Urinary Diversions 17. What are 5 indications for a urinary diversion? a. cancer of the bladder b. radiation injury to the bladder c. fistulas d. trauma to the bladder e. chronic infections with deterioration of renal function f. neurogenic bladder g. congenital anomalies h. strictures N155: Ostomy care key 9 18. Fill in the table. Type of urinary diversion Continent or Incontinent Urine Characteristics Drains Continuously? Needs catheterization? Requires a pouch? Ileal conduit (loop) Incontinent Mucus in the urine from the ileum Yes No Yes Cutaneous ureterostomy Incontinent Normal urine Yes No Yes Nephrostomy Incontinent Normal urine Yes No Yes Continent reservoir Mucus in the urine No Yes No Continent 19. What are 3 potential complications of a urinary diversion and nursing interventions to prevent them? a. thrombophlebitis: there is an increased incidence after pelvic surgery Interventions -sequential compression devices -TED hose when ambulating -ambulation ASAP after surgery -foot and leg exercises when in bed -prophylactic heparin or enoxaparin b. paralytic ileus: there is an increased incidence after surgery involving the bowel Interventions -assessment of bowel sounds, abdominal distention -proper NG tube care and maintenance -monitoring of use of narcotic analgesics -maintain fluid and electrolyte balance through appropriate use of IV fluids and potassium replacement c. small bowel obstruction: there is an increased incidence after surgery involving the bowel Interventions -assessment of bowel sounds, abdominal distention -proper NG tube care and maintenance -monitoring of use of narcotic analgesics -maintain fluid and electrolyte balance through appropriate use of IV fluids and potassium replacement N155: Ostomy care key 10 d. peristomal skin irritations from alkaline encrustations, yeast infections, irritation from appliances, product allergies Interventions -acidify the urine -ensure proper fit of appliances -ensure meticulous care of the skin surrounding the stoma and that products appropriate for the client are used 20. List 2 nursing diagnoses specific to a client who has had urinary diversion surgery and 3 nursing interventions for each diagnosis. a. Nursing diagnosis: anxiety r/t to effect of diversion on lifestyle and relationships Interventions -instruct pt in preop, operative, and postop procedures; diet, medications, NG tubes, IVs, NPO status, pain management, turning, deep breathing, and leg exercises -demonstrate how to apply appliance if appropriate, and use equipment -answer questions honestly and provide emotional support -arrange for visit with person who has had urinary diversion surgery b. Nursing diagnosis: risk for UTI r/t surgical procedure, ureteral obstruction, chronic use of external appliance or self-catheterization, incorrect or inadequate stoma care. Interventions -assess VS, especially temperature, back pain or abdominal pain, bloody or cloudy urine, decreased urinary output -empty appliance q2-3 hours or when 1/3 full -catheterize at appropriate intervals -instruct pt about symptoms to be reported -encourage high fluid intake c. body image disturbance r/t effects of change in body function Interventions -encourage pt to share feelings demonstrate willingness to listen and answer questions -provide information about surgery and expected effects -determine the need for additional support -encourage gradual involvement in self-care N155: Ostomy care key 11 d. ineffective management of therapeutic regimen r/t lack of knowledge regarding stoma and appliance care Interventions -demonstrate proper method of changing stoma bag and have pt give return demonstration -teach measures such as high fluid intake, regular activity, and urine acidification -teach practices such as proper stoma and pouch care, or proper catheterization technique e. risk for impaired skin integrity r/t ill-fitting appliance, inadequate hygiene, and lack of knowledge regarding stoma care Interventions -assess for improperly fitted appliance and reddened and irritated skin around stoma -check appliance position, if appropriate -cleanse stoma as ordered -allow no tight clothing or binders over stoma f. risk for altered sexuality patterns r/t perceived or actual effects of surgery on sexual activity Interventions -assess patient’s concerns related to sexuality -provide accurate information related to sexual activity -inform female pt about water-based vaginal lubricant for intercourse N155: Ostomy care key