InterFacility STEMI Transfers-1.19.2011
advertisement
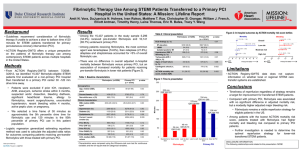
Interfacility Transfers: The Joker’s Wild of STEMI Care Systems January 19, 2011 Dr. Peter O’Brien, Centra Health, Lynchburg Dr. Michael Kontos, VCU, Richmond Dr. David Burt, UVa, Charlottesville Part I: STEMI Transfers: The Jokers WILD Pete O’Brien VHAC Part II: STEMI Fireside Chat Dr. Pete O’Brien Dr. Mike Kontos Dr. David R Burt Drs. Burt, Kontos, and O’Brien: Nothing to Disclose The Big Picture NATIONALLY… Provider of: STEMI System Science, Resources, Collaboration … 5 MISSION: LIFELINE Mission: Lifeline is the American Heart Association’s national initiative to advance the systems of care for patients with ST- segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). The overarching goal of the initiative is to reduce mortality and morbidity for STEMI patients to and improve their overall quality of care 4/13/2015 ©2010, American Heart Association 6 ….In Virginia … www.virginiaheartattackcoalition.org The Virginia Heart Attack Coalition (VHAC) is a volunteer collaboration dedicated to improving care of heart attack patients throughout Virginia via the implementation and promotion of Mission: Lifeline guidelines and by fostering cooperation and coordination among the Commonwealth's STEMI care providers. Patient Care….Not Market Share 8 System Delay and Mortality in STEMI Patients 35 Same old Story! 30 30.8 28.1 25 23.3 20 Mortality, % 15 15.4 10 5 0 0 to 60 min 61 to 120 min Terkelsen CJ JAMA 2010;304:763-771 121 to 180 min 181 to 360 min Interhospital Transfer for PCI Mortality (%) 20 On-site fibrinolysis Transfer for PCI 14 15 12.1 10 6.7 6.7 7 8.4 10 8.5 6.8 6.5 5 0 LIMI1 PRAGUE-12 AIR-PAMI3 PRAGUE-24 DANAMI5 (n=150) (n=200) (n=137) 1. Vermeer F, et al. Heart . 1999;82:426-431. 2. Widimsky P, et al. Eur Heart J. 2000;21:823-831. 3. Grines CL, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;39:1713-1719. 4. Widimsky P, et al. Eur Heart J. 2003;24:94-104. 5. Andersen HR, et al. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:733-742. (n=850) (n=1129) 10 AHA : System Goals FIRST MEDICAL CONTACT DOOR To NEEDLE : Fibrinolytics OR DOOR IN 2 DOOR OUT DOOR To BALLOON Primary PCI EMS To BALLOON Primary PCI 60 4/13/2015 30 90 90 MINUTES MINUTES MINUTES 11 Point Of Entry Protocol : GOAL Less than 90 Minutes Improving the System of Care for STEMI 12 Patients LET’S TAKE A CLOSER LOOK 4/13/2015 13 JOKER runs Amok!! Riddle me this Batman!! • EMS and Self-Driven/Emergent Triage Decisions, Bypass? • Referral Facility Recognition, System Activation • Lytic Administration -OR- Transfer for PCI – Drip, Ship, or Drip and Ship??? • Interfacility Transport - Ground, Air • Receiving Facility – “Automatic” Acceptance, One Call Activation, Direct to Cath lab, Stop in ED • System Optimization and Feedback, multiple EMS agencies, providers, institutions, etc Point of Entry Protocol Hospital w/o PCI PCI center Hospital w/o PCI Improving the System of Care for STEMI Patients WHY IS THIS AN ISSUE 4/13/2015 ©2010, American Heart Association 16 INHERENT CHALLENGES 44 4/13/2015 ©2010, American Heart Association 17 ACTION REGISTRY DATA 4/13/2015 National ARG Data and GWTG 18 Recommendations for Triage and Transfer for PCI (for STEMI) Each community should develop a STEMI system of care following the standards developed for Mission Lifeline including: NEW Recommendation I IIa IIb III • Ongoing multidisciplinary team meetings with EMS, non-PCIcapable hospitals (STEMI Referral Centers), & PCI-capable hospitals (STEMI Receiving Centers) 19 Recommendations for Triage and Transfer for PCI (for STEMI) (cont.) NEW Recommendation I IIa IIb III STEMI system of care standards in communities should also include: • Process for prehospital identification & activation • Destination protocols to STEMI Receiving Centers • Transfer protocols for patients who arrive at STEMI Referral Centers and are primary PCI candidates, and/or are fibrinolytic ineligible and/or in cardiogenic shock 20 AHA: STEMI System Blueprints Mission: Lifeline Recommendations for Criteria for STEMI Systems of Care The criteria are divided into: • EMS • Non-PCI Hospital/STEMI Referral Center • PCI Hospital/STEMI Receiving Center • Systems Improving the System of Care for STEMI Patients The Ideal EMS Agency • EMS equipped with 12 Lead capability • EMS educated to recognize STEMI • Prearranged transport destination protocols – By Pass Non-PCI – PCI – Fibrinolytic Checklist • EMS utilization for Interfacility Transfers • Cath Lab Activated on Paramedic Interpretation – On paramedic’s description /interpretation – With or Without EKG Transmission • EMS actively attends Multidisciplinary Meetings • EMS involvement at a state level The Ideal STEMI-Referral Hospital • In an ideal system: • Standardized POE protocols dictate transport of STEMI patients directly to a STEMI-receiving hospital based on: – Patients presenting to a STEMI-referral hospital are treated according to standardized triage and transfer protocols – Incentives are provided to rapidly: • Treat STEMI patients in accordance with ACC/AHA guidelines • Transfer to a STEMI-receiving hospital for primary PCI using: – Reperfusion checklists – Standard pharmacological regimens and order sets – Clinical pathways – There is rapid and efficient data transfer, data collection and feedback – Integrated plans for return of the patient to the community for care are provided Improving the System of Care for STEMI 23 Patients CODE STEMI TRANSFER FLOW SHEET Patient enroute to ED by EMS Field ECG indicates STEMI Patient arrived to ED by POV ED ECG Indicates STEMI Initiate Interfacility Transport Plan Treat STEMI per regional protocols EMS Patient Arrives to Referral ED Assess Patient Transfer upon transport arrival INTERFACILITY TRANSPORT PLAN: COUNTY 911 SERVICE (843-911-1111) PRIVATE GROUND SERVICE (843-991-2222) AIR SERVICE (843-991-3333) LAST RESORT (843-991-4444) 4/13/2015 ETA:________________ ETA:________________ ETA:________________ ETA:________________ ©2010, American Heart Association 24 Time Savers aka Best Practices for Referral Facilities GOAL : Door In to Door Out = 30 MINUTES GOAL : Arrival to ECG < 10 Mins Do Not Delay transport team Do not wait on lab results FAX Patient Care Record Call Report after patient leaves Non-PCI KNOW the STEMI Protocol 4/13/2015 ©2010, American Heart Association 25 TIME SAVERS aka BEST PRACTICES for Transport Turn off all drips (Administer NTG via SL or NTG Paste) NTG and Heparin drips are not required * Minimize time at Bedside (~10 Minutes – Standard scene time for trauma) TIME IS NOT ON YOUR SIDE Do not delay transport waiting on patient care records : FAX * For short distances (not defined) 4/13/2015 ©2010, American Heart Association 26 Collaborative Initiatives • Participate in Drafting of UNIVERSAL interfacility transport practice standard – – – – Pre-Determined Transport Decision Scheme Patient Care in ED Patient Care during transport NO DRIPS • Early activation of the Code STEMI – Provides update – Lytics given or not? – More prep time allows the patient to be taken directly to cath lab Improving the System of Care for STEMI Patients Ideal STEMI-Receiving Hospital • STEMI protocols adopted and followed to include single call activation. – Criteria for EMS activation. • 24/7 coverage with expectation that Primary PCI is the standard reperfusion strategy • ED activation of cath lab • Volume/Quality standards • CCL staff/MD to report in 30 minutes or less • Universal Acceptance—No Diversion!! Ideal Receiving Cont’d • STEMI-receiving hospital’s administration puts their support in writing (AHA Memorandum of Understanding..MOU) • Lead multidisciplinary/multiagency team meeting to regularly identify processes done well and to collaboratively fix those that need improvement • A continuing education program is designed and instituted • A consistent mechanism for monitoring performance, process measures and patient outcomes is established—ACTION REGISTRY/GWTG Improving the System of Care for STEMI Patients SAMPLE ML Report from Action Registry 4/13/2015 30 Financial Sensitivities • • • • Learn local EMS resources/limitations Work as a team to address needs Offer 12 Lead STEMI identification classes Provide MD level updates on lytic admin • Feedback assures appropriate Non-PCI Facility Bypass • Goal is to get the STEMI patient back to their local community for rehab and follow up • Involve Non-Invasive Cardiologists on multiple levels 31 Mortality With 1° PCI vs Time Absolute Risk Difference in Death (%) For every 10 minutes delay in PCI-> 1% of the advantage is lost 15 Circle sizes = sample size of individual study 10 Solid line = weighted meta-regression P=.006 5 62 min Favors PCI Favors lysis 0 -5 0 20 40 60 80 100 PCI-Related Time Delay (Door-to-Balloon minus Door-to-Needle) For every 10-min delay to PCI: 1% reduction in mortality difference vs lytics. Nallamothu BK, Bates ER. Am J Cardiol. 2003;92:824-826. 32 TRANSFER-AMI: Efficacy Kaplan Meier Curves for Primary Endpoint Primary end point: composite of death, reinfarction, recurrent ischemia, new or worsening CHF, or shock within 30 days pharmaco-invasive group=11.0% vs. standard treatment group=17.2% 17.2% Cumulative Incidence 11.0% p=0.004 Days RR= 0.64, 95 CI% (0.47-0.87) Cantor et al. N Engl J Med 2009;360:26 33 Figure 1. The results of the primary outcome from contemporary randomized trials comparing a pharmacoinvasive strategy with conservative care after initiating fibrinolytic therapy. In these trials, conservative care was defined as either an ischemia-guided or a delayed invasive approach. Recommendations for Triage and Transfer for PCI (for STEMI) (cont.) NEW Recommendation I IIa IIb III It is reasonable to transfer high risk patients who receive fibrinolytic therapy as primary reperfusion therapy at a non-PCI capable facility to a PCI-capable facility as soon as possible where either PCI can be performed when needed or as a pharmacoinvasive strategy. 35 Nearest Facility ~vs~ PCI Facility Improving the System of Care for STEMI Patients Acute STEMI Protocol for Halifax Regional (for acute ST elevation MI or new LBBB) The Cardiovascular Group of Central Virginia and the Stroobants Heart Center of Centra Health 1. Notify Transport of need for emergent transfer to LGH. 2. Call 1-434-947-3098 (or 1-434-947-5252) and ask for Cardiologist on call. Please be prepared to provide via phone: • Patient’s name • Age • Weight, Height • EKG interpretation • Brief report (i.e., treatment to this point, V, medications) 3. ASA 325 mg chew and swallow 4. Plavix 300 mg 5. Lovenox 30 mg IV. 6. Lovenox 1 mg/kg sub Q (up to 100 mg.) 7. Administer IV Thrombolytic therapy (if no contraindications) 8. IV fluids TKO. 9. If full dose TNK is not given, then give Integrilin 180 mcg ug V bolus. Repeat bolus in 10 minutes. If possible, avoid drips such as IV nitroglycerin that may delay transport and time to treatment. “Code STEMI…When time equals muscle, every minute counts!” Centra Health 1/05/2010 4/13/2015 37 Lessons Learned So Far • Transfers are more complicated, but just as important to get right • EMS involvement and predetermined plans are CRITICAL • Standardized Referral Center treatment protocols. Determine Strategy: Lytic Administration vs Transfer forPCI – Time of s/s onset, patient condition, and time to PCI • Relationships between nonPCI and PCI hospitals worked out – And visited frequently • Interfacility transportation decision scheme • PCI center commitment to non-diversion and rapid system activation. • Continual performance feedback 4/13/2015 ©2010, American Heart Association 38 Part II: STEMI Fireside Chat Dr. Pete O’Brien Dr. Mike Kontos Dr. David R Burt