Therapeutic Uses
advertisement

PHARMACOLOGY OF
PARASYMPATHETIC NERVOUS
SYSTEM
Circular and ciliary muscle
of eye
III
VII
IX
Spinal cord
Cervical
Salivary and tear
glands
X
heart
Toracic
lung
superior GI tract
Lombar
Pelvic
Ganglia
inferior GI tract
Sacral
Bladder, kidney
genital
2
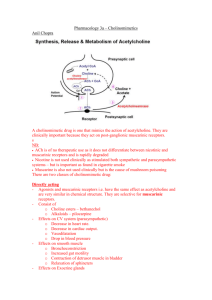
General organisation
parasympathetic nervous system
Spinal cord
Ganglia
target tissue
Muscarinic
Receptors
Acetylcholine
Acetylcholine
Nicotinic Receptors
3
General aspects of PNS
cholinergic mediator is acetylcholine
(Ach).
Acetylcholine = biogenic amine
sintetized in the body from choline and
acetylcoenzime A under the action
colinacetil-transferase
Ach released from presynaptic endings
can bind to:
cholinergic receptors → activate them
acetylcholinesteraze → inactivate Ach
4
There are two types of cholinergic
receptors :
muscarinic receptors (M)
nicotinic receptors (N)
5
HO
H3C
CH3
+N CH3
CH3
N
N
CH 3
Nicotine
tobacco
Muscarine
Amanita muscaria
6
Muscarinic Receptors
specific activated by de muscarine
(toxine from Amanita muscaria)
muscarinic receptors subtypes : M1, M2,
M3, M4, M5
localised in:
neuroefector parasympathetic synapses in
the smooth muscle
heart muscle
exocrine glands
neuroefector sympathetic synapses
in the sweat glands
and brain
7
Nicotinic Receptors :
specific activated by nicotine
nicotinic receptors subtypes :
NM receptors = muscle R / end plate R;
are located in somatic neuroefector
synapses
NN receptors = neuronal R / ganglia R;
are located in interneuronal synapses from
all ganglia of the autonomic
(parasympathetic, sympathetic) nervous
system and
medulosuprarenal
8
Localisation of Nicotinic Receptors
Spinal cord
ACh (Nicotinic)
Skeletal muscle
Somatic eferent
Simpathetic
{
ACh (Nicotinic)
Ganglia
Parasimpathetic
{
ACh (Nicotinic)
Ganglia
Noradrenaline
Blood vassels
Sweat glands
ACh (Muscarinic)
ACh (Muscarinic)
exocrin glands
s.muscles
9
Structure of muscular receptor (NM)
K+ Na + Ca 2+
a
g/e
a
Pentameric (2a,b,d,g/e)
Comutator dezvoltare g/e
A
A
b
d
2 biding sites of ACh
Receptor ~ 250 kDa
ordine agadb (abadg)
2 binding sites for Ch on
interference ag (ae) si ad
selective cationic channel
10
ACh
ACh
Acetat
+ Cholina
11
Clasification
A. Parasympathomimetics (Cholinergics,
cholinergic Agonists)
1. With direct mechanism :
a) coline esters :
naturals: Acetylcholine;
synthetics: Carbachol, Betanechol,
Metacholine
b) Alkaloids : Pilocarpine
2. With indirect mechanism
(anticholinesterases):
a) Reversible: Fizostigmine, Edrofoniu, Neostigmine,
Piridostigmine
b) Ireversible: Ecotiopat, Metrifonat, Fluostigmine,
Paraoxon, Sarin
12
B. Parasympatholitics
1. Naturales:
a) Atropine
b) Scopolamine
2. Sinthetics:
a) Pirenzepine, Telenzepine,
Propanteline, Oxifenciclimine,
Butilscopolamine
b) Homatropine, Tropicamide,
Ciclopentolat
c) Trihexifenidil
13
A. Parasympathomimetics
substances that produce similar
effects of parasympathetic stimulation
and activation of muscarinic and
nicotinic neuroeffector cholinergic
synapses
direct parasympathomimetics;
indirect parasympathomimetics
(anticholinesterases)
14
1. DIRECT PARASYMPATHOMIMETICS
Mechanism of action: agonist of
cholinergic receptors
a) choline esters prototype:
Acetylcholine,
chemical mediator of parasimpathetic,
strong agonist of muscarinic and nicotinic R
Pharmacodinamic effects:
Ach induses 2 type of effects :
muscarinics
nicotinics
15
1. DIRECT PARASYMPATHOMIMETICS
– mechanism of action
colinergic receptors – increase the
permeability of cells membrane for some ions
on excitoconductor heart tissue – increase the
permeability for K+ şi Cl- - hiperpolarisation
of membrane – decrease the heart rate (M)
On autonomic ganglia, smooth muscles (M),
skeletal muscles (N) – increase the permeability
for Na+ - depolarisation of membrane –
increases the muscles tone
On exocrine glands (sweat, salivary (M)) –
increases the permeability for Ca+ - gland
secretion
Muscarinic effects
colinergici R from the postsynaptic membrane of
the effectors cells; on small doses.
This effects are antagonised by Atropine.
a) cardiovascular system : depression
heart depression:
decreses atrial contraction force (negativ inotrop
effect)
bradicardia by depression of sinusal node (negativ
cronotrop)
decreasing of atrio-ventricular driving by depression
of A-V node and Hiss fasciculum (negativ
dromotrop)
vessels:
vasodilation (decrease BP) by releasing of NO
(nitric oxid) from endothelial cells
17
Muscarinic effects
b)
respiratory system :
bronchoconstriction
bronchial gland hypersecretion
crisis of dyspnea expiratory (in
asthmatics)
18
c) digestiv sysytem:
stimulation of g-i smooth muscle
increses of digestive glands secretion;
gastric acid hypersecretion
sphincters relaxation
stimulating bile and gall bladder
d) renal excretory system:
bladder contracts, the sphincter relaxes
e) Eye
active miosis (contraction of circular smooth
muscle of the iris)
lowers intraocular pressure (local instilation)
f) CNS stimulation
g) exocrine glands (salivary, sweat, tears):
stimulation → hypersecretion
19
1. DIRECT PARASYMPATHOMIMETICS –
mechanism of action
nicotinic receptors - coupled to
Na+/K+channels - moderately
increases of the number of Na open
channels
Binding of a large number of molecules
of Ach at nicotinic receptor blocking
sodium channels in open position
(membrane stabilization),
respectively - off the nervous
impulse.
20
2. Nicotinic effects
nicotinic R –
autonomic ganglia
and motor end plates;
high doses (experimentaly
conditions)
21
Matural esters of choline - ACETYLCHOLINE
Therapeutic Uses:
- local ophthalmology - Miochol
(acetYlcholine), eye drops 1%
- Systemic administration - TPSV
- Intracoronary - heart surgery
Contraindications
- Asthma
- Thyrotoxicosis
- Peptic Ulcers
22
Synthetic esters of choline
representatives :
Carbachol
Metacholine
Betanechol
Farmacokinetics:
cholinei esters are hydrolysed:
very rapid: Acetylcholine (not use as
medicine)
more slow: Metacholine
not hydrolised in the body (Carbachol,
Betanechol) → persistent effect
Mechanism of action: Ach-like.
23
Carbachol
Pharmacodinamic action:
muscarinic and nicotinic effects
predominant action: digestive tract, bladder and eye
(and is more persistent than Ach)
Therapeutic Uses (limited)
- as miotics - in glaucoma (local)
- stimulating s.muscle - postoperative bowel and
bladder inertia (systemic)
Side effects:
- strong gastric hypersecretion
Ex: ISOPTO CARBACHOL, sol. ophthalmic 3%.
24
Methacholine - is hydrolysed more slowly
Pharmacodynamic Action:
- predominant cardiovascular action.
Therapeutic Uses:
paroxysmal tachycardia
arteritis
Raynaud's syndrome
25
Betanechol
Pharmacodinamic action:
Only muscarinic effecte – predominantly on digestiv
and urinal system.
Relativly long action (resistant to cholinesterase)
Therapeutic use:
intestinal and vezical atonia (oral or s.c)
Side effects: relatively frequent
abdominal colic
weating
dyspnea
hTA
Contraindications: (intramuscular and i.v)
mechanic obstruction of the digestive tract or
urinary tract
Prezentation: URECHOLINE, f., cpr.
26
Pilocarpine
alkaloid from din leaf of Pilocarpus jaborandi
Pharmacodinamic action:
Muscarinic effects - predominantly:
miosis
iris circular muscle contraction - decrease in
intracellular pressure
ciliary muscle contraction - to foster close
Miosis and ciliary muscle contraction favors
increasing aqueous humor drainage
through Schlemm canal → lowers intraocular
pressure.
hypersecretion of exocrine glands (salivary
and sweat mostly)
27
Pilocarpine
Therapeutics use:
glaucoma (local conjunctival sac) takes effect
4-6 hours
irites, irido-cyclites
Atropine poisoning (in administration iv) only
antagonizes the peripheral effects. (limited to systemic
adm)
sialogog in salivary gland stones
Side effects:
pain in the eyebrows (at the beginning of treatment in
glaucoma)
may develop tolerance to the effects of eye
Prezentation:
DROPIL eye drops. 2%; ISOPTO CARPINE eye drops. 1%, 2%;
PILOGEL gel oft., ointment with nitric pilocarpin, oint. oft.
OCUSERT PILO-20, OCUSERT PILO-40 oftalmic insert (tank-type
therapeutic system with controlled local release, the effect
lasts seven days).
28
2. INDIRECT PARASYMPATHOMIMETICS –
(Anticholinesterases)
Clasification
Depending on the reversibility of action:
reversible:
Fisostigmine
Edrofoniu
Neostigmine
Piridostigmine
Ambenonium Cloride
ireversible: organo- fosfate derivatives
Ecotiophate
Metriphonate
Fluostigmine
Paraoxon
Sarin
29
2. INDIRECT
PARASYMPATHOMIMETICS –
(Anticholinesterases)
Mechanism of action:
Anticholinesterases are substances that
make a complex with
acetylcholinesterase - block (inhibit)
the hydrolyse activity on Ach.
And therefore accumulates Ach - Ach
effects occur stronger and more
prolonged
30
Reversible indirect parasimpathomimetics
Neostigmine - is a quaternary ammonium
compound
Farmacokinetics:
difficult to cross biological membranes
intestinal absorption is low and variable
oral dose is much higher than the injection (x 15)
effect during 30 min
Mechanism of action: moderate reversible block
colinesterazele
Pharmacodinamic action: Ach-like
muscarinic effect:
stimulate digestive tract motility and urinary bladder
nicotinic effect :
selective contracting striated muscle (small doses)
31
Neostigmine
Therapeutic use:
inertia intestinal and urinary retention (postoperative)
myasthenia gravis (diagnosis and treatment)
antidote for poisoning with Nondepolarizing skeletal
(type d-tubocurarine)
glaucoma (rare)
Side effects (overdose):
nausea
vomiting
salivation
bronchial hypersecretion, welders, abdominal colic
Contraindications:
asthma, Parkinson's disease
mechanical obstruction of the digestive - urinary tract;
be avoided in pregnant women.
Dosage forme: MIOSTIN tb. 15 mg, amp, 0,5‰.
32
Fizostigmine (Eserine)
Mechanism of action: moderate reversible block
cholinesterase
Pharmacodinamics action: Ach-like, predominantly:
miosis - reduces intraocular pressure, the effect is
maintained 24-48 h
Somatic stimulant nicotine effects → somatic
striated muscle contraction.
Therapeutic use:
Glaucoma - topically applied
corneal ulcer - topically applied
antidote properties on overdose anticholinergic
drugs (atropine, phenothiazines, tricyclic
antidepressants)
Side effects:
local iritation after long period of administration
Dosage forme: eye drops 0,5% şi 1% (4 - 6 x 1
33
drop/day).
Piridostigmine
has Fisostigmine- like actions,
more intense and prolonged
Therapeutic use:
postoperative bowel inertia
myasthenia gravis
Edrophonium
Acts predominantly on striated muscles
Action is short (150 sec)
Therapeutics use:
diagnostics of myastenia gravis
anticurarizant antidote (type d-tubocurarine)
34
Indirectly ireversible
parasimpathomimetic
(organofosfate derivatives)
Depending on the compound they has the
muscarinic and nicotinic action in diferent
territories
Mechanism of action:
ireversibly bind to (covalentely bonds) the
esterasic site of colinesterase (phosphorilase
the hidroxyl of serine) – block the enzime
activity
Enzyme reactivators (cholinesterase
reactivators): - Obidoxima
35
Pharmacotoxicology:
When the free colinesterazelor falls below
30% of normal - marker for poisoning by excess
accumulation of Ach in the CNS
Cholinergic crisis manifests itself:
muscarinic Symptoms
miosis
Salivary, bronchial hypersecretion
nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
bronchospasm with respiratory disorders → asphyxia,
bradycardia
hypertension then hypotension
Nicotinic Symptoms
fascicular skeletal muscle contractions, convulsions
High doses cause death by respiratory depression
36
Treatment of intoxication with
organophosphate compounds
Antidots:
Atropine i.v. 2 → 4 amp
Cholinesterase reactivators:
TOXOGONINE (obidoxima) i.v. – in first 6
hours
37
Indirectly ireversible
parasimpathomimetic (organofosfate
derivatives)
Therapeutic use:
purely local in glaucoma due to increased toxicity
Ecotiophate - pressure-lowering effect of intense
and lasting eye lasting 1-2 weeks
Sides effects:
specific cataract after prolonged treatment
with high doses.
Dosage form: eye drops 0,03 - 0,25% de 1-2x/d.
Fluostigmine – effects like ecotiophate
Duration of eye pressure lowering effect - 1
week
Dosage form: ointment, eye drops
38
Parasympatholitics
Clasification
Natural compounds
Atropine
Scopolamine
Semisynthetic and synthetic compounds
Quaternary amines indicated for the treatment of
gastrointestinal and genitourinary tract disorders
Anisotropine
Isopropamide
Clidinium
Glicopirolate
Metanteline
Propanteline
Metscopolamine
Butilscopolamine
39
Parasympatholitics
Clasification
Semisynthetic and synthetic compounds
tertiary amines indicated for the treatment of
gastrointestinal and genitourinary tract disorders
Pirenzepine
Oxifenciclimine
Oxibutinine
Tridihexetil
Tolterodine
Propiverine
quaternary amine indicated in the treatment of asthma
Ipratropium
tertiary amine indicated in the treatment of Parkinson's
disease / pseudoparkinsonism
Benztropine
40
Parasympatholitics
Clasification
Semisynthetic and synthetic compounds
indicated in the treatment of central anticholinergic drug
pseudoparkinsonismului
Biperiden
Orfenadrine
Prociclidine
Trihexifenidil
central anticholinergic indicated localized in skeletal muscle
spasm
Carisoprodol
Ciclobenzaprine
Clorzoxazone
Metaxolon
Metocarbamol
Orfenadrine, Clorfenesine
41
Parasympatholitics
Clasification
Semisynthetic and synthetic compounds
antimuscarinic used in ophthalmology to produce
mydriasis for diagnostic
Homatropine
Ciclopentolate
Tropicamide
42
Parasympatholitics
Parasimpaticoliticele are substances that oppose the effects of
Ach and muscarinic excitation of parasympathetic effects
1. Natural parasympatholitics
a) Atropine - It is an alkaloid extracted from the leaves and
roots of Atropa Belladona and other Solanaceae.
Pharmacokinetics:
is absorbed rapidly after oral administration or injection;
Diffuses well in all organs and tissues;
→ inactive metabolites hepatic metabolism;
Urinary elimination (60% Unchanged)
Mechanism of action:
Atropine in an competitiv antagonist of the Ach.
Muscarinic effects
It is bind on muscarinic cholinergic receptors, it blocks
and prevents the formation of complex R-Ach → it oppose
characteristic effects of such substances with
parasimpaticomimetic
43
Pharmacodynamic action:
a) Cardiovascular system
Low doses and normal vagal tone →
bradicardia şi hTA (poor);
Usual dose→ tachicardia;
b) Digestiv system
Decrese the salivary secretion (the most
intense action)
hiposecreţie weak stomach;
relaxes gastrointestinal smooth muscle
→antispasmodic action;
Biliare device at moderate antispasmodic
44
Pharmacodynamic action:
Renal/excretory system
diminish the tone and amplitude of ureteral
contractions and bladder smooth fibers →
moderate antispasmodic effect.
d) Respiratory system
reduces bronchial secretions;
bronchodilator effect (relaxes bronchial
muscles);
antibronhoconstrictor effect (by inhibition of
vagal component of bronchospasm);
stimulates breathing by stimulating the
bulbar respiratory center.
c)
45
c) Eye - Atropine applied topically in the
conjunctival sac and produces strong
effects:
passive mydriasis by circular fibers of
the iris paralysis;
cycloplegic = paralysis of
accommodation for near vision, the ciliary
body muscle relaxation
increased intraocular pressure
decreased tear secretion
46
f) CNS
Depending on the dose:
high doses, stimulates the CNS
(agitation, hallucinations, delirium, bulbar
paralysis and death)
usual doses of atropine in cholinergic
receptor blockade of nigro-striatal system
can restore a balance between dopamine
and Ach (favorable effect in Parkinson's
disease)
47
Therapeutic use:
preanesthesia (reduces bronchial hypersecretion induced by
some general anesthetics)
antidote in poisoning with anticholinesterase (pilocarpine and
organophosphorus)
sinus bradycardia, AV block (pacemaker);
in ophthalmology: mydriatic fundus exam and treatmentciclitelor irido
Side effects:
dry mouth
constipation
cycloplegic mydriasis, Photophobia
urinary retention
Contraindication:
closed-angle glaucoma
prostate adenoma
pyloric stenosis
48
Acute poisoning with atropine (symptoms):
mydriasis, photophobia
Tachycardia,
dysphagia, constipation
urinary retention (peripheral effect);
agitation, hallucinations, convulsions, coma (central effect)
hyperthermia
Treatment of poisoning:
Specifically: physostigmine i.v.;
Symptomatic: benzodiazepines (diazepam) during the
excitation.
Dosage form: ATROPINE SULFAT
amp. 1‰ şi 0,25‰ (s.c., i.m., i.v. slowly);
Eye drops
included in standard preparations
49
b) Scopolamine - It is an alkaloid extracted from Datura
stramonium.
Pharmacodynamic effect:
parasimpaticolitice atropine-like effects, but two times
more intense and of shorter duration,
predominant action on exocrine glands and eyes;
central effects: inhibits CNS depressant psychomotor →
low doses.
Therapeutic use:
the preanesthesia (in combination with hydromorphone,
morphine);
the motion sickness;
in Parkinson (Atropine increased as the tremor).
Dosage form: SCOPOLAMINE BROMHIDRATE
amp.; SCOPODERM TTSpatch applied
retroauricular, maintain max. 3 days, the
motion sickness.
50
2. Synthetic Parasimpatholitics - parasimpaticolitice
are drugs with selective actions
a) Gastric Anti-secretives
parasimpatholitics - use in ulcer treatment aims to reduce
excitosecretorii vagal influences
Propanteline-
is associated with antimuscarinic action
and ganglioplegic (at the intramural plexus) → inhibitory
effects of gastric and intestinal motility are more selective.
Therapeutic use:
hyperacidity gastritis;
gastric ulcer.
Side effects: atropinic-like, but lower.
Dosage form: PROPANTELINA, dg.
51
Pirenzepine
Does gastric antisecretory action intense. Selectivity for
gastric acid secretion is probably due to muscarinic M1
receptor blockade.
Therapeutic efficacy of cimetidine ulcer is close.
Therapeutic use:
peptic ulcer, reflux esophagitis, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
(high dose).
Atropinic unwanted effects are more rare than other
anticholinergics.
Dosage forme: GASTROZEPIN, tb. (de 2 x /zi).
Telenzepine
Parasympathcolitic potent gastric anti-secretoary 4-10
times Pirenzepine.
Oxifenciclimine
Atropinic like antisecretory action lasting effect (6-8
hours), relatively well tolerated.
52
Ipratropium
early asthma.
in bronchial asthma with long-term trend, producing an
increase in viscosity of bronchial secretions with bronchial
collapse.
Oxibutinine
improving bladder spasms after surgery
It is also indicated in children with meningomyelocele or
other neurological disorders urinary incontinence.
Oxybutynine is administered orally or as instilaţii
bladder catheter (bladder continence increases, reduce
the risk of infection and renal damage).
53
b) Anticholinergic mydriatic - are predominantly
acting anticholinergic mydriatic substances.
Pharmacodynamic action:
produce mydriasis and cycloplegic effect shorter than
atropine.
Therapeutic use: in ophthalmology for retinal examination
and preoperative for cataract.
Homatropine, eye drops 1%
Mydriasis and cycloplegia are fast and durază 1-3 days.
Ciclopentolate, eye drops 1%
Mydriasis and cycloplegia durază 24 h.
Tropicamide
Mydriasis and cycloplegia maintained ~ 6 hours.
Dosage forme: MYDRIUM, eye drops
54
Thank you
You are free
55