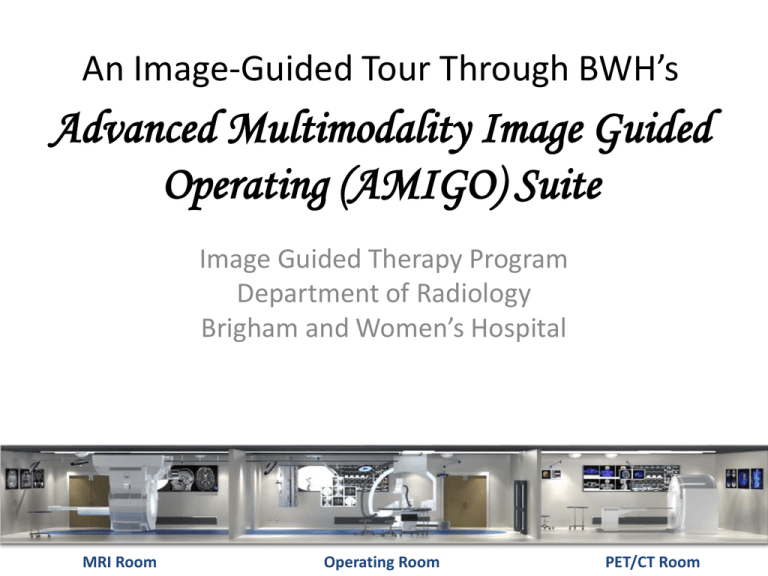
An Image-Guided Tour Through BWH’s
Advanced Multimodality Image Guided
Operating (AMIGO) Suite
Image Guided Therapy Program
Department of Radiology
Brigham and Women’s Hospital
MRI Room
Operating Room
PET/CT Room
Supported by
National Center for Image Guided Therapy (NCIGT)
P41 RR019703 (Jolesz, Tempany) 2005-2015
Credits
• This presentation researched and created by
Mallika Winsor
• Photographs by Junichi Tokuda and Dan
Kacher
From Conceptualized Sketch…
...To Completed Suite
Advanced Multimodality Image Guided Operating (AMIGO) Suite
P41 RR019703 – National Center for Image Guided Therapy (NCIGT) 2005-2015
Ferenc Jolesz, MD
Clare Tempany, MD
The OR and MR rooms of AMIGO
Advanced Multimodality Image Guided Operating (AMIGO) Suite
P41 RR019703 – National Center for Image Guided Therapy (NCIGT) 2005-2015
Ferenc Jolesz, MD
Clare Tempany, MD
Imaging Equipment in AMIGO
• Room 1: MRI Room
– Siemens 3T Verio MR scanner that moves along a ceiling track between the
MRI room and the OR
• Room 2: PET-CT Room
– Siemens PET-CT
• Room 3: Operating Room
– BK Medical Pro Focus UltraView Surgical Ultrasound with Prostate Transducer
– Siemens S2000 Ultrasound
– Siemens Artis Zee ceiling mounted X-ray Fluoroscopy system with Navigation
Package and DynaCT
– Zeiss Pentero surgical microscope
• Navigation
–
–
–
–
–
BrainLAB navigation system
Sentinelle Medical (Hologic) Aegis Navigation Workstation
St Jude Medical mapping and navigation system
IntraMedical Imaging Node Seeker and Beta Probe
Robin Medical Endoscout
The OR and MR rooms of AMIGO
Advanced Multimodality Image Guided Operating (AMIGO) Suite
P41 RR019703 – National Center for Image Guided Therapy (NCIGT) 2005-2015
Ferenc Jolesz, MD
Clare Tempany, MD
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Goal: Highly detailed anatomical images
What Does It Do?
• Strong magnetic field is applied,
causing the nuclei within the
patient’s body to rotate and align
– Scanner detects, records, and
combines the different rotating
fields into a single image
– Gradients in all directions are
combined to create a 3D image
• Strong contrast between different
soft tissues within body
• Better at producing images of
brain, muscles, heart, cancers
than CT or x-rays
• Applications
– Used to distinguish
pathological tissue from normal
tissue
– Comparable resolution, much
better contrast resolution
(between arbitrarily different
but not identical tissues) than
CT
• Advantages
– Harmless to patient
• What it uses
– Strong magnetic fields
– Non-ionizing radiation
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Terminology
Parameters of Image Acquisition
• TE = echo time
• TR = repetition time
• TI = inversion time
– Time between inversion and
excitation pulses
Edema
• Abnormal accumulation of
fluid beneath the skin or in
cavities of the body
• Caused by increased
secretion of fluid into the
interstitium or impaired
removal of fluid
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Basic Scans
T1-weighted MRI scan
• Highlights fat deposits
– Water = dark; fat = bright
• Good grey v. white matter
contrast
• Commonly run clinical scan
• Short TE; short TR
T2*-weighted MRI scan
• Gradient Echo (GRE) sequence
•
Additional loss over T2 decay
• Air/tissue boundaries
susceptible
• Increases contrast of specific
tissues
• Long TE; long TR
T2-weighted MRI scan
• Highlights fluids
– Fat = dark; water = light
• Good for imaging edema
• Heavily used for clinical scans
of cerebral spinal fluid
• Long TE; long TR
Spin density weighted MRI scan
• No contrast from either T1 or
T2 decay
• Uses spin echo (sometimes
gradient echo) sequences
• Short TE; long TR
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Specialized Scans
Diffusion MRI scan
•
•
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) enables diffusion to be
measured in multiple directions
Make brain maps of fiber directions
– Examine connectivity of different regions of brain
– Examine areas of neural degeneration and
demyelination
Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery (FLAIR)
•
•
•
•
Functional MRI (fMRI)
•
•
•
Measures signal changes in the brain due to changing
neural activity
Low resolution, rapid rate scans
BOLD (Blood-Oxygen-Level Dependent) effect
•
Increases in neural activity cause changes in MR
signals via T2* changes
•
Increased neural activity increases demand
for oxygen
•
Vascular system overcompensated, increasing
oxygenated hemoglobin
•
High resolution 3D maps of venous vasculature
within neural tissue
Inversion-recovery pulse sequence that nulls fluid
signals
– Free water = dark; edematous tissue = bright
Most sensitive way to evaluate brain for
demyelinating diseases
Carefully-selected TI allows signal from any
particular tissue to be suppressed
Conversion of T2-weighted sequence via additional
radio frequency pulse and manipulation of
magnetic gradients
Real-Time MRI
•
•
•
Continuous monitoring ("filming") of moving
objects in real time
Should help provide information about diseases
of the joints and heart
May make MRI examinations easier and more
comfortable for patients
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Medical Applications
Interventional Therapy
Radiation Therapy Simulation
• MRI images used to guide
minimally invasive procedures
both intraoperatively and
interactively
• No ferromagnetic instruments
used
• Some specialized systems
allow imaging concurrent with
surgery
•
– Usually, surgical procedure is
temporarily interrupted so MR
images can be acquired to
verify success/guide
subsequent surgical work
•
•
•
MRIs used to specifically locate
tumors within body in preparation
for radiation therapy treatments
Patient placed in specific,
reproducible, body position and
scanned
MRI system computes precise
location, shape and orientation of
the tumor mass, correcting for
spatial distortion inherent in the
system
Patient is marked/tattooed with
points that, when viewed in
specified, reproducible body
position, permit precise
triangulation for radiation therapy
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
What is MRI Compatibility?
Safety Concerns
• MR-Safe = device or implant that
is completely non-magnetic, nonelectrically conductive, and nonRF reactive
•
– Titanium and its alloys
• MR-Conditional = device that is
safe, provided the safety
conditions are defined and
observed
• MR-Unsafe = objects that are
significantly ferromagnetic and
pose a clear and direct threat to
persons and equipment within
the magnet room
• Patients always asked for
complete information about all
implants prior to entering the
MRI suite
Radio frequency energy
–
•
Peripheral Nerve Stimulation
–
•
Appropriate ear protection is necessary for anyone inside
MRI scanner room during examination
Cryogens
–
–
•
Rapid switching on and off of the magnetic field gradients
may cause nerve stimulation
Acoustic noise
–
•
Powerful radio transmitter can heat the body to the point
of risk of hyperthermia in patients
Cryogenic (extremely cold) liquids enable superconducting
capabilities of the electromagnetic coils
MRI support rooms should be equipped with pressure
relief mechanisms and an exhaust fan in case of a quench
(shut-down of superconduction electromagnet)
Pregnancy
–
Increasingly important for diagnosing and monitoring
congenital defects of the fetus (no contrast agents used)
• Fetal tumors (primarily teratomas)
• Facilitating open fetal surgery
• Other fetal interventions
• Planning to safely deliver and treat babies whose
defects would otherwise be fatal
Siemens MAGNETOM Verio 3T
AMIGO’s MRI:
Siemens MAGNETOM Verio 3T
Who Can It Accommodate?
• Patients up to 550 lbs
• Pediatric and elderly patients
• Claustrophobic patients
• Intensive Care Unit patients
• Patients dependent upon
medical equipment
How Does It Help BWH?
• Minimizes scan rejections due
to claustrophobia
• Reduces necessary sedations
• Capture sharper images (due
to reduced anxiety-related
movement)
• Early access in interventional
MRI
• Opportunities to perform
more kinematic studies
AMIGO’s MRI:
Siemens MAGNETOM Verio 3T
Features
→
• VQ engine
• Ultra-light (6.3 tons) magnet
with zero helium boil-off
• Total Imaging Matrix (TMI)
• TrueForm design
– Larger imaging volume, higher
image quality, better fat
saturation
– Whole body imaging up to 6' 4“
• Shortest 3T system available
• 70 cm Open Bore
• Moves along ceiling into OR
Why this machine?
• Higher speed, increased image
quality
• Safer scanning environment
• Increase flexibility, accuracy
and speed
• Enhanced image quality for a
wide range of applications
• Ensures uniform RF
distribution in all body regions
(optimizes homogeneity)
Bottom Line: Exceptional diagnostic capabilities,
patient comfort, and efficient workflow
A view of OR table and the MR through the PET/CT Bore
Advanced Multimodality Image Guided Operating (AMIGO) Suite
P41 RR019703 – National Center for Image Guided Therapy (NCIGT) 2005-2015
Ferenc Jolesz, MD
Clare Tempany, MD
Positron Emission TomographyComputed Tomography (PET-CT)
Goal: Precise localization of metabolic functions
What Does It Do?
How Does It Work?
•
•
•
•
Hybrid modality of PET and x-ray CT
Takes both types of images
sequentially, in the same session
Images can be combined into a
single 2D or 3D superposed image
Detecting changes in molecular
activity:
–
–
–
–
•
Reveal primary tumors
Detect metastases
Quantify uptake
Improves accuracy in oncology,
surgical planning, radiation therapy,
cancer staging
Increased image quality, speed, and
accuracy of diagnosis
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Patient fasts for 4 hours or more
Intravenous bolus (tracer) injected patient's arm
1-2 hours later, patient placed into PET-CT,
usually with arms at the sides or above the head
Automatic bed moves head first into the gantry,
first obtaining a topogram (whole body flat
sagittal section)
Operator uses PET-CT console to identify patient
and examination, selects the scanning
parameters and starts image acquisition period
Patient automatically moved head-first into CT
gantry, where x-ray tomogram is acquired
Patient automatically moved through PET
gantry, parallel to CT gantry; PET slices acquired
Software reconstructs/aligs PET and CT images
Whole body scan (mid-thigh to top of head)
takes 5-40 min
Positron Emission TomographyComputed Tomography (PET-CT)
Positron Emission Tomography
• Uses radionucleotide decay to
generate 3D image of functional
processes in the body
– Detects gamma rays emitted by a
positron-emitting radionucleotide
("tracer")
• Tracer enters patient's body via a
biologically active molecule
• FDG is a tracer used to display
metabolic activity of tissue in
terms of regional glucose uptake
– Computer analyzes
location/concentration of tracer
within patient to construct 3D
images
X-ray Computed Tomography
• Uses computer processed
tomography to generate 3D
images from a collection of
2D x-ray images taken
around a single axis of
rotation
– Tomography = imaging by
sections
– Supplements x-rays and
medical ultrasonaography
– Used in
preventative/screening
medicine
TIME Magazine declared PET-CT "Medical Invention of the Year" in 2000
AMIGO’s PET-CT:
Siemens Biograph TruePoint
Features
•
•
•
World's first HD PET platform
190 cm patient scan range
6-, 16-, 40- or 64- slice CT
→
Benefits
•
•
•
•
•
21.6 cm axial PET field of view with TrueV
Best NEMA spatial resolution in the industry •
Extremely sharp, highly-detailed images
Wide range of performance options
Largest PET field of view in the industry,
increasing count rate performance by
over 70%
10 minute whole-body PET•CT imaging
with TrueV
Exceptional lesion detectability
•
•
•
2 mm uniform PET resolution
•
2x improvement signal-to-noise
Distortion-free throughout entire field of
•
view
More accurate visualization of fine detail at
•
all angles
•
More accurate visualization of fine
detail at all angles
Enhanced detectability and highest
level of detail
Sharper images
Greater distinction within image
–
•
Customizable:
–
–
–
•
0.33 second rotation time on 64-slice CT
Multisclice CT configurations,
High or standard resolution options
Clinical configuration options
•
AMIGO’s PET-CT:
Siemens Biograph TruePoint
Technological Features
• Lutetium Scintillator
Oxyorthosilicate (LSO) crystal
– Faster scans
• HI-REZ
– Exceptional resolution
• TrueV
– Longest axial field of view
available
• TrueC
– Model-based scatter correction
• Ultra-Fast Ceramic (UFC)
detector
– Stunning CT image quality
• SureView
– Maximum image quality at
any scan speed
• CARE Dose4D
– Real-time dose modulation
• z-Sharp
– Highest spatial resolution
available
Siemens Artis Zee Ceiling-Mounted C-Arm, Operating Table and MRI in OR of AMIGO
Advanced Multimodality Image Guided Operating (AMIGO) Suite
P41 RR019703 – National Center for Image Guided Therapy (NCIGT) 2005-2015
Ferenc Jolesz, MD
Clare Tempany, MD
AMIGO’s Angiogram:
Siemens Artis Zee Ceiling-Mounted C-Arm
Features
• Large flat detector
• Easy patient access
• Full body coverage
• Ergonomically designed
controls
56" full-color medical-grade screen
• View multiple inputs
simultaneously
• Get the "whole picture" directly,
at tableside
• Change layout according to
individual workflow step
• Extremely high resolution (4x
that of standard HD)
• 8 megapixel resolution at 4 x HD
(3840 x 2160 pixels)
• Over 200 layout combinations
• 21 video source inputs
• Fully integrated tableside control
Siemens Artis Zee Ceiling-Mounted C-Arm
AMIGO’s Angiogram:
Siemens Artis Zee Ceiling-Mounted C-Arm
CARE program
• Reduces patient and operator
radiation dose to a minimum
– Addresses broader patient base
of dose-sensitive patients (ex:
children)
• Provides dose monitoring
during procedure
• Enhances in-house reporting
• Standard with all Artis Zee
systems
• Imaging
• Improved visualization of
therapeutic devices
• Advanced 3D applications,
allow greater speed and
precision
• Workflow
• Ergonomically designed
controls
• Streamline workflow,
increased efficiency
Ultrasound
What is Ultrasound?
Applications
•
•
•
Cyclic sound pressure with a frequency (20 kHz 200 MHz) greater than the upper limit of human
hearing (typically 20,000 hertz in healthy young
adults)
Uses many different fields to penetrate a medium
and measure the reflection signature or supply
focused energy
–
•
Diagnostic sonography (AKA ultrasonography) =
ultrasound-based diagnostic imaging technique used
to visualize subcutaneous body structures such as
tendons, muscles, joints, vessels and internal organs
for possible pathology or lesions)
•
–
–
This property is used by bats to locate prey while
hunting
Most well-known application is use in sonography
to image a fetus in a human womb
–
–
–
–
–
Reflection signature can reveal details about the inner
structure of the medium
•
Able to determine size, structure, and any
pathological lesions using real-time tomographic
images
Soft tissue imaging
Cardiac (heart)
Renal (kidney)
Hepatic (liver and gallblader)
Muscuko-skeletal (muscles, ligaments,
tendons)
Ophthalmic (eyes)
Superficial (just under the skin) structures
•
•
Ex: testicles, thyroid, salivary glands,
lymph nodes
Guiding interventional procedures in
real time
–
–
Fine needle aspiration/biopsy (FNA/NAB) =
diagnostic procedure
Biopsy of masses for cytology or histology
testing in breast, thyroid, liver, kidney,
lymph nodes, muscles, joints
Ultrasound
Obstetric Imaging
Emergency Ultrasound
•
•
Used to identify many conditions harmful to
both mother and fetus
–
•
Risk of leaving such conditions undiagnosed is far
greater than the small risk associated with
undergoing the actual US scan
•
–
Primary uses:
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
Assess gestational age
Confirm fetal viability
Determine location of fetus, intrauterine v.
ectopic (displaced anywhere besides uterine wall)
Check the location of the placenta in relation to
the cervix
Detect multiple pregnancies
Detect major physical abnormalities
Assess fetal growth for evidence of intrauterine
growth restriction (IUGR)
Check for fetal movement and heartbeat
Determine the sex of the baby
Specialized application by emergency
responders to guide immediate first aid care
Pros
–
–
–
•
Cons
–
–
–
•
Images muscle, soft tissue, and bone surfaces
well; particularly good at delineating interfaces
between solid and fluid-filled spaces
Renders "live" images, helps narrow down
problem area
Determines severity and sources of trauma
within region
Portable, narrowly-focused, easy to use
Cannot penetrate bone
Depth of penetration limited, especially in
obese patients
Operator-dependent (high skill needed for good
quality images and accurate diagnoses)
Scanning methodologies
–
Focused Assessment with Sonography for
Trauma (FAST)
•
•
–
Detects internal bodily fluid in between organs in
cases of blunt abdominal trauma
Screening test for blood around the heart or
abdominal organs after trauma
CARDIASOUND
•
Detects blockages/clots/penetrations of the heart
Ultrasound
Biomedical Applications
•
•
•
Detection of pelvic abnormalities, involving abdominal/vaginal/rectal US
Break calculi (stones formed in the body) into fragments small enough to
be passed without excessive difficulty via lithotripsy
Ablate tumors non-invasively via High Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU)
–
•
•
•
•
Acoustic Targeted Drug Delivery (ATDD) = enhanced transportation of
molecules across specified tissues via high frequency ultrasound
(frequency: 1-10 MHz; sound intensity: 0-30 watts/cm2)
Cataract treatment via phacoemulsification (surgery in which the eye's
internal lens is emulsified with an ultrasonic handpiece and aspirated from
the eye; aspirated fluids replaced with balanced salt solution)
Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound used to stimulate bone and tooth
regeneration, disrupt blood-brain barrier for drug delivery
Ultrasound-guided sclerotherapy and endovenous laser treatment
–
–
•
Magnetic Resonance-Guided Focused Ultrasound (MRgFUS) = guided by
MRI, a lower frequency (250-2000 kHz) than medical diagnostic ultrasound
is applied in significantly higher time-averaged intensities
Ultrasound-guided sclerotherapy = ultrasound is used to visualize the
underlying vein, allowing the physician to deliver and monitor the injection
of the vein-shrinking drug
Endovenous Laser Treatment (ELT) = minimally-invasive ultrasound-guided
technique used to treat varicose veins with laser energy
•
An optical fiber is inserted into the vein to be treated, a laser
light is shone into the interior of that vein, causing the vein to
contract; optical fiber is slowly withdrawn
Elastography = non-invasive method in which stiffness or strain images of
soft tissue are used to detect and classify tumors
–
–
When a mechanical compression or vibration is applied, the tumor
deforms less than the surrounding tissue (strain in the tumor is less than
that in the surrounding tissue)
Elasticity can discern health from unhealthy tissue in specific
organs/growths
•
Ultrasound Identification (USID)
–
Real Time Locating System (RTLS) or Indoor
Positioning System (IPS)
•
RTLS = used to wirelessly track and identify the
location of objects in real time
–
•
•
IPS = network of devices used to wirelessly
locate objects or people inside a building
Nonlinear propagation effects
–
•
Does not include speed, direction, or
spatial orientation
US waves usually display nonlinear
propagation (distortion) due to their high
amplitude to wavelength ratio
Safety Concerns
–
–
–
–
Occupational exposure to ultrasound in
excess of 120 dB may lead to hearing loss
Exposure in excess of 155 dB may produce
heating effects harmful to the human body
Exposures above 180 dB may lead to death
Recommended to avoid routine use of
ultrasound scans in low risk pregnancies
AMIGO’s Ultrasound #1:
BK Pro Focus UltraView
Capabilities
Features
•
•
•
•
Locate and map lesions, evaluate blood flow,
biopsy suspicious areas
Easy-to-create images for accurate diagnosis
Full line of specialized transducers
–
–
•
–
•
•
•
•
–
Breast, abdominal, vascular, cardiac, obstetric,
gynecological
Compatible with many other contrast-enhancing
transducers
Monitor therapeutic interventions
–
IQPAC technology (for abdominal imaging)
Breast biopsy, cyst drainage, radioactive seed
implantation, other therapies (RFA, cryotherapy,
microwave, laser)
Guide tip of catheter during RF ablation and
drainage
Intuitive keyboard and simple user interface
makes scanner simple to learn and use
Compact, mobile design
High contrast imaging
HistoScanning interface
–
Angular Compound Imaging (ACI): organ definition
• Reduced presence of artifacts, shadowing and
speckle
• Compounds images from up to 5 different angles
into a single, enhanced image
• Enhances anatomical structures (tissue structure,
vessel borders) during acquisition
Enhanced Tissue Definition (ETD): reduced speckle noise
• Smooth out potential irregularities in an image
• Speckle suppression algorithm continuously
analyzes ultrasound image for irregularities, then
smoothes them out without loss of frame rate
• Improved anatomically correct continuous border
• Improved ability to visualize lesion margins
AMIGO’s Ultrasound #1:
BK Pro Focus UltraView
Specifics
Scanning Modes
B- and M-mode
CFM, PW and CW Doppler
Tissue Harmonic
Contrast imaging
Display
19” LCD flat screen
Features
IQPAC
Coded excitation
Auto Doppler
Auto Gain
CHI acc.
Split screen
3D
DICOM
Palm Control
Dimensions (approx)
Height: 1475-1565
Width: 525mm
Depth: 765mm
Weight
70kg
Ultrasound Transducer #1:
BK 8818 Triplane Prostate
Features
Applications
• Images all three prostate planes
• Transrectal prostate scanning
• Transrectal puncture and
biopsy
• Transperineal puncture and
biopsy
• Transvaginal scanning
• Spectral and CFM Doppler
examinations
• Tissue harmonic imaging
• Contrast imaging
– Switches between planes at the
click of a button
– Increases diagnostic value with 3D,
Contrast and Doppler
• Sterile single-use needle guides
– Individually sterile-packed, preassembled and ready to use
• UA1322-S Biplane guide
– Simultaneously biopsy the
peripheral, transition and
central zones
• UA1323-S Endfire guide
– Apical biopsies
• UA1329-S Dual guide
– Minimal manipulation
• All are suitable for 17G needles
Ultrasound Transducer #1:
BK 8818 Triplane Prostate
Specifications
Frequency range
4 - 12 MHz
Contact surface (acoustic)
34.4 x 5.5 mm
Focal range
3 - 60 mm
Scanning modes
B, M,BCFM, Doppler, Contrast*,
Tissue Harmonic
Frame Rate
60 Hz
Image field (expanded)
Triplane / 140°
Dimensions
36 x 39 x 323 mm
Weight
230 g
Disinfection
Immersion
STERIS SYSTEM 1
STERIS SYSTEM 1E
STERRAD 50, 100S and 200
Ultrasound Transducer #2:
BK 8838 Endocavity 3D
•
High Resolution Color and 3D Imaging
– World's first electronic transducer, for endovaginal, endoanal and transrectal imaging, with
built-in high resolution 3D
•
Built-In 3D Acquisition
– Built-in linear array rotates 360° inside the transducer
– No need for additional accessories or mover
– No moving parts come in contact with the patient, for excellent patient comfort
•
Unsurpassed Image Quality
– For both dynamic 2D and 3D scanning
– Wide frequency range 12- 4 mHz, excellent imaging capabilities across all frequencies
– Enhanced focus capabilities for prostate 3D and pelvic floor imaging
•
Premium Ease
–
–
–
–
Slim 16mm diameter for more comfortable patient imaging
Easy to hold and manipulate
2D scanning plane controlled remotely from the system keyboard
Silent operation
Ultrasound Transducer #2:
BK 8838
Specifications
Frequency range
12-4 MHz
Focal range (typical)
3-60 mm
0.1-2.4 in
Frame rate
>150
Disinfection
Immersion
STERIS SYSTEM 1
STERIS SYSTEM 1E
Scanning modes
B,M,CFM, Doppler,Power
Doppler, Tissue Harmonic
Imaging, Contrast Imaging
Contact surface (acoustic)
Transverse:
65 x 5.5 mm
2.6 x .2 in
Image field (expanded)
65 mm/2.6 in wide acoustic
surface able to rotate 360º
Weight (approx.)
450 g
1 lb
Ultrasound Transducer #3:
BK 8848 Intracavity
•
•
A resolution revolution in image guided prostate therapy. Resolute, clear and detailed images of the
prostate, for accurate volume studies and source dose planning
Image guided prostate therapy
–
–
–
–
–
•
Pelvic Floor scanning
–
–
–
•
Sagittal scanning of any size prostate from base to apex
Resolute, clear, detailed image for accurate volume studies and source dose planning
Customizable sagittal grids and preferences for brachytherapy
Clear visualization of seminal vesicles
Clear view of needle placement
Best broad view of anterior and posterior compartments for functional and anatomical studies
Reproducible 3D studies with external mover
Detailed high-resolution biplane with 6.5 cm linear and convex views
Applications
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
Prostate brachytherapy
Transrectal scanning
Transperineal puncture
Transvaginal scanning
Prostate cryotherapy
Spectral and CFM Doppler
Contrast imaging
Ultrasound Transducer #3:
BK 8848 Intracavity
Specifications
Frequency range
5-12 MHz
Focal range (typical)
3-60 mm
Frame rate
>150
Disinfection
Immersion,
STERIS SYSTEM 1
STERIS SYSTEM 1E
STERRAD 50, 100S and 200
Scanning modes
B,M, Doppler, BCFM, Tissue
Harmonic Imaging
Contact surface (overall)
Transverse: 127 mm2
Sagittal: 357 mm2
Image field (expanded)
180˚(transverse)
Weight (approx.)
250 g
Microscope
AMIGO’s Microscope:
Zeiss OPMI Pentero
Features
• Intra-operative fluorescence
• Integration of entire digital
video chain
• Integration of surgical
microscope into hospital's
information and
communication
infrastructure
• User-friendly solutions for
OR staff
Intraoperative Fluorescence technologies
(enhance efficiency via vital info)
•
INFRARED 800: Fluorescence-based angiography
–
Immediately visualize and interpret intraoperative blood flow
•
•
•
–
Button activates INFRARED and guides it automatically to the point of interest
•
•
•
•
•
•
–
•
Digital videos saved automatically
Still images easily taken and transferred to DVD/USB
AutoRecord: synchronous video of white light and infrared view
AutoGain: brightness of infrared image automatically adjusted to respective application
AutoReplay: repeat function jumps directly to start of inflow on video, skips over blank
recording
Picture-in-Picture: direct comparison of white and infrared recordings on touch screen
Completely integrated into OPMI Pentero
FLOW 800: Visual analysis of vascular blood flow dynamics
–
–
•
Delivers critical information quickly and conveniently to surgeon
No procedural disruption
Specially tailored to requirements of neurosurgery for management of vascular
diseases (Ex: cerebral aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations (AVM, and bypass
procedures)
Analytical visualization tool for rapid and reliable interpretation of fluorescence video
sequences generated using INFRARED 800
Supports an in-depth interpretation of fluorescence videos by creating objective
evaluation of results visually and in color
BLUE 400: Fluorescence-guided tumor resection
–
Visible differences
•
•
•
•
–
Excellent aid for visualizing tumors clearly at any time during the procedure
Extremely clear fluorescent images
Precise definition of tumor margins during removal of malignant brain tumor tissue
Helps preserve vital and functional areas of the brain and to ensure that the patient’s
quality of life is not impaired
Workflow unchanged
•
•
BLUE 400 integrated procedure supporting intuitive performance of fluorescent-guided
tumor resection
Activate and switch between BLUE 400 (tumor visualizing) and xenon white light
(normal) views instantly
AMIGO’s Microscope:
Zeiss OPMI Pentero
•
State of the art apochromatic optics
–
–
–
•
•
Ergonomically correct design for cranial, spinal and posterior fossa procedures
Surgeon can be standing or seated
Design is 30% more compact
Allows for freedom of hand and instrument movement, short distance to surgical field
Overhead design
•
Suspension system can be placed in any position (even behind surgeon)
Several different configurations available
Stereo co-observation tube remains in same position as microscope
is repositioned
Light
–
–
–
•
•
20% more light for surgeons (more for assistants)
Spot illumination
•
Precisely adjusts light cone without reflections
Two-channel illumination system
•
Higher-contrast images in narrow and deep canals
Autofocus
–
–
High-speed autofocus
•
Razor-sharp images, regardless of magnification
Manual focus
•
Intuitive laser-focusing aid helps select exact focal point
•
Robotic X/Y movements
•
Controls
–
–
–
–
Can move easily in any direction
Handgrip
Mouth switch
Foot switches
Integrated digital visualization: immediately produce and process
digital video
Simply Unique (user-friendly solutions for OR staff)
–
–
Convenience
–
–
–
–
–
•
•
Crystal-clear images, sharp details, natural colors
Variskop provides a larger working range and comfortable conditions
17% field depth increase
•
–
–
•
AutoBalance: one-touch button
AutoDrape: air evacuation to precisely fit sterilization drape over
microscope
FlexiTrak: easy transportation
Superlux 330: easy to change lamps and modules
Workflow Integration
–
–
Fast and easy connection to all leading navigation systems without
external components and wiring
Open interface system
–
–
Binocular, color injection and superimposition of navigation data
Robotic X/Y design with three motorized axes
•
•
–
Provides real tool tracking for viewing every point in working and tilting
range of OPMI
Laser-guided, high-speed autofocus system
•
•
–
Use same workstation and cable with other ZEISS surgical microscopes
Delivers precise navigation by focusing to a fraction of a millimeter
Precisely identifies displayed point
MultiVision
•
•
Enables surgeon to inject information and data into the eyepiece
Touchscreen interface can be injected into MultiVision display and
controlled using the joystick
AMIGO’s Microscope:
Zeiss OPMI Pentero
•
•
FDA cleared for any MRI-guided
intervention on MRI scanners
Clinical procedures on open scanners
–
•
Research on close-bore scanners
–
•
•
Prostate brachytherapy and cryotherapy,
RF ablation of liver tumors, cryotherapy of
renal cancer, breast biopsy, brain surgery
MRI catheterization and endoscopy,
motion artifact elimination
Clinical Applications
Many MR-guided diagnostic and
therapeutic procedures:
–
–
–
–
–
Biopsy and aspiration (breast, brain, liver,
prostate).
Tumor RF/laser ablation (liver).
Brachytherapy (prostate, kidney).
Image-guided neurosurgery.
Pain management (nerve blockage).
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Specifications
Realtime 6 degrees-of-freedom tracking during MR imaging
with FSE, FGRE, SPGR, SSFSE.
Number of Tracking Devices: 2 out of 4 ports.
Tracking Accuracy: Location: 2mm, Orientation: 1 degree
(values represent 2 standard deviations of the tracking error
population).
Tracking Range: Up to 30cm from the center of the scanner.
Tracking Angle: Unlimited (360 degrees).
Tracking Rate: Up to 16Hz.
Input Power: 120VAC/0.8A (60Hz) or 230VAC/0.4A (50Hz).
Comes with a set of mechanical tools that help the physician
navigate a needle to a specific location inside the patient
Sensors
Acquires the location and orientation of a sensor during an
MRI scan
Sensor is a 3 dimensional magnetic field sensor made by 3
orthogonal pick up coils
–
–
Comes in different sizes and shapes, to fit the specific
application
Most popular:
•
•
Basic cube sensor for hand held guided tool
Micro sensor with about 1.5 mm diameter for small tools,
catheters and more
To be continued…