Overview - DigiCampus
advertisement

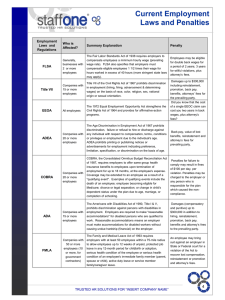
Intro to Human Resources Regulatory Concepts Presented by Colleen Kilroy, PHR, SHRM-CP, MBA Course Outline Top 10 HR Regulations 1. Anti-Discrimination Laws (x5) 2. Leave Laws (x2) 3. The Three Compliance Giants (x3) Section 1: Regulatory Compliance Managing people means acknowledging their legal rights Stay informed! navigate your way through the ever-changing river of legal regulation. #10: Anti-Discrimination Title IIV Name: Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 Overview: Prohibits discrimination in hiring, firing or pay decisions based on a person's race, religion, sex, or national origin. It also prohibits sexual harassment. Threshold: 15 or more employees Authority: Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) #9: Disability Discrimination ADA Name: Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA or ADAAA) Overview: Prohibits job discrimination against qualified people with disabilities who can do the job with or without reasonable accommodation. Threshold: 15 or more employees Authority: EEOC #8: Gender Pay Inequality Name: Equal Pay Act (EPA) Overview: Employers can't pay female employees less than male employees for equal work on jobs that require equal skill, effort and responsibility. Threshold: 20 or more employees Authority: EEOC #7: Age Discrimination Name: Age Discrimination in Employment Act of 1967 (ADEA) Overview: Employers can't discriminate in any way against applicants or employees older than 40 because of their age. Threshold: 20 or more employees (unless in Public Sector) Authority: EEOC #6: Pregnancy Discrimination Name: Pregnancy Discrimination Act (PDA) of 1978 Overview: Prohibits job discrimination on the basis of pregnancy, childbirth and related medical conditions. Threshold: 15 or more employees Authority: EEOC #5: Family/Medical Leave Name: Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) Overview: Says eligible employees can take up to 12 weeks per year of unpaid, job-protected time off for the birth of a child or adoption of a child or to care for themselves or a sick dependent, spouse, or parent who has a "serious" health condition. Threshold: 50 or more employees Authority: Department of Labor (DOL) #5: Family/Medical Leave (cont) Serious Health Condition Triggers: Out more than 3 days, continuation of or multiple treatments, incapacity, chronic conditions, permanent/longterm conditions, birth of child What is NOT covered: cold, flu, ear aches, cosmetic treatments, upset stomach, minor ulcers, headaches (barring migraines), routing dental/orthodontia problems… #4: Military Leave Name: USERRA: Uniformed Services Employment and Reemployment Rights Act of 1994 Overview: Prohibits discrimination against employees who volunteer or are called to military duty. When reservists return from active duty tours of less than five years, you must reemploy them to their old jobs or to equal jobs. Threshold: ALL EMPLOYERS! Authority: DOL #3: Immigration Name: The Immigration Reform and Control Act (IRCA) Overview: It is illegal for employers to hire and employ illegal aliens in the United States. Form I-9 is required for every employee. Threshold: ALL EMPLOYERS! Authority: U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) #3: Immigration (cont) Form I-9 tips! 1. Find the most recent version of the I-9 2. Starting now, complete an I-9 for each employee hired past 1986. 3. Get clear on columns A, B, and C 4. Complete an audit of I-9 forms and note errors and missing forms. 5. Follow the three day rule 6. Verify ORIGINAL documents only 7. Be consistent in your documentation collection 8. Provide employees information, not “directions” 9. Follow record-keeping requirements- note E-verify process 10. Reverify and research (rehires and expired visa) #2: Workplace Safety Name: The Occupational Safety & Health Act (OSHA) Overview: Employers must run a business free from recognized hazards Threshold: ALL EMPLOYERS! Authority: DOL (the occupational safety and health administration) #2: Workplace Safety (cont) Safety Compliance Tips 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Identify your industry Start compiling your written plan Locate governing or expert authorities for assistance Complete a hazard assessment Take action to correct hazards Check your state’s worker’s compensation requirements OSHA log record keeping and reporting Talk to employees Investigate accidents Utilize free small business resource on OSHA’s site #1: Wage and Labor Name: Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) Overview: Establishes minimum wage, overtime pay, recordkeeping, and youth employment, and other labor standards affecting employees in the private sector and in Federal, State, and local governments. Threshold: ALL EMPLOYERS! Authority: DOL #1: Wage and Labor (cont) Colleen’s Quick Tips Audit your workforce infrastructure: Contractor vs Employee 2. Determine overtime eligibility: Exempt vs Non-Exempt 3. Develop consistent payroll practices surrounding time tracking, recordkeeping ,and overtime. 4. Make these policies known to the employee 5. Audit your minimum wage standards at the state level 1. #1: Wage and Labor (cont) Colleen’s Quick Tips 6. Know your meal break rules – varies by state 7. Get a grip on what “time worked” is and be consistent 8. Calculate overtime the FLSA way- don’t forget to include total compensation in your calculation 9. Be careful in wage deductions 10. Don’t discount travel time #1: Wage and Labor Name: Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) Overview: Establishes minimum wage, overtime pay, recordkeeping, and youth employment, and other labor standards affecting employees in the private sector and in Federal, State, and local governments. Threshold: ALL EMPLOYERS! Authority: DOL Course Recap 1. Anti-Discrimination Laws (x5) 2. Leave Laws (x2) 3. The three compliance giants (x3) Colleen’s Quick Tips Conclusion Always check state regulations When in doubt, consult with a legal council See you soon!