Common Skin Infections Presentation
advertisement

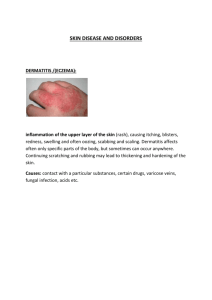
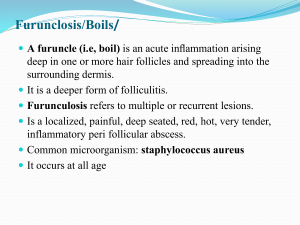
Lecture 5 Common Skin Infections Marcella Debeck Common Skin Infections Impetigo Lymphaginitis Ecthyma Molloscum Folliculitis Contagiosum Verrucae Herpes simplex Herpes zoster Dermatophyte infections candida albican infection Erysipelas Necrotising fasciitis Erythrasma Pitted Keratolysis Cellulitis onychomycosis Impetigo Superficial skin infection due to staphylococci or streptococci infections Contagious blisters which rupture leaving yellow crusted exudate Two types Bullous Impetigo Ecthyma Strep. Or Staph. Infection circumscribed, ulcerated and crusted lesions heal with scarring mostly in legs Ecthyma Folliculitis Infection of the hair follicles any hairy area Erysipelas Dermal infection May be accompanied by systemic symptoms - malaise, shivering, fever well defined advancing edge AKA St Anthony’s fire Erysipelas Necrotising fascitis very serious bacterial infection of the superficial fascia progresses very quickly Erythrasma Dry, reddish brown, slightly scaly and asymptomatic eruption wood’s light - coral-pink imidazole cream, oral ab’s, fusidic acid Toe webs Slide 2 Dockery, G.L. (1997).Cutaneous Disorders of the lower extremity. Phila delphia:WB Saunders Pitted Keratolysis maloderous, pitted erosions and discoloured areas. cornebacterium Cellulitis Infection of the subcutaneous tissues deeper and more extensive than erysipelas systemic symptoms swelling, redness, and local pain antibiotics Lymphaginitis inflammation of the lymph vessels appearance of a red line that follows the blood vessels up the leg Lymphadenitis - inflammation of the lymph nodes Molluscum contagiosum discrete pearly, pink, umbilicated dome shaped papules DNA pox virus contain a cheesy material face, neck and trunk usually multiple and grouped Verrucae Vs Corns Rapid Onset Slow growing Any site Sites of compression and friction Middle aged and older Young Superficial cappillaries which bleed easily Capillary bleeding is rare Herpes Simplex Acute vesicular eruption two virus types reoccurence Differential diagnosis: impetigo Herpes Slide 3 Dockery, G.L. (1997).Cutaneous Disorders of the lower extremity. Philadelphia:WB Saunders Herpes Zoster Varicella zoster virus Dermatomal distribution Post herpetic neuralgia rest, analgesia, drying lotions acyclovar and prednisone Slide 7 Gawkrodger, D. J. (1992) Dermatology. London: Churchill Livingstone Dermatophyte infections Microsporum Trichopyton Epidermophyton Form hyphae Tinea Pedis: T.rubrum, Tmentagrophytes var interdigitale, Epidermophyton floccosum Dermatophyte infections Differential diagnosis: – Psoriasis – Contact dermatitis – erythrasma Tinea pedis Interdigital moccasin acute vesicular Interdigital tinea pedis Slide 3 Gawkrodger, D. J. (1992) Dermatology. London: Churchill Livingstone Tinea pedis Candida albicans infections yeasts intertrigo paronychia Differential diagnosis (intertrigo) – Psoriasis, seborrhoeic dermatitis, bacterial seconadary infection Differential diagnosis (Paronychia): – bacterial infection, chronic eczema: Slide 1 Dockery, G.L. (1997).Cutaneous Disorders of the lower extremity. Philadelphia:WB Saunders Candida Paronychia Onychomycosis Fungal Infection of the nails generally dermatophyte occasionally mould or candiida Four types: – distal and lateral subungual – superficial white – proximal subungual – total dystrophic Slide 7 Gawkrodger, D. J. (1992) Dermatology. London: Churchill Livingstone