Duane`s Syndrome - Minnesota Optometric Association
advertisement

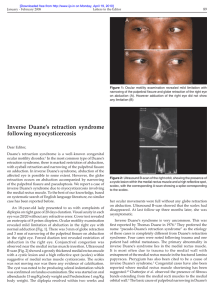
Duane’s Syndrome Violent Violation of Sherrington’s Law Definition Disturbance of ocular movement characterized by simultaneous contraction of the medial and lateral rectus muscles in adduction History 1879 1887 1895 1896 1899 1900 1905 - Heuck describes a case of retraction in adduction - Stilling - Sinclair - Bahr - Turk – Wolff - Duane presents 54 collected cases Duane's known as Stilling-Turk-Duane Syndrome in Europe Prevalence Types I, II, and III Incidence 1-4 percent of all strabismus Female 54-62% Left eye 60-75% where unilateral Bilateral 18-22% Many associated congenital anomalies Occasionally familial Diagnostic Features Reduced abduction Retraction of the globe on adduction Co-contraction of the lateral and medial recti on adduction Associated Features Upshoot or downshoot in adduction Narrowing of palpebral fissure - minimal in some cases Low angle esotropia or exotropia Head turn for fusion "Y" or "V" pattern Synergistic divergence Differential Diagnosis Abducens palsy - usually larger angle esotropia in primary gaze Ocular myasthenia Spasm of the near reflex Medial rectus entrapment with medial orbit wall fracture Strabismus fixus Ocular neuromyotonia Graves ophthalmopathy Duane’s-Associated Syndromes 33% of All Duane’s Klippel-Feil Anomaly 3-4% Labyrinthine deafness 8-16 % Wildervanck Syndrome both of above Goldenhar Syndrome Crocodile tears Arthrogryposis multiplex congenita Marcus-Gunn Jaw Winking Syndrome Many others Etiology Neuroanatomy 1. Deficient innervation of lateral rectus 2. Innervation of lateral rectus by anomalous branch of 3rd nerve 3. Brainstem origin Embryology 1. Teratogenesis at 8 weeks gestation 2. Absence of abducens motor neurons Type I Duane’s Most Common – 78% Very reduced abduction Globe retraction with attempted adduction Narrowing of palpebral fissure with adduction Typically esotropic Absent sixth nerve nucleus Duane’s Retraction Syndrome Type I Duane’s EMG MR – Adduction + LR – Adduction + MR- Abduction LR – Abduction - Type II Duane’s Least common -7% Fair abduction Reduced adduction Globe retraction and narrowing of palpebral fissure with adduction Often Exotropic Type II Duane’s EMG MR – Adduction + LR – Adduction + MR- Abduction LR – Abduction + Type III Duane’s Syndrome Incidence about 15% Poor abduction and adduction Globe retraction and narrowing fissure in adduction Minimal deviation in primary gaze Tonic firing of horizontal rectus muscles Type III Duane’s EMG MR – Adduction + LR – Adduction + MR- Abduction + LR – Abduction + Secondary Effects of Duane’s Pseudo-overaction of inferior oblique Due to leash effect of contracting LR V, Y and X patterns Face turn Treatment of Duane’s Rationale for treatment Disruptive head turn Diplopia (rare) Suppression and amblyopia (uncommon) Large angle deviation in primary gaze Deviation in up or downgaze Treatment modalities Many cases require no intervention Prism in spectacles Surgery Surgery-Type I For minimal co-contraction do large ipsilateral MR recession For severe co-contraction-small ipsilateral MR recession and large contralateral MR recession Avoid lateral rectus resection Approach transposition with caution because of vertical deviations Recession MEDIAL RECTUS Transposition Surgery for Type II Ipsilateral lateral rectus recession Contralateral medial rectus resection Surgery for Type III Fadenoperation on Contralateral medial rectus and lateral rectus Surgery for Upshoot or Y-pattern Y-splitting of lateral rectus Fadenoperation of lateral rectus Bilateral Duane’s Danger of consecutive XT Simultaneous recession of medial and lateral rectus M.R FIN