10.9- Eye Notes
advertisement

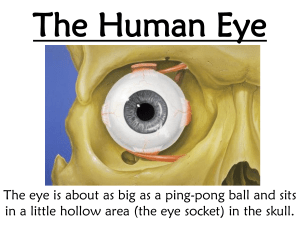
Do Now • Research the following diseases and give a sentence summarizing them • • • • • • Glaucoma Conjunctivitis “Floaters” Corneal Abrasion Astigmatism Night vision blindness 10.9 Sense of Sight Objectives • To identify different visual accessory organs. • To compare and contrast rods and cones. • To explain various diseases of the eye. Accessory Organs of the Eye • Eyelids: contain skin, muscle, connective tissue, and conjunctiva. • Main Eye Muscles: – Orbicularis Oculi: closes lid upon contraction. – Levator Palpebrae Superioris: opens lid Accessory Organs of the Eye • Conjunctiva: mucous membrane lining eyelids and anterior surface of eyeball (except the cornea) • Lacrimal Apparatus: – Lacrimal gland- secretes tears – Superior and inferior canaliculi- collect tears – *Tears contain lysozyme which acts as an antibacterial agent. “Conjunctivitis” Inflammation of the conjunctiva. Can be causes by a viral infection or an allergic reaction. Most commonly caused by bacteria which people call “Pink Eye” Accessory Organs of the Eye • Extrinsic Eye Muscles: – Superior Rectus – Inferior Rectus – Medial Rectus – Lateral Rectus – Superior Oblique – Inferior Oblique Accessory Organs of the Eye • Extrinsic Eye Muscles: Eye Structure *The eye is about 2.5cm and is hollow It contains 3 layers 1) An outer fibrous layer 2) A middle vascular layer 3) Inner nervous layer Outer Layer • Cornea: – focuses entering light rays – Made of connective tissue + epithelium – Avascular • Sclera: (the white part) – Collagenous + elastic fibers – Protects eye – Provides a place for muscle attachment Middle Layer • Choroid coat: – Provides blood vessels – Contains melanocytes • Ciliary Body: – Aids in focusing – Holds lens in place • Lens: – Changes shape to focus – Flat=focus on distance – Convex=focus on close objects. Middle Layer • Iris: – Colored part – Contains muscles that control pupil size – Divides anterior/posterior chambers • Pupil: – Opening in the iris • Aqueous Humor: – Watery fluid – Secreted between cornea and lens – Provides nourishment “Glaucoma” Excessive production of aqueous humor causes pressure on the blood supply from the optic nerve which deprives cells of oxygen causing them to die and the patient to become blind. Inner Layer • Retina: – Contains photoreceptors • Optic Disc: (“Blind Spot”) – Contains nerve fibers – Contains central arteries and veins – Lacks receptors • Viterous Body: – Maintains shape – Nourishes the posterior cavity “Floaters” Bits of vitreous humor clump and cast shadows on the retina which causes “floaters”. They can be seen most commonly when looking at the sky or a blank wall. Do YOU have floaters? Do Now • • • • • What is the colored part of your eye called? The white part? What holds the lens in place? Where are photoreceptors located? What part of the eye does glaucoma effect? Objectives – Explain different diseases associated with the eye. – Identify different parts of a cow eyeball through dissection. – Perform various eye tests to observe different functions and capabilities of the eye. Light Refraction • Light waves enter your eye and your lens focuses and “bends” the light, projecting the image on your retina Visual Receptors • The eye contains modified receptors in the retina – Rods: black and white – Cones: color (3 types) “Color Blindness” The person usually lacks one of the 3 types of cone receptors causing them to have trouble distinguishing reds and greens. “Night Blindness” A deficiency in Vitamin A reduces production of retinal which is necessary for rod sensitivity and seeing at night. “Astigmatism” Curvature of the eye is incorrect and causes blurriness or distorted vision Lab- Cow Eye Dissection – Gather all materials necessary for the dissection. – YOU MUST WEAR GOGGLES, AN APRON, AND GLOVES!!!! – Complete the dissection as instructed in the lab handout and be sure to show me the pinned structures for points!