Document
advertisement

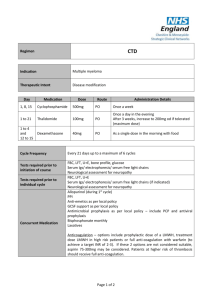
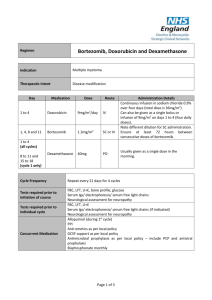
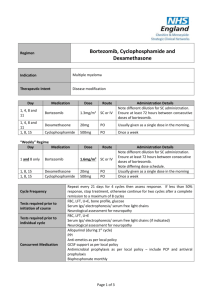
Drugs Used in the Treatment of Multiple Myeloma Myeloma Canada National Conference 2011-September-24 Toronto, Ontario Carlo De Angelis, RPh, PharmD Clinical Pharmacy Coordinator - Oncology Objectives At the end of this educational program, you will be able to: • Recall common side effects associated with Multiple Myeloma treatment • Apply the information discussed to help prevent or reduce the severity of side effects of Multiple Myeloma treatment Improved Survival in Multiple Myeloma Kumar SK et al. Blood 2008 Advances in Multiple Myeloma Kyle RA and Rajkumar SV Blood 2008 Thalidomide - Adverse Effects Mateos MV Cancer Treat Rev 2010 • Single agent • Somnolence, asthenia, rash, peripheral edema, dizziness, constipation, dyspnea, leukopenia • Peripheral neuropathy • Cummulative and dose dependent • Parasthesia, hyperaesthesia, numbness, coldness, pallor • Symmetrical hands and feet • Caution in patient with predisposition • Early detection critical • Discontinue at first sign of symptoms Thalidomide - Adverse Effects • Combination with dexamethasone • Grade 3 (alone versus combination) • • • • • • Constipation - 68% versus 55% Fatigue - 39% versus 55% Thrombosis - 4% versus 15% Infection - 14% versus 13% Neuropathy - 3% versus 5% Rash - 0% versus 4% • Overall Grade 4 - 15% versus 31% Thalidomide - Dose Adjustment for Peripheral Neuropathy Mateos MV Cancer Treat Rev 2010 Grade 1 • Maintain dose and monitor Grade 2 • Reduce dose of thalidomide 50% Grade 3 or 4 • Discontinue therapy • Resume at 50% previous dose Therapeutic Interventions for Peripheral Neuropathy • Opioids • Morphine, hydromorphone, oxycodone • Gabapentin • Pregabalin • Duloxetine • Tricyclic antidepressants Thrombosis Mateos MV Cancer Treat Rev 2010 • Single agent - 2% to 4% • In combination - 10% to 35% • Ususllay occurs within the first 3 - 12 months of therapy • Risk factors • Previous history of VTE, obesity, presence of central venous catheter, high tumor burden, high dose dexamethsone • Prevention • ≥ 2 risk factors - anticoagulation • LMWH or warfarin • 1 risk factor - low dose aspirin Lenalidomide - Adverse Effects Morgan GJ et al. Lancet Oncol 2006 Lenalidomide and Myelosupression • Lenalidomide is primarily eliminated through the kidneys • Thrombocytopenia increased when creatinine clearance was < 50 mL/min 14% versus 5% • Starting Dosing • Moderate renal impariment • CrCl ≥ 30 to < 60 mL/min • 10 mg daily • CrCl < 30 mL/min not on dialysis • 15 mg every 48 hours • CrCl < 30 mL/min on dialysis • 5 mg daily Lenalidomide and Myelosupression Bortezomib - Adverse Effects San Miguel J et al. Oncologist 2006 Bortezomib - Thrombocytopenia • Transient; Not cumulative • Greater risk if significant bone marrow involvement with MM • If platelet count < 30,000/L on day 11 of cycle • Repeat count on day 14/15 • Transfuse if necessary • Reduce dose 25% next cycle • Caution in patients with platelet count < 50,000/L at start of Tx Bortezomib - Peripheral Neuropathy Richardson PG et al. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2006 • Symptoms are primarily sensory • Feet affected more than hands • Symptoms include: • Pain • Paresthesias or dyesthesias • Abmornal touch sensations such as wetness, itchiness, creeping, crawling, numbness, tingling • Burning • Numbness Bortezomib - Peripheral Neuropathy Richardson PG et al. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2006 • SUMMIT and CREST trial data • 35% patients all grades • Grade 3 - 13%, Grade 4 - < 1% • • • • • • Symptom improvement or reversible 70% patients Median time to improvement = 47 days (range 1-529) Dose reductions in 12% patients Discontinuation 5% patients Preexisting peripheral neuropathy - 80% Patients with no pre-existing peripheral neuropathy 3% developed Grade 3 • In extension study 73% patients reported no worsening Bortezomib - Peripheral Neuropathy Richardson PG et al. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2006 • Dose reduction • Grade 1 without pain or loss of function • No action required • Grade 1 + pain or Grade 2 - reduce dose • 1.0 mg/m2 • Grade 2 + pain or Grade 3 - hold until resolved; resume at dose 0.7 mg/m2 – once weekly • Grade 4 - Discontinue Tx Bortezomib Adverse Effects Take Home Messages • While common, side effects can be managed and are reversible • Bruising or bleeding may be a sign of low platelets • Contact your care team at the cancer centre • Peripheral neuropathy • Make sure you inform your care team of any symptoms Shift in Treatment Paradigm Current • Use medications at maximum tolerated doses Future? • Use optimal effective dose • • • • Reduced intensity Improved side effect profile Prolong duration of therapy Improved Efficacy Summary • The availability of new active agents has revolutionized the treatment of Multiple Myeloma • Standard first line therapy include use of drug combinations of immune modulating drugs (thalidomide, lenalidomide) and/or bortezomib • Side effects prevention/ management and adherence to treatment are important factor contributing to success of treatment Multiple Myeloma Word Cloud Rajkumar SV et al. Blood 2010