Chapter 43 Assessment of Renal and Urinary Tract Function
advertisement
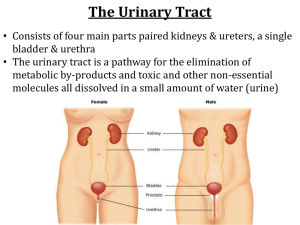
Assessment of Renal and Urinary Tract Function Renal and Urinary Systems • Function to maintain the body’s state of homeostasis by regulating fluid and electrolytes, removing wastes, and providing hormones involved in red blood cell production, bone metabolism, and control of blood pressure. • Structures: – – – – Kidneys Ureters Bladder Urethra Kidneys, Ureters, and Bladder Internal Structure of the Kidney Nephron Formation of Urine Renin Angiotensin System Functions of the Kidneys: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Urine formation Excretion of water products Regulation of electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance Regulation of water balance Control of blood pressure Renal clearance ( the ability of the kidneys to clear solutes from the plasma Regulation of red blood cell production Synthesis of vit.D to active form Secretion of prostaglandins (PGE2) ( vasodilatation effect and maintaining renal flow Assessment: • • • • Health history Patient chief concern Pain ( characteristic, location, duration,…. Etc) Dysuria, Hesitancy, urine incontinence, urinary frequency, Hematuria, Nocturia, polyuria, oliguria (less than 400/day), and anuria ( urine less than 50 ml/day) • The present of renal calculi • History of GI symptoms • History of UTI Cont… • • • • History of sexual transmitted disease Habits: smoking, alcohol, drugs Medication History of any renal diagnostic test ( catheterization) • Any risk factors ( DM, Hypertension, Sickle cell anemia, Benign prostatic hypertrophy, spinal cord injury, immobilization Physical examination Diagnostic Studies • Urinalysis and urine culture • Renal function tests (See Table 43-5) • Ultrasonography • CT and MRI • Nuclear scans • Intravenous urography, retrograde pyelography, cystography, renal angiography (See Chart 43-2) • Endoscopic procedures • Biopsies Diagnostic Evaluation: 1. 2. 3. Urine analysis: urine color (light yellow), Urine clarity ( clear and translucent), urine odor ( arometic), urine PH ( acidic: 6.0 or 4.6-8), urine specific gravity, detect protein, glucose and ketone bodies in the urine, microscopic examination of the urine sediments to detect RBC’s, WBC’s, casts, crystals, pus (pyuria), and bacteria Urine Culture and sensitivity Renal function test (KFT): Renal concentrate test (Specific gravity, and urine osmolarity) creatinine clearance test ( 24-hour urine collection test), serum creatinine, BUN, and serum electrolyte level Continue • X-Ray film and other Imaging modalities: 1. KUB studies: to detect size, shape, location and position of the kidneys, to reveal stone, hydronephrosis ( distention of the kidney pelvis), Cysts, tumors, and any surrounding tissue abnormalities. 2. CT scan and MRI: cross section view of the kidney and urinary tract: metal objects should be removed, sedative or certain contrasts may given, contraindicated in patient has pacemaker, surgical clips, or any metal objects Cont… 3. General Ultrasonography: assess fluid accumulation, masses, congenital malformation, changes in size, shape, or any obstruction, fluid intake should be encouraged before the procedure 4. Bladder Ultrasonography: to measure fluid volume in the bladder, indicated for urinary frequency, inability to void after removal of FC or postoperative, measuring residual volume of urine after voiding Cont…. 5. Intravenous urography: intravenous pyelography (IVP) or intravenous urogram (IVU). History of iodine or any contrast allergy should be obtained before the procedure. Patient should be instructed he may have temporary feeling of wormth, flushing of the face and unusual flavor (seafood) in the mouth. Monitor the patient closely for any allergic reaction. Cont. 6. Retrograde pyelography: catheter induced 7. 8. through ureters to the kidney pelvis by means of cystoscopy. Provide direct visualization of the kidney. Cystography: direct visualization of the bladder walls. Assessing vesicoureteral reflux ( back flow of urine from the bladder to one or both of the ureters), bladder injury Renal Angiography: provide an image of the renal arteries preparation done same as Cardiac cathetarization Cont…… 9. Urologic Endoscopic Procedure ( Endourology): through Cystoscope inserted via urethra or percataneously. • Direct visualization of the system, • removal of stone, • obtaining urine specimen from the kidney. • Sedation or anesthesia may performed, patient should be kept NPO. • Post- procedure: • moist heat to the lower abdomen and warm sitz bath are helpful in relieving pain and relaxing the muscles, • monitor the patient with prostatic hyperplasia for urine retention, • intermittent catheterization may needed for few hours • monitor for S/S of UTI, monitor for signs of retention Cont… 10. Kidney biopsy: • Indications: 1. Unexplained acute renal failure, 2. persistent proteinuria or hematuria, 3. transplant rejection, 4. and glomerulopathies. • Contraindications: 1. Serious bleeding disorders, 2. excessive obesity, and sever hypertension. • It is usually performed percataneously with a biopsy needle Procedure for kidney biopsy include: 1. 2. 3. 4. • 1. 2. 3. Place patient in prone position with a sandbag under the abdomin The skin site of biopsy is infiltrated with local anesthesia The needle biopsy is inserted just inside the renal capsule The patient is instructed to breath in and hold the breath to immobile the kidney during insertion of the needle Nursing diagnosis for the patient undergoing assessment of urinary or renal function include the following: Knowledge deficit regarding the procedure and diagnostic test Acute pain related to renal invasive diagnostic procedure Fear related to possible procedure or serious illness Cystoscopic Examination Nursing Care of the Patient Undergoing Diagnostic Testing of the Renal-Urologic System—Assessment • • • • • • • Patient knowledge Psychosocial and emotional factors; fear, anxiety Urologic function, include voiding habits/pattern Fluid intake Hygiene Presence of pain or discomfort Allergies Nursing Care of the Patient Undergoing Diagnostic Testing of the Renal-Urologic System—Diagnoses • Knowledge deficient • Pain • Fear Nursing Care of the Patient Undergoing Diagnostic Testing of the Renal-Urologic System—Planning • Patient goals may include understanding of procedures, tests and expected behaviors; decreased pain or absence of discomfort; and decreased apprehension and fear. Interventions • Patient teaching: providing a description of the tests and procedures in language the patient can understand. • Use appropriate, correct terminology. • Encourage fluid intake unless contraindicated. • Instruct in methods to reduce discomfort; sitz baths, relaxation techniques. • Administer analgesics and antispasmodics as prescribed. • Assess voiding and provide instruction related to voiding practices and hygiene. • Provide privacy and respect.