Diabetes and Pregnancy
advertisement

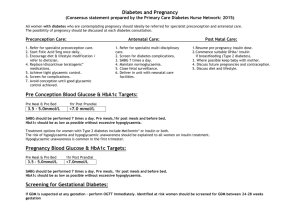
Dr. Miems Kleynhans Can a “normal” person also become diabetic in pregnancy? Gestational Diabetes Definition: Diabetes with onset or first recognition in pregnancy Pregestational diabetes: Diabetes diagnosed before pregnancy, type I or II Gestational diabetes : 87% of all diabetes in pregnancy Who will get gestational diabetes? It could happen to anybody Should we screen and when? YES!!! Ideal world - between 24-28 weeks gestation Glucose tolerance test – 75mg In South Africa? Selective screening : 10 factors History of previous gestational diabetes Certain ethnic groups Older than 35 years Weight more than 85 kg First degree family history of DM History of typical diabetic symptoms Previous infant over 4kg Previous stillbirth Severe polihydramnios Repeated glycosuria Why should we screen ? What are the effects of diabetes on the pregnancy? Antepartum: Congenital abnormalities 2. Macrosomia 3. Intrauterine death 4. Polyhydramnios – preterm labour 1. What are the effects of diabetes on the pregnancy? Delivery: 1. Shoulder dystocia 2. Erb’s palsy What are the effects of diabetes on the pregnancy? Postpartum: 1. Neonatal hypoglycaemia 2. Polycythaemia 3. Hyperbilirubinaemia 4. Respiratory distress syndrome Biggest fear? Unexplained intrauterine death Fetal hyperglycaemia and hyperinsulinemia Increased fetal oxygen consumption Fetal hypoglycaemia and acidosis Management Confirm diagnosis Ophthalmologist Kidney function – 24 hour protein clearance Blood pressure Urine – MCS First trimester screening and detailed anatomy sonar TSH HbA1C Fetal monitoring Treatment Control known diabetic patients optimally before conception Diet Insulin – gold standard Oral hypoglycaemic agents – more studies needed Delivery : When? Often preterm Corticosteroids in hospital Glucose abnormal up to 5 days Multidisciplinary decision Mom vs. fetus Delivery : How? The big debate Caesarean section vs. normal vaginal delivery All factors into consideration – macrosomal, timing, urgency, maternal choice . . . Conclusion We have to screen Increasing problem world wide We can improve outcome dramatically Thank you