Diabetes in pregnancy

Diabetes in pregnancy- an update
Seema Chakravarti
MRCOG, MRCPI
Consultant Obstetrician BHR
Trust
CEMACH DIABETES REPORT
Perinatal mortality 5 fold increased
3 fold increase in neonatal deaths in first month of life
2 fold increase in cong abnormalities
(NTD/Cardiac)
Adverse outcomes same for type 1 and 2 DM
Prem delivery 5 fold, macrosomia
High csection rate 70%
Severe PET
Subtypes
Type 1
Type 2
Gestational Diabetics
SOME WOMEN WITH
GDM WILL HAVE PRE
EXISTING DIABETES!!
Factors associated with poor pregnancy outcome
Maternal social deprivation
Lack of contraceptive use in 12 months preceding pregnancy
No folic acid intake pre pregnancy 5mg
Suboptimal diabetes management
Suboptimal preconception care
Suboptimal glycemic control before and during pregnancy
Key recommendations for specialist preconception services
Multidisciplinary- diabetic physician/obstetrician/midwife/diabetic nurse
Appropriate contraception
High dose folic acid supplementation
Assess and manage diabetic complications
Optimise glycemic control HbA1c <7
Counsel regarding risks and management strategies
Booking HbA1c and pregnancy outcome
Pregnancy putcome by booking
HbA1c
100%
80%
60%
40%
20%
0%
<7.8 >7.8>14
14
Hb A1c
SB
Cong abnormality
Normal
Solutions
Pre- conception counselling- good diabetic control at conception and pregnancy reduce incidence of miscarriage, malformation, SB and NND
Contraceptive advice, importance of avoiding unplanned preg should be an essential component of diabetic education for all diabetic women DOCUMENT
Only 1/3 women currently get PPC, 40% pregnancies unplanned
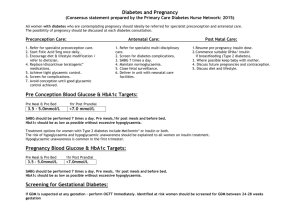
Targets
Pre conception Hb A1c <7.0% if safe
Increase frequency of self monitoring
Pre meal 5.5 mmol/l
Post meal 7.7mmol/l
Retinal screening treat pre pregnancy if proliferative retinopathy
Assess nephropathy- PCR/renal biochem
Review medication
Review medication
Stop ACE inhibitors discuss pros and cons
Beta blockers with caution as higher R/O
IUGR
Methyl dopa, nifedepine,hydralazine
Stop statins
Metformin/glibenclamide can be used in pregnancy, early referral
Assess diabetes
Retinopathy digital pictures and mydriasis
If retinopathy need preconception advice and possible treatment
Percentage of women developing sight threatening DR in pregnancy
30
20
10
0
60
50
40
No retinopathy
Minimal retinopathy
Mod to severe retinopathy
Nephropathy
1.
2.
3.
Warn risk of PET/IUGR/SB
Refer for hospital PPC if creatinine more than 120micromole/litre and 24 hr urine protein >2gm
Consider asprin/clexane especially if proteinuria as increased thromboembolic risk
General advice
Diet and lifestyle
Optimise weight( BMI>35 independent risk factor for maternal mortality and morbidity)
Adequate contraception
Folic Acid 5mg until 12 weeks gestation.
Diabetes UK and CEMACH guidance on pre preg care Leaflet
Other changes
Can continue/start metformin/glibenclamide in pregnancy
HAPO Trial- safe, no increased risk of malformations, better control in Type 2
Dimples hypos with tighter control
Watch for lactic acidosis – euglycemic acidosis
Breast feeding
Metformin safe NICE
Thank you