Alison Barry
advertisement

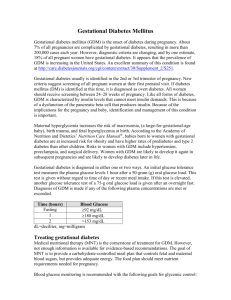
Alison Barry GESTATIONAL DIABETES FORUM Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Education Objectives • GDM rates in Metro South • Components of diabetes education plan specific to women with GDM • Resources available • Barriers and challenges • Benefits of multidisciplinary approach • GP engagement GDM GDM in QLD All QLD HHS Rates of GDM among pregnant women 8.0% 7.0% 6.0% 5.0% 4.0% 3.0% 2.0% 1.0% 0.0% 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 GDM diagnosis Report released from RANZCOG have endorsed new diagnostic criteria – 2 weeks ago July 2014 – 28/40 universal OGTT Cease to offer 50g GCT To be adopted no later than 01.01.2015 RANZCOG – Michael Permezel - President GTT Diagnosis Fasting 1 hour 2 hours Current <5.5 New <5.1 <11 unreported in some labs <8.0 <10 <8.5 Differs at individual health centres OLD NEW FASTING <5.5 mmol/L <5.0 mmol/L 1 HOUR <8.0mmol/L <7.4mmol/L 2 HOUR <7.8mmol/L <6.7mmol/L Diabetes Education Following diagnosis -> education is vital Optimal -> within 1/52 of diagnosis Reduce maternal anxiety Correct information – up to date Encourage partner or support person to attend Challenge of working within a limited timeframe Key Components of Education • Overview of Gestational Diabetes • Implications for mother and baby • Home blood glucose monitoring (HBGM) or (SBGM) • Review by Dietitian • NDSS – National Diabetes supplies scheme • Obstetric assessment • Medical assessment Education Tools DVD – Diabetes Australia Brochures/Pamphlets Demonstration Useful websites eg ADIPS, DA, ADEA, You2 connect • Must be culturally appropriate. • • • • Blood glucose monitoring • • • • • • • Arrange use of meter – free of charge scheme Demonstrate use of meter Lancet / finger pricking device Record book Disposal of sharps Sites for performing tests Timing of tests – ie QID -Before breakfast & 1 or 2 hrs after each main meal – refer to local protocols Physical Activity • Recognised as important adjunct therapy • Appropriate for pregnancy • Eg walking, swimming, pregnastic, water aerobics • Recommended in absence of obstetric & medical complications • Culturally appropriate Insulin Therapy • Decision made by treating doctor • Based on BSL’s, gestation and clinical evidence eg SGA or LGA baby • Individual education session • Dose • Device • Injection Sites • Injection Technique • Timing of injections • Disposal of sharps • Management of hypo’s Metformin • Studies conducted in Aust and NZ to assess safety and efficacy of use during pregnancy • MiG study • Follow up studies on offspring • Increased usage since MiG study Insulin & Metformin Translations Arabic Bengali Farsi Filipino Hindu Juba Vietnamese Punjabi Simple Chinese Tamil Thai Traditional Chinese Turkish Insulin Therapy Arabic Insulin & Metformin Translations Arabic Begali Farsi Filipino Hindu Juba Vietnamese Punjabi Simple Chinese Tamil Thai Traditional Chinese Turkish Metformin Bengali Post natal follow up Vital GTT – 6 - 8 weeks postnatally Follow up by dietitian Follow up by midwife Discuss – lifestyle issues, weight management, diet, exercise, future pregnancy, contraception • Annual fasting glucose with GP • • • • • Alerts Need to look at the whole picture Sometimes clinical scenario doesn’t match GDM What to consider BGL – good glycaemic control Self reported dietary modifications and increased physical activity • Clinically LGA • Significant maternal weight gain • USS – fetal macrosomia • • • • • Meter downloaded Psychosocial Issues • • • • • • • Normal pathway now altered Heightened anxiety and stress at diagnosis Impedes ability to learn Guilt Concern for baby Potential separation from baby at birth Will my baby have diabetes? Management • • • • • • • • • • Full explanation of GDM Implications for pregnancy Regular contact with specialist team Ensure plan for birth in partnership with woman Education – management of diabetes during delivery and postpartum Routine care during labour Monitor BGL’s – local protocols Anticipate shoulder dystocia Notify Paediatricians. Neonatal hypoglycaemia – test @ 1,2 & 4 hours. Useful websites ADIPS – Australasian Diabetes in Pregnancy Society www.adips.org Diabetes Australia www.diabetesaustralia.com.au You2 Connect www.You2.org.au Conclusion When a pregnancy is complicated by diabetes a multidisciplinary team approach provides the best care for a mother and her baby to achieve an optimal outcome. Avoid Aim to achieve Healthy mother and baby Questions & Discussion