Body Directions and Movement
advertisement

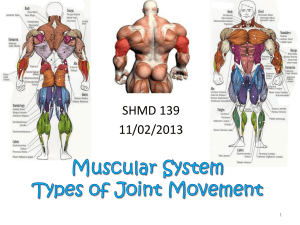
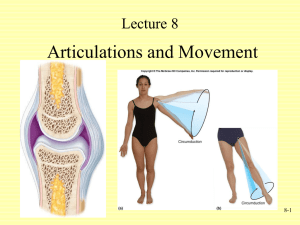
BODY DIRECTIONS AND MOVEMENT Athletic Medicine 1 BODY POSITIONS When we describe body position, we assume the person is in anatomical position. Body is upright, with the person facing forward, feet flat on the ground, arms at the side, and palms facing forward. REGIONS Principle regions of the body Head Skull Face Trunk Chest Abdomen Pelvis Upper limbs Lower limbs BODY PLANES When the body is in anatomical position, it can be divided into three imaginary planes. These planes help clarify and specify movements. Sagittal Plane: Divides the body into right and left portions. Frontal (or coronal) Plane: Divides the body into front (anterior) and back (posterior) portions. Transverse Plane: Divides the body into upper (superior) and lower (inferior) parts. DIRECTIONAL TERMS In order to locate various body structures, anatomists use specific body directional terms. Describe the position of one body part in relation to another. Directional Term Definition Example Superior Toward the head The head is superior to the neck Inferior Away from the head The belly button is inferior to the chest Anterior Posterior Medial Lateral Directional Term Definition Example Superior Toward the head The head is superior to the neck Inferior Away from the head The belly button is inferior to the chest Anterior Nearer to or at the front of the body The knee cap is on the anterior side of the body. Posterior Nearer to or at the back of the body The shoulder blade is on the posterior side of the body. Medial Lateral Anterior Posterior Directional Term Definition Example Superior Toward the head The head is superior to the neck Inferior Away from the head The belly button is inferior to the chest Anterior Nearer to or at the front of the body The eyes are anterior to the brain Posterior Nearer to or at the back of the body The brain is posterior to the eyes Medial Nearer to the midline The pinky is medial to the thumb Lateral Farther from the midline The thumb is lateral to the pinky Directional Term Definition Ipsilateral On the same side of the The right shoulder is body as another structure ipsilateral to the right hip Contralateral On the opposite side of the body as another structure Proximal Distal Superficial Deep Example The right shoulder is contralateral to the left hip Directional Term Definition Ipsilateral On the same side of the The right shoulder is body as another structure ipsilateral to the right hip Contralateral On the opposite side of the body as another structure The right shoulder is contralateral to the left hip Proximal Nearer to the attachment of a limb to the trunk The shoulder is proximal to the wrist Distal Farther from the attachment of a limb to the trunk The elbow is distal to the shoulder Superficial Deep Example Directional Term Definition Example Ipsilateral On the same side of the body as another structure The right shoulder is ipsilateral to the right hip Contralateral On the opposite side of the The right shoulder is body as another structure contralateral to the left hip Proximal Nearer to the attachment of a limb to the trunk The shoulder is proximal to the wrist Distal Farther from the attachment of a limb to the trunk The elbow is distal to the shoulder Superficial Toward or on the surface of the body The ribs are superficial to the lungs Deep Away from the surface of the body Bones are deep to the skin QUIZ! The The The The The The The The knee is _______ to the hip. elbow is ______ to the wrist. navel is on the ________ side of the body. buttocks is on the _______ side of the body. nose is ________ to the mouth. neck is ______ to the chin. big toe is _______ to the little toe. little toe is ______ to the big toe. BODY CAVITIES Body cavities are spaces within the body that help protect, separate, and support internal organs. Cranial cavity: Formed by the cranial bones and contains the brain. Vertebral cavity: Formed by the vertebrae and contains the spinal cord. Thoracic cavity: Formed by the ribs and contains the heart and lungs. Abdominopelvic cavity: contains all other internal organs. PLAY-DOH LAB! 1. Choose a partner. 2. Come get toothpicks (14), play -doh, a knife, and tape from me. 3. Make a person out of play -doh (they have to have a head, a trunk, two arms and two legs). Please put a face on your person. 4. Stick a toothpick in the most superior aspect of the person. 5. Make a transverse cut through the person’s navel. 6. Make a frontal cut through the person’s head. 7. Make a sagittal cut through the person’s left (your right) leg. 8. On the person’s right arms and legs, mark the most proximal and distal portions. Also, mark the medial and lateral portions. 9. Label the anterior and posterior portions of the person’s head. 10. Everything in RED needs to be toothpicked and labeled! 11. Have me come check when you’re done! BODY MOVEMENTS BODY MOVEMENTS All of these body movements take place at joints. Four main categories: Gliding Angular Rotation Special movements Movement Description Type Flexion Decrease in the angle Angular between articulating bones Extension Increase in the angle Angular between articulating bones Lateral Flexion Angular Abduction Angular Adduction Angular Circumduction Angular Flexion Extension Movement Description Flexion Decrease in the angle Angular between articulating bones Extension Increase in the angle Angular between articulating bones Lateral Flexion Movement of the trunk/head in the frontal plane Angular Abduction Movement of a bone away from the midline Angular Adduction Movement of a bone toward the midline Angular Circumduction Type Angular Lateral Flexion Abduction/Adduction Circumduction Movement Description Type Flexion Decrease in the angle Angular between articulating bones Extension Increase in the angle Angular between articulating bones Lateral Flexion Movement of the trunk/head in the frontal plane Angular Abduction Movement of a bone away from the midline Angular Adduction Movement of a bone toward the midline Angular Circumduction Flexion, abduction, Angular extension and adduction in succession, in which the distal end of a body part moves in a circle Lateral Flexion Abduction/Adduction Circumduction Movement Description Type Supination Movement of the forearm that turns the palm anteriorly Special Pronation Movement of the forearm that turns the palm posteriorly Special Dorsiflexion Special Plantarflexion Special Inversion Special Eversion Special Supination Pronation Dorsiflexion/Plantarflexion Movement Description Type Supination Movement of the forearm that turns the palm anteriorly Special Pronation Movement of the forearm that turns the palm posteriorly Special Dorsiflexion Bending the foot towards the face Special Plantarflexion Bending the foot towards the ground Special Inversion Special Eversion Special Supination Pronation Dorsiflexion/Plantarflexion Movement Description Type Supination Movement of the forearm that turns the palm anteriorly Special Pronation Movement of the forearm that turns the palm posteriorly Special Dorsiflexion Bending the foot towards the face Special Plantarflexion Bending the foot towards the ground Special Inversion Medial movement of the soles so they face each other Special Eversion Lateral movement of the soles so that they face away from each other Special Inversion/Eversion Rotation: Movement of a bone around its longitudinal axis; in limbs, it may be medial or lateral. STAND UP! Show Show Show Show Show Show Show Show Show Show Show me me me me me me me me me me me flexion of the elbow. flexion of the knee. extension of the elbow. extension of the knee. ABDuction of the shoulder. ADDuction of the shoulder. supination. pronation. lateral flexion of the head. Dorsiflexion. plantarflexion. STAND UP! Show Show Show Show me me me me flexion of the hip. flexion of the shoulder. extension of the wrist. flexion of the wrist. BODY MOVEMENT POSTER Your assignment is to create a poster with a partner that displays the body movements. You may choose your partner. Your poster MUST contain: Flexion Extension Lateral Flexion Abduction Adduction Supination Pronation Dorsiflexion Plantarflexion Worth 100 points; MUST BE NEAT AND PRETT Y