PPT12Chapter12Autonomicnervoussystem
advertisement

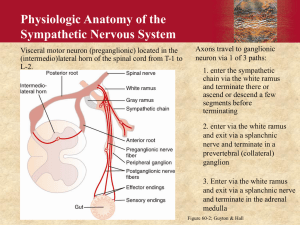
Joe Pistack MS/ED Automatic response-the body’s way of unconsciously and automatically making decisions and carrying them out for you. The autonomic nervous system-is part of the peripheral nervous system that supplies motor activity to the visceral effector organs, glands, smooth muscles within the organs and the heart. The two divisions of the ANS are: sympathetic Parasympathetic Dual Innervation a single organ receives nerve fibers from both divisions of the ANS Sympathetic nervous system- is activated during periods of stress or times when a person feels threatened. Called the “fight or flight” response. Causes you to either confront (fight) or remove yourself from the threatening situation (flight). Sympathetic nervous system is activated during periods of stress, normally short-lived periods. Heart rate increases Bronchial tubes dilate(increase airflow) Iris of the eye dilates (pupils enlarge) Blood vessels constrict Sweat glands stimulated Inhibited intestinal mobility Adrenal medulla stimulates secretion of epinephrine and norepinephrine Salivary glands stimulate thick secretions Parasympathetic nervous system-most active during quiet, non-stressful conditions. Has a calming effect on the body. Plays an important role in the regulation of digestion and reproductive function. Referred to as “feed and breed” or resting and digesting. The parasympathetic system is activated in situations that are perceived hopeless and where “fight or flight” seems futile. Symptoms are the opposite of sympathetic nervous system Body’s reaction to a more restful situation. Ex. Nice spring day, sitting under a tree. Decreased heart rate Bronchial tubes constrict Pupils Constrict Salivary glands are stimulated with a watery secretion Increased motility and secretion of the intestine Stimulus that can effect the parasympathetic nervous system may be stimulation of the vagus nerve, diagnostic testing that may stimulate a parasympathetic response. Ex. Colonoscopy. A massive parasympathetic response may result in uncontrolled urination or defecation. Bradycardia There is a decrease in the speed of nerve conduction. Decrease in reflexes. Less efficient sympathetic nervous system response may cause transient hypotension and fainting. Decline in nerve activity supplying changes in pupillary response and reactivity. Decrease in the cranial nerves mediating taste and smell.